* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plant Book of Notes
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Pollination wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
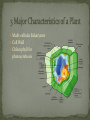
Multi-cellular Eukaryotes Cell Wall Chlorophyll for photosynthesis ALGAE Mosses Ferns Gymnosperms Cone bearing Angiosperms Flowering plants Become less dependent on water More resistant to sun rays More capable of conserving water More capable of reproducing without water Life cycle depends on water for reproduction NO SEEDS Hornworts, liverworts & mosses SEEDLESS VASCULAR PLANTS Ferns, horsetails, club mosses Vascular SEEDS (In CONES) Conifers, Douglas firs Vascular Bear Seeds (within Flowe All Vascular Consist of: Roots Stems Leaves Dermal Vascular Xylem – tracheids & vessels elements Phloem – sieve tube elements & companion cells Ground Tap Root (ex: carrot) Fibrous Root (ex: grass) Roots grow from the cells at the tip which are continuