* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slayt 1
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Cassiopeia (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Corona Australis wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Fermi paradox wikipedia , lookup
Gamma-ray burst wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Outer space wikipedia , lookup
History of supernova observation wikipedia , lookup
Crab Nebula wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Observable universe wikipedia , lookup
Abundance of the chemical elements wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Chronology of the universe wikipedia , lookup
Type II supernova wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Stellar evolution wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Cosmic distance ladder wikipedia , lookup
Nucleosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Hubble Deep Field wikipedia , lookup
Stellar kinematics wikipedia , lookup
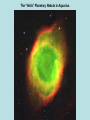
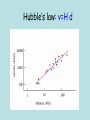
Our Evolving Universe -Origin of Elements- by Yavuz Ekşi Enka Schools April 25th, 2007 http://www.fizik.itu.edu.tr/eksiy/ The Planets MNEMONIC: My Very Educated Mother Just Sent Us Nine Pizzas With the exception of Pluto each of the planets can be thought of as belonging to one of two distinct groups: terrestrial or Jovian Imagening the distances • Imagine the Solar System being a soccer ground (about 100 m long). • The Sun would be a glaring orange in the centre. • Pluto would encircle the sun at the edge of the soccer ground, having the size of a dust particle. • The Earth would be 1,30m away from the “orange“, having the size of a sesame seed. Origin of Our Solar System Solar nebula theory • cloud of gases and dust • formed a rotating disk • condensed and collapsed due to gravity • forming solar nebula – with an embryonic Sun – surrounded by a rotating cloud Milky Way: the Galaxy • A hazy band of white light in the summer skies. • Actually a myriad of stars. Milky Way Milky way contains about 400 billion stars. The Local Group The Milky Way is a member of a group of galaxies called the Local Group Our Neighbour Galaxy: Andromeda (M31) 2.5 million ly away (just 25 times the diameter of our galaxy). Contains about one trillion stars. Downtown: The Virgo Super Cluster: 50 m.l.y The Coma Cluster 350 m.l.y. LargeScale Structure of the Universe to 500 m.l.y. Stars in the Milky Way do not collide • The radius of the Sun is 700.000 km (about 2 light seconds) • The closest star other than the Sun is about 4 light years away. • Mean separation between the stars is much greater than the mean diameters of the stars (approx. 50 million times). • It is very unlikely that two stars moving in the galaxy collide. Galaxies Colliding Galaxies do collide because mean separation is not much larger than the typical diameter of a galaxy. Where does the elements come from? • Only hydrogen and helium was created in the Big Bang. • We have Carbon, Nitrogen, Oxygen, and iron in our body. • Where does these elements come from? Four Forces of Nature • • • • Gravity Electromagnetism Strong interaction (short range) Weak nuclear interaction (short range) Hydrogen (proton) fusion Like electrical charges repel. So, protons in a gas avoid `collisions’ p+ p+ Hydrogen (proton) fusion However, as a gas temperature goes up, the average speed of the particles goes up and the protons get closer before repelling one another. If the proton get very close, the short-range nuclear force fuses them together. p+ p+ Stellar Evolution • Heavy elements are formed in stars during their evolution. • Thermonuclear reactions produce elements up to iron. • All fusion reactions before iron are exotermic. • After iron, endothermic. Onion Skin Model C shell Ne shell H shell He shell O shell Fe core Si shell • But how did these elements came into our body? • What happens to a star after it exhausts all matter? • The core collapses and the outer layers of the star are expelled in a gigantic explosion. Supernova 1987a in the Large Magellanic Cloud Before After Crab Nebula Supernova Remnant With Supernova Explosions… • The outer layers of the stars are expelled into the interstellar medium. • Even higher elements like gold, uranium etc are formed during the SN explosion. • Now the interstellar medium is richer with heavy elements. • …but how did these elements in the interstellar medium came to our body? Horsehead Nebula Stars form from gas clouds in the interstellar medium. The solar system formed out of a gas cloud that had been injected with heavy elements from many generations of supernova explosions. Eagle Nebula Star formation is an ongoing process in the Galaxy... Our galaxy is not complete yet! It is rather an evolving system in which new stars are born and some stars die! The Cycle of Matter Not all stars end with a supernova explosion • The Sun will not die with a SN explosion. • All stars with mass smaller than 1.4 solar masses at the end of their life will end with a much less energetic explosion called a planetary nebula. • Such objects will form white dwarfs. The “Helix” Planetary Nebula in Aquarius Inside stellar remnants Aristoteles: The celestial objects are made up of a separate element called ether. Modern Science: Celestial objects are made of the same stuff that the Earth is made up of. ...because the Earth itself is a celestial object! All celestial objects are subject to change. The Earth is a celestial object and so it must be changing. August 17, 1999 The Lands are moving! The Earth is not complete yet! • The lands, insensitive to our presense, continue their motion that they started millions of years ago. • The Earth is not a complete place but rather an evolving celestial object. The Universe Expanding Doppler Effect The first crest travels out in circle from the original position of the plane Shorter wavelength (more blue) At a later time, a second crest is emitted from the planes new position, but the old crest keeps moving out in a circle from the planes original position The same thing happens again at a later time Longer wavelength (more red) For galaxies, we can use the doppler effect to measure velocity. The Universe is Expanding … The universe is like a raisin bread! Expansion of the Universe – All galaxies are moving away from us – More distant galaxies moving away faster Raisins move with dough, not through it. Galaxies move with space, not through it! Expansion is observed to be the same in all galaxies What DO we know? – All galaxies are moving away from us – More distant galaxies moving away faster -1 0 1 2 Raisins separated by meters 3 Distances Double in 1 sec Singing Raisin Moves at 1 m/s -2 -1 Radio Raisin Moves at 3 m/s 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 Hubble’s law: v=H d The End The notes are at http://www.fizik.itu.edu.tr/eksiy/