* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download week3bioinformatics
Protein folding wikipedia , lookup
Protein purification wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Intrinsically disordered proteins wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Protein mass spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Protein domain wikipedia , lookup
Alpha helix wikipedia , lookup
Homology modeling wikipedia , lookup
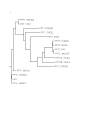
John Reiser 3/29/11 Bioinformatics: Week 3 Blast at NCBI 1) PPT1 FASTA File: >gi|4506031|ref|NP_000301.1| palmitoyl-protein thioesterase 1 isoform 1 precursor [Homo sapiens] MASPGCLWLLAVALLPWTCASRALQHLDPPAPLPLVIWHGMGDSCCNPLSMGAIKKMVE KKIPGIYVLSLEIGKTLMEDVENSFFLNVNSQVTTVCQALAKDPKLQQGYNAMGFSQGGQ FLRAVAQRCPSPPMINLISVGGQHQGVFGLPRCPGESSHICDFIRKTLNAGAYSKVVQERLV QAEYWHDPIKEDVYRNHSIFLADINQERGINESYKKNLMALKKFVMVKFLNDSIVDPVDS EWFGFYRSGQAKETIPLQETSLYTQDRLGLKEMDNAGQLVFLATEGDHLQLSEEWFYAHII PFLG 2) Homologs for the PPT1 (palmitoyl-protein thioesterase 1 isoform 1) protein date back all the way to eukaryotic organisms of the fungi/metazoa family. The first known organism with a conserved domain in this sequence is Naegleria ruberi. This is the initial lineage where hits are seen for this protein. There are 171 hits in 63 organisms dating back to the evolutionary beginning of eukaryotic cells. This means that this gene must be highly conserved and highly important in all organisms. 3) Amino acids 42, 47, 48, 116, 123, 124, 125, 130, 153, 243, 248, 251, 254, and 280 are single, fully conserved amino acids within 15 model organisms (all mammals). The cynomolgous monkey has an identical amino acid sequence for the PPT1 protein as humans. This is evidence that this gene is highly conserved. The conserved domains are amino acids that are most likely imperative to the function of the PPT1 enzyme in its catabolism of lipid-modified proteins in the lysosome. A point mutation in the DNA sequence that substitutes a different amino acid at any of the conserved domains could be the cause of a dysfunctional protein. Biology Workbench 1) Boxshade 2) 3)