* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Kingdom Plantae
Magnesium in biology wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
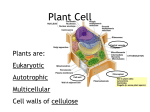
Kingdom Plantae Plant Characteristics • Eukaryotic • Multicellular • Cell walls made of cellulose • Develop from multicellular embryos • Carry out photosynthesis • Contain chlorophyll a & b • Reproduce by alternation of generations Plant Adaptations to Land Problems: • Need minerals • • • • Solutions: • Roots absorb H2O & minerals • Lignin & cellulose in cell Gravity walls Increase in • Vascular Transport Height for Light System Adaptations for • Waxy cuticle & Drier stomata with guard environment cells • Pollen containing sperm Reproduction Parts of a Leaf What do plants need to survive? O2 CO2 Plant Evolution • First plants evolved from organisms similar to today’s multicellular green algae.(from kingdom protista) Bryophytes • Life cycle that depends on water so the sperm can swim to the egg. • Lack vascular tissue, so they obtain water through osmosis (this limits their height) • Includes mosses, liverworts, & hornworts Tracheophytes: seedless vascular plants • Includes club mosses, horsetails and ferns • Tracheid: new cell type that specializes in water transport. -Hollow cells with thick walls that resist pressure. • Xylem: primary fluid transport • Phloem: transport nutrients and carbs Tracheophytes • Seedless vascular plants • Contain xylem & phloem (vascular tissue) – Xylem – carries water up from the roots – Phloem – transports products of photosynthesis Tracheophytes • Have roots, stems, and leaves with veins • Include club mosses, horsetails, and ferns. • Ferns have rhizomes & fronds with sori – Rhizomes – fern stems – Fronds – fern leaves – Sori – fern spores Spermatophytes • Seed Plants • Have adaptations that allow them to reproduce without water – Flowers or cones – Transfer of sperm by pollination – Protection of embryos in seeds • Two types: – Gymnosperms – Angiosperms Gymnosperms • Bear their seeds directly on the surface of cones • Means “naked seeds” • Include conifers, ginkgo, cycads, and gnetophytes Angiosperms • Flowering plants • Bear seeds within ovaries which surround and protect the seed. • Two types: – Monocot – Dicot Monocots • All monocots have the following characteristics: – – – – Single cotyledon – seed leaf Parallel veins Flower petals in multiples of 3 Vascular tissue scattered throughout the stem – Fibrous roots Dicots • All dicots have the following characteristics: – – – – – Double cotyledon seeds Branched veins Flower petals in multiples of 4 or 5 Vascular tissue arranged in a ring Taproot Angiosperm Life Spans • Annuals – complete life cycle in one growing season • Biennials – complete life cycle in two years – First year: grow roots, short stems and sometimes leaves – Second year: grow new stems, leaves, produce flowers and seeds • Perennials – live many years Plant Structure • Flower – Male reproductive structures - Stamen – Female reproductive structures - Carpal Root Function • Anchor plant to the ground • Absorb water and dissolved nutrients from the soil – Water – through root pressure – Nutrients – through active transport Types of Roots Fibrous: root formed in bundles where it is not possible to determine the primary root. Cauline: roots that shoot from the stem. Tubercular: root in the form of a tubercle. Taproot: root that grows vertically into the earth. Plant Growth • Most plants grow and produce new cells at the tips of their roots and stems for as long as they live. – Meristematic tissue – cluster of tissue responsible for continuing growth throughout the plant’s lifetime.