* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Abnormal Psychology
Claustrophobia wikipedia , lookup
Panic disorder wikipedia , lookup
Depersonalization disorder wikipedia , lookup
Test anxiety wikipedia , lookup
Memory disorder wikipedia , lookup
Personality disorder wikipedia , lookup
Asperger syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Behavioral theories of depression wikipedia , lookup
Antisocial personality disorder wikipedia , lookup
Schizoaffective disorder wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive behavioral therapy wikipedia , lookup
Drug rehabilitation wikipedia , lookup
Social anxiety disorder wikipedia , lookup
Diagnosis of Asperger syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Anxiety disorder wikipedia , lookup
Schizophrenia wikipedia , lookup
Treatments for combat-related PTSD wikipedia , lookup
Death anxiety (psychology) wikipedia , lookup
Glossary of psychiatry wikipedia , lookup
Spectrum disorder wikipedia , lookup
Mental disorder wikipedia , lookup
Sluggish schizophrenia wikipedia , lookup
Treatment of bipolar disorder wikipedia , lookup
Child psychopathology wikipedia , lookup
Depression in childhood and adolescence wikipedia , lookup
Separation anxiety disorder wikipedia , lookup
Generalized anxiety disorder wikipedia , lookup
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders wikipedia , lookup
Externalizing disorders wikipedia , lookup
Dissociative identity disorder wikipedia , lookup
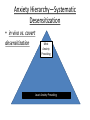
Abnormal Psychology and Treatment Calendar for this Unit • Art or Music, and Mental Illness—Sign up for your day—Week 1: Diagnose and Week 2: Treat • Vocabulary—Chapter 16 Due Friday! • Vocabulary—Chapter 17 Due Next Friday! • Mental Illness and Treatment Role Play – Groups of 3 (patient, therapist, narrator) – 5 sources – Have fun—props, puppets, drama, etc. Q--What is normal? Defining Abnormality • 1/7 Americans and 1/10 Worldwide—Why? • Is it an illness? – Yes! Schizophrenia vs. Type 1 Diabetes • DSM IV TR—Designed to diagnose—not treat! • Abnormality – Maladaptive – Disturbing to others – Atypical – Irrational Defining Abnormality • Insanity is a legal term • Causes of Abnormality—Mobile Survey/Notes – Psychoanalytic – Humanistic – Behavioral – Cognitive* – Sociocultural – Biomedical – Eclectic* Psychoanalytic • Cause of mental illness--Internal, Unconscious Conflicts mostly stemming from childhood • Freud, Horney, Erikson, Adler, and Jung Humanistic • Cause of mental illness--Failure to strive toward one’s potential— self actualization or being out of touch with one’s true feelings • Maslow and Rogers Behavioral • Cause of mental illness—reinforcement history and the environment • Skinner, Watson, and Bandura Cognitive • Cause of mental illness—irrational, dysfunctional thoughts or maladaptive ways of thinking Sociocultural • Cause of mental illness—Dysfunctional society; not you but the society that you live in Biomedical • Cause of mental illness—organic problems, biochemical imbalances, genetic predispositions • Psychiatrists Eclectic • Clinical psychologists do not tend to subscribe to just one perspective, but instead utilize many and accept and use ideas from a number of perspective Sybil—Scenes 1,2,3 • What aspects of abnormality are displayed? • What perspective of mental illness best explains Sybil’s problems? Types of Disorders • • • • • • • Intern Syndrome???? Anxiety Somatoform Dissociative Mood or Affective Schizophrenic Personality Anxiety Disorders Simple or Specific Phobia Claustrophobia Arachnophobia Agoraphobia Social Phobia Anxiety Disorders GAD Panic Disorder • Generalized Anxiety Disorder • Constant Low Level Anxiety • http://www.webmd. com/video/generaliz ed-anxiety-disorder • Acute /Instense Anxiety ANXIETY DISORDERS OCD—Obsessive Compulsive Disorder •Germs •Medical Issues •Symmetry •Cleanliness •Numbers •And more! Look at Checklist! http://www.brainph ysics.com/screener.p hp http://www.webmd.com/vid eo/teen-with-ocd ANXIETY DISORDERS • PTSD— • Post Traumatic Stress Disorder •Caused by trauma from war, rape, accidents, etc. •Symptoms— Flashbacks Nightmares Severe Anxiety Drug Abuse Causes of Anxiety • Psychoanalytic—unresolved, internal conflicts between ID, Ego, and Superego – EX.—ID wishing to rid yourself of a bad parent and the Superego saying that it is wrong to have such a wish • Behaviorists—anxiety is learned – EX.--classical conditioning of phobias • Cognitive—dysfunctional, irrational thinking – EX.