Niraj D. Welikala Thesis - D-Scholarship@Pitt
... and on these scales the density fluctuations are small in size (rms fluctuations of the order ∼ 0.1 at 1 Gpc). However, on scales of the order of 10 Mpc, the density fluctuations are large (∼ 1). The most apparent overdensities are therefore on small scales, less than 10 Mpc which are the typical sc ...
... and on these scales the density fluctuations are small in size (rms fluctuations of the order ∼ 0.1 at 1 Gpc). However, on scales of the order of 10 Mpc, the density fluctuations are large (∼ 1). The most apparent overdensities are therefore on small scales, less than 10 Mpc which are the typical sc ...
environmental effects on galaxy evolution in nearby clusters
... The environmental effects on galaxy evolution in nearby clusters are investigated using a multiwavelength dataset. The present analysis is focused on the properties of three (Abell 1367, Virgo and Coma) among the best studied clusters in the local Universe. Due to the variety of their environmental ...
... The environmental effects on galaxy evolution in nearby clusters are investigated using a multiwavelength dataset. The present analysis is focused on the properties of three (Abell 1367, Virgo and Coma) among the best studied clusters in the local Universe. Due to the variety of their environmental ...
11115002
... as early as 1939—who suggested that a neutron star was an ideal gas of free neutrons. Being extremely heavy particles by themselves, neutrons can account for the heavy mass of the neutron stars (~1014 g/cm3). It is believed that pulsars were finally discovered because of World War II—the remnant rad ...
... as early as 1939—who suggested that a neutron star was an ideal gas of free neutrons. Being extremely heavy particles by themselves, neutrons can account for the heavy mass of the neutron stars (~1014 g/cm3). It is believed that pulsars were finally discovered because of World War II—the remnant rad ...
THE STAR FORMATION AND NUCLEAR ACCRETION HISTORIES OF NORMAL GALAXIES
... dominated by star formation, while that from early-type galaxies is dominated by a combination of hot gas and active galactic nucleus (AGN) emission. We find that the mean star formation and supermassive black hole accretion rate densities evolve like ∼ (1+z)3±1 , in agreement with the trends found ...
... dominated by star formation, while that from early-type galaxies is dominated by a combination of hot gas and active galactic nucleus (AGN) emission. We find that the mean star formation and supermassive black hole accretion rate densities evolve like ∼ (1+z)3±1 , in agreement with the trends found ...
Report from the Subaru Telescope for External
... indicates that young galaxies in the distant Universe (at least some of them) emit more ionizing radiation than expected and that they may have played an important role in the cosmic reionization. This is consistent with Ouchi et al. (2009b), which estimated the total ionizing photon budget from the ...
... indicates that young galaxies in the distant Universe (at least some of them) emit more ionizing radiation than expected and that they may have played an important role in the cosmic reionization. This is consistent with Ouchi et al. (2009b), which estimated the total ionizing photon budget from the ...
Galaxies - hwchemistry
... of galaxies, however, they find that the measured masses are much larger than expected from the luminosities of the galaxies. • This seems to be true of most galaxies. – Measured masses of galaxies amount to 10 to 100 times more mass than you would expect from the appearance of galaxies. ...
... of galaxies, however, they find that the measured masses are much larger than expected from the luminosities of the galaxies. • This seems to be true of most galaxies. – Measured masses of galaxies amount to 10 to 100 times more mass than you would expect from the appearance of galaxies. ...
Mapping the Pathways of Galaxy Transformation Across Time and
... outcomes from the IMACS Cluster-Building Survey: our finding that most z∼0.5 poststarbursts are rejuvenated passive galaxies, and a simple model positing that every galaxy has a lognormal SFH whose parameters are set at birth. Both studies reinterpreted key metrics of galaxy evolution typically seen ...
... outcomes from the IMACS Cluster-Building Survey: our finding that most z∼0.5 poststarbursts are rejuvenated passive galaxies, and a simple model positing that every galaxy has a lognormal SFH whose parameters are set at birth. Both studies reinterpreted key metrics of galaxy evolution typically seen ...
Elliptical Galaxies
... of the galaxy) at Re . This law can be integrated to give a finite total light of Itot = 7.22πRe 2 Ie . de Vaucouleurs’ law, as it is known, fits remarkably well to many of the most accurately determined luminosity profiles of elliptical galaxies and provides a convenient measure of the size and tot ...
... of the galaxy) at Re . This law can be integrated to give a finite total light of Itot = 7.22πRe 2 Ie . de Vaucouleurs’ law, as it is known, fits remarkably well to many of the most accurately determined luminosity profiles of elliptical galaxies and provides a convenient measure of the size and tot ...
Galaxies
... underlying dark matter. We have started to understand how baryonic gas within the dark matter halos cools and collapses to form stars, and how the energy from star formation can feed back into the surrounding gas and regulate subsequent star formation. However, at a fundamental level we still lack a ...
... underlying dark matter. We have started to understand how baryonic gas within the dark matter halos cools and collapses to form stars, and how the energy from star formation can feed back into the surrounding gas and regulate subsequent star formation. However, at a fundamental level we still lack a ...