—setting too high of standards for yourself Sybil—Scenes 4,5,6 • What examples of anxiety did you see? • If you were going to diagnose Sybil with an anxiety disorder, what would it be? • What is the most probable cause for Sybil’s anxiety? Somatoform Disorders Psychological problem manifests in a physical way Somatization Hypochondriasis Conversion Psychophysical Munchausen Munchausen by Proxy Causes of Somatoform • Psychodynamic or psychoanalytic—unresolved conflicts that cannot be resolved • Behaviorists—have been reinforced for being sick or for their behavior either through an actual reward or the removal of something unpleasant • Cognitive—don’t know how to positively get attention Dissociative Disorders—disruption in cognition Psychogenic Amnesia • No organic or physical basis • Selective, Localized, Generalized • Fugue DID • Dissociative Identity Disorder • AKA—multiple personality disorder Causes of Dissociative Disorders • Psychoanalytic—extremely traumatic events have been repressed and the split consciousness results • Behaviorists—patients find dissociating rewarding because they don’t have to think about the trauma. Amnesia is “easier” than dealing with it • Very rare and many question legitimacy • E. Loftus would question it—why? Sybil—Scene 7, 10, 11 • What signs of somatoform disorders did Sybil and/or her mom show of a somatoform disorder? • What is the likely cause of the mother’s somatoform behavior? • What signs does Sybil show of DID? • What is the likely cause of the disorder? Mood or Affective Disorders • Major Depression—aka: Unipolar Depression • DSM says you have to: – depressed more than 2 weeks – Absence of clear reason – Loss of Appetite – Fatigue – Change in sleep – Lack of interest – Feelings of worthlessnes • Seasonal Affective Disorder--SAD • Bipolar Depression—aka: Manic-Depression • Depressed episodes are similar to major depression • Manic episodes – High energy – Heightened sense of confidence & power – Anxious/Irritable – Risky Behavior – Don’t think about negative consequences Causes of Mood Disorders • Psychoanalysts –anger directed inward, loss during early stages, overly punitive superego • Behaviorists—brings some amount of reinforcement such as attention or sympathy • Aaron Beck (cognitive) caused by unreasonably negative ideas about themselves, world, and future— Cognitive Triad • Cognitive psychologists would also look at attributions— pessimism, internal, external, global, specific Causes of Mood Disorders • Martin Seligman— Learned Helplessness • Shocked Dogs • Relate to humans?!? – Unable to fix the situation, so they give up • Biological— • low levels of serotonin and or norepinephrine and unipolar • More receptors for acetylcholine and bipolar • Genetic Component— run in families • Types of Schizophrenia Schizophrenia Most severe mental illness Disorder characterized by: Disturbed thoughts, behaviors, movement Hallucinations Delusions—persecution and grandeur Disorganized thoughts and speech—word salad, clang associations – Paranoid • Delusions of persecution – Disorganized • Clang association (+ symp.) • Neologisms (+ symp.) • Innappropriate Affect – Flat Affect (neg. symp.) – Catatonic (negative symp.) • Waxy flexibility (neg. symp.) – Undifferentiated • Disorganized thinking Schizophrenia Simulator • http://www.janssen.com/mindstorm_video.ht ml Causes of Schizophrenia • Genetic—if a close family member has schizophrenia, then you are more likely to suffer—5th chromosome abnormality (bio) – Twin Studies—Monozygotic vs. Dizygotic • Dopamine Hypothesis—more dopamine (bio) • Enlarged ventricles—takes away frontal lobe development in late teen years, early 20s (bio) • Double Bind parent??? (cognitive, sociocultural) • Diathesis-Stress Model—environmental stressors activate genetic predispositions (bio/) • Drug use (bio) Sybil—Scenes 19,20, 21 • What symptoms of depression does Sybil or one of her personalities display? • What is the cause of her depression? • What symptoms of schizophrenia does Hattie display? • What do you think caused her schizophrenia? Personality Disorders Histrionic Paranoid Dependent Anti-social Narcissistic—DSM? Compulsive Obsessive Passive-Aggressive Schizoid/Avoidant Borderline • Personality Disorders are characterized by a maladaptive way in behaving that seems to be imbedded in the personality during development Causes of Personality Disorders • Psychoanalytic—unresolved conflict between the id and superego • Behavioral—some maladaptive aspect of the personality has been reinforced • Sociocultural—dysfunctional society has caused personality flaws • Cognitive—maladaptive thinking cause personality flaw • Humanistic—personality flaw developed by conflict between ideal self and real self Other Mental Illnesses in the DSM-IV-TR • Paraphillias—sexual disorders – Pedophillia, zoophillia, fetish, voyeur, masochist, sadist • Anorexia-Nervosa and Bulemia – Loss of 15% of body mass, fear of food, distorted body image • Substance Use Disorder— – Substance dependence—addiction • ADHD??? – Overdiagnosed • Autism – Less social and emotional contact, language delayed, and don’t seek parent assistance Sybil—Scenes 26, 27, 28 • Does Sybil suffer from any personality disorders? If so, why do you think she developed it? • Does her dad seem to suffer from a personality disorder? If so, why do you think it developed? Caution!!!!!!!! • Is it a good idea to label people as depressed or as a hypochondriac? Is there really a benefit to giving a person a label? • Rosenhan—Who’s Crazy Here Anyway? – Discuss with a neighbor what Rosenhan concluded and what info we can take from his study! – Clinical Psychologists more likely to label— Counseling Psychologists not so much! History of Treatment • • • • Trephining Enlightenment—Dorothea Dix Deinstitutionalization Preventative Efforts – Primary—reduce socieatal problems – Secondary—work with at risk persons – Tertiary—keep mental illness from getting worse • Finish Sybil—29, 31 Treatment Options Psychoanalytic Humanistic Behavioral Cognitive* Sociocultural Biomedical Eclectic* • What type of therapy do you think Dr. Wilbur uses with Sybil? • Do you think it was ethical/appropriate for Dr. Wilbur to get so close to Sybil? http://abcnews.go.com/GMA/video/charlie-sheennot-bipolar-bi-winning-13017875 Patient: Charlie Sheen Diagnosis:______________ Treatment Proposal:_____________________ http://abcnews.go.com/GMA/video/lindsay-lohanspeaks-out-13026910 Patient: Lindsay Lohan Diagnosis: ___________________ Treatment Proposal:____________________ Patient: Marshall Bruce Mathers III aka Eminem, Slim Shady Diagnosis:____________ Treatment Proposal:____________ Psychoanalytic • Must bring repressed memories and conflict with id/superego to the surface so ego and conscious can deal with it. • If you do the work, you won’t have symptom substitution • Hypnosis • Free Association – Role play! • Dream Analysis – Manifest vs. Latent • Resistance • Transference – Countertransference • Dr. Wilbur—Example • Psychodynamic--Insight Humanistic • Must help CLIENT remove roadblocks to self actualization and resolve incongruence between real self and ideal self in a nondirective way • Need for unconditional positive regard • Carl Rogers—I’m OK, You’re OK • Active Listening – Role Play! • Free Will vs. Determinism • Client Centered or Person Centered Therapy • Modeling Congruence Other Types of Humanist Therapies • Existential Therapy – Life is worthwhile – Has purpose – Don’t Worry, Be Happy! • Gestalt Therapy – – – – – Much more directive Empty Chair Technique WHOLE selves Integrate self into one Who would be in your empty chair and what would you say to them? Behavioral • Must counter condition the patient in a more adaptive way • Mary Cover Jones— Counter Conditioning • Joseph Wolpe— Systematic Desentization – Relaxation • Flooding – In vivo vs. Convert – Extinguishing Fear • Aversive Conditioning • Token Economy • Biofeedback Anxiety Hierarchy—Systematic Desensitization • in vivo vs. covert desensitization Most Anxiety Provoking Least Anxiety Provoking Cognitive • Must fix maladaptive thinking in a directive way • Fix unhealthy attributional styles and replace it with more effective attributions • Aaron Beck—Cognitive Therapy—Cognitive Triad • Cognitive Behavioral Therapy or CBT • Rational Emotive Behavioral Therapy or RBET • Albert Ellis Role Play with someone in class to get rid of an irrational belief they have! Sociocultural • Most help patient by fixing his/her environment—ie— family, friends, workplace, etc. • YOU don’t exist in a vacuum • • • • • Family Therapy Couples Counseling Group Therapy AA/NA Self Help Groups Biological or Somatic Therapies • Treating mental illness from a biological approach like you would any illness • Psychiatrists • Family MDs • Other MDs • NOT typically Psychologists • Medicine • Psychosurgery – Lesioning vs. Lobotomy • Diet/Exercise • ECT/Shock Therapy Psychopharmacology or Chemotherapy – Anti Depressants— increase serotonin activity • Tricyclics • MAOIs • SSRIs – Prozac – Anti Anxiety • Barbiturates – Miltown • Benzodiazapines – Valium and Xanax Mood Stabilizers— Lithium—Heavy Metal Treat Bipolar Anti Psychotics-Schizophrenia • Thorazine • Haldol – Side Effects: » Tardive Dyskenia A Beautiful Mind • Insulin Shock Therapy Scene—Scene 15 Eclectic • Using a variety of • Write here! approaches to help your patient/client • What combo would you prefer to use? Types of Therapists • Psychiatrists—MD – Only therapist type that can prescribe medicine – Favor biomedical and not as well trained in psychotherapy • Psychoanalysts – Freudian Methods • Clinical Psychologists – PhDs--Diagnose • Counseling Psychologists – Masters in Family Therapy--JEFF – Deal with less serious issues How Effective is Therapy??? Very Effective Not Very Effective Outdated studies indicate that 66% of people get better with therapy or without therapy! However, new research indicates that even if people who get better are not seeking formal counseling, they are seeking therapy in less formal ways! Schizophrenia FRQ—Stand Up Review! • Often misunderstood, schizophrenia is a psychological disorder affecting one percent of the population. In treating the disorder, psychologists work to identify its nature and origins. – Identitify two characteristics used to diagnose schizophrenia – Discuss a research finding that supports a genetic basis for schizophrenia – What is the dopamine hypothesis regarding the origins of schizophrenia? – Describe how medications used to treat schizophrenia affect the actions of neurotransmitters at the synapse. – Identify a risk inherent in the treatment of schizophrenia. – People often times confuse schizophrenia with DID (Dissociative Identity Disorder). Identify two characteristics that differeniate DID from Schizophrenia.