ROSAT Ian R. Stevens* and David K. Strickland*
... Contini (1998) lists a further eight EL galaxies with narrow He II l4686. Of these only one, Mrk 49, a blue compact dwarf galaxy (also classified as Mrk 1318), has been observed. However, there seems to be emission from a point source near to but not coincident with Mrk 49 (the X-ray emission is cen ...
... Contini (1998) lists a further eight EL galaxies with narrow He II l4686. Of these only one, Mrk 49, a blue compact dwarf galaxy (also classified as Mrk 1318), has been observed. However, there seems to be emission from a point source near to but not coincident with Mrk 49 (the X-ray emission is cen ...
Evolution of galaxy morphology - Lecture 1 - NCRA-TIFR
... Where e refers to effective values and n is the Sérsic index. For n=4 it becomes the de Vaucouleurs function; for n=1 an exponential, and when n=0.5, a Gaussian! For values in the range 1-4, approximately, it describes bulges in late-type spiral galaxies (or pseudo-bulges) to bulges in early-type sp ...
... Where e refers to effective values and n is the Sérsic index. For n=4 it becomes the de Vaucouleurs function; for n=1 an exponential, and when n=0.5, a Gaussian! For values in the range 1-4, approximately, it describes bulges in late-type spiral galaxies (or pseudo-bulges) to bulges in early-type sp ...
The environment of high-redshift AGN OLIMPIA JUDIT FOGASY
... In order to understand the formation and evolution of local massive galaxies and to reveal the processes that engineered the tight correlations found between their supermassive black hole (SMBH) mass and bulge mass or velocity dispersion, the study of powerful, high-redshift active galactic nuclei ( ...
... In order to understand the formation and evolution of local massive galaxies and to reveal the processes that engineered the tight correlations found between their supermassive black hole (SMBH) mass and bulge mass or velocity dispersion, the study of powerful, high-redshift active galactic nuclei ( ...
Article PDF - IOPscience
... galaxies, as seen through their stellar light distributions, contain enough physical information to offer this classification. We argue through the use of 240 images of nearby galaxies that three model-independent parameters measured on a single galaxy image reveal its major ongoing and past formation ...
... galaxies, as seen through their stellar light distributions, contain enough physical information to offer this classification. We argue through the use of 240 images of nearby galaxies that three model-independent parameters measured on a single galaxy image reveal its major ongoing and past formation ...
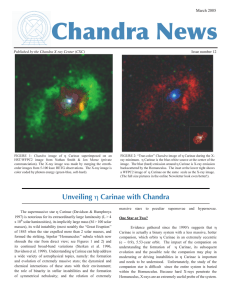
Chandra News March 2005 Published by the Chandra X-ray Center (CXC)
... first five-plus years of operation. We were especially pleased to acknowledge the tremendous contribution of Riccardo Giacconi. We noted that the true origin of this Observatory traces directly to Riccardo’s 1963 proposal, “An Experimental Program of Extra-Solar X-Ray Astronomy”, written barely 15 m ...
... first five-plus years of operation. We were especially pleased to acknowledge the tremendous contribution of Riccardo Giacconi. We noted that the true origin of this Observatory traces directly to Riccardo’s 1963 proposal, “An Experimental Program of Extra-Solar X-Ray Astronomy”, written barely 15 m ...
Local Group Encyclopedia of Astronomy & Astrophysics eaa.iop.org Mario L Mateo
... concentration of stars and GLOBULAR CLUSTERS towards the constellation Sagittarius all confirm this classification—the specific spiral subtype is extremely difficult to determine reliably from our unfavorable vantage point inside the Galaxy. Various indirect indicators suggest that our Galaxy can be ...
... concentration of stars and GLOBULAR CLUSTERS towards the constellation Sagittarius all confirm this classification—the specific spiral subtype is extremely difficult to determine reliably from our unfavorable vantage point inside the Galaxy. Various indirect indicators suggest that our Galaxy can be ...
Digital Universe Guide - American Museum of Natural History
... night sky as seen from Earth. With the left mouse button pressed, you can pan around the sky to your heart’s content. How do you move away from the Sun, though, and begin flying around the stars? Turn on the stars and turn off the open clusters and globular clusters (click on their group buttons). B ...
... night sky as seen from Earth. With the left mouse button pressed, you can pan around the sky to your heart’s content. How do you move away from the Sun, though, and begin flying around the stars? Turn on the stars and turn off the open clusters and globular clusters (click on their group buttons). B ...
Annual Report 2011 - Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics
... 4.2 PhD Thesis 2011/Diploma thesis 2011 . . . . 4.2.1 Ph.D. theses 2011 . . . . . . . . . . . 4.2.2 Diploma theses 2011 . . . . . . . . . . 4.2.3 PhD Thesis (work being undertaken) . 4.3 Visiting scientists . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...
... 4.2 PhD Thesis 2011/Diploma thesis 2011 . . . . 4.2.1 Ph.D. theses 2011 . . . . . . . . . . . 4.2.2 Diploma theses 2011 . . . . . . . . . . 4.2.3 PhD Thesis (work being undertaken) . 4.3 Visiting scientists . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...
the stebbins galaxy: the origins of interstellar medium studies
... 1) The distribution of globular clusters, presumed to be centered around the center of mass of the Galaxy, shows the Sun to be far from that center. 2) The measured distances to globular clusters show the Galaxy to be about 70,000 parsecs (200,000 light-years or so) in diameter (Shapley, 1930a: 221) ...
... 1) The distribution of globular clusters, presumed to be centered around the center of mass of the Galaxy, shows the Sun to be far from that center. 2) The measured distances to globular clusters show the Galaxy to be about 70,000 parsecs (200,000 light-years or so) in diameter (Shapley, 1930a: 221) ...
X. Nuclear star clusters in low-mass early-type galaxies
... that the evolution of NSCs and SMBHs may possibly somehow be linked. Likely there is some interaction between NSCs and SMBHs, such that one may prevent the growth of the other or even destroy it (McLaughlin, King & Nayakshin 2006; Merritt 2009; Nayakshin, Wilkinson & King 2009). The Milky Way was th ...
... that the evolution of NSCs and SMBHs may possibly somehow be linked. Likely there is some interaction between NSCs and SMBHs, such that one may prevent the growth of the other or even destroy it (McLaughlin, King & Nayakshin 2006; Merritt 2009; Nayakshin, Wilkinson & King 2009). The Milky Way was th ...
Building galaxies Hunt, Leslie Kipp
... New General Catalogue (NGC) and its successors the First and Second Index Catalogue (IC), published from 1888 to 1908. The combined NGC+IC contains more than 12000 objects, and to this day the brightest extragalactic objects are denoted by their numbers in Dreyer’s catalogue. The nature of these neb ...
... New General Catalogue (NGC) and its successors the First and Second Index Catalogue (IC), published from 1888 to 1908. The combined NGC+IC contains more than 12000 objects, and to this day the brightest extragalactic objects are denoted by their numbers in Dreyer’s catalogue. The nature of these neb ...
Gamma Ray Bursts
... Assuming typical comet and netron star sizes one can calculate released energy. Comparing to the observed energy one can estimate the distance: 10-1000 l.y. 10 l.y. ~ distance to closest neutron stars 1000 l.y. ~ thickness of the galactic disk ...
... Assuming typical comet and netron star sizes one can calculate released energy. Comparing to the observed energy one can estimate the distance: 10-1000 l.y. 10 l.y. ~ distance to closest neutron stars 1000 l.y. ~ thickness of the galactic disk ...
Lab 14 Galaxy Morphology
... a small disk that is composed of only old, red stars, and have no gas, little dust and no star forming regions. They are mostly a large bulge with a weak disk, with difficult-to-detect spiral arms. They actually share many properties with elliptical galaxies. Sa galaxies have large bulges, and tight ...
... a small disk that is composed of only old, red stars, and have no gas, little dust and no star forming regions. They are mostly a large bulge with a weak disk, with difficult-to-detect spiral arms. They actually share many properties with elliptical galaxies. Sa galaxies have large bulges, and tight ...
Chapter 24
... consumption. Now entire galaxies become the “atoms” from which the universe is built—distant realms completely unknown to scientists just a century ago. We know of literally millions of galaxies beyond our own. Most are smaller than the Milky Way, some comparable in size, a few much larger. Many are ...
... consumption. Now entire galaxies become the “atoms” from which the universe is built—distant realms completely unknown to scientists just a century ago. We know of literally millions of galaxies beyond our own. Most are smaller than the Milky Way, some comparable in size, a few much larger. Many are ...
W.M. Keck Observatory Annual Report 2009
... of these worlds identified within the last fifteen years, modern astronomers continue their hunt for the planets with the lowest possible mass. The Keck I telescope has been the most prolific scientific instrument in the world for finding exoplanets, the majority of them being gas giants, like Jupit ...
... of these worlds identified within the last fifteen years, modern astronomers continue their hunt for the planets with the lowest possible mass. The Keck I telescope has been the most prolific scientific instrument in the world for finding exoplanets, the majority of them being gas giants, like Jupit ...
Science with the Constellation
... probe of the physics of the accretion flow as well as the space-time geometry close to the black hole. The high throughput and broad-band response of Constellation-X will allow us to utilize the iron-line diagnostic in an unprecedented manner. Observations of many individual sources will allow us to ...
... probe of the physics of the accretion flow as well as the space-time geometry close to the black hole. The high throughput and broad-band response of Constellation-X will allow us to utilize the iron-line diagnostic in an unprecedented manner. Observations of many individual sources will allow us to ...
History of supernova observation

The known history of supernova observation goes back to 185 CE, when, supernova SN 185 appeared, the oldest appearance of a supernova recorded by humankind. Several additional supernovae within the Milky Way galaxy have been recorded since that time, with SN 1604 being the most recent supernova to be observed in this galaxy.Since the development of the telescope, the field of supernova discovery has expanded to other galaxies. These occurrences provide important information on the distances of galaxies. Successful models of supernova behavior have also been developed, and the role of supernovae in the star formation process is now increasingly understood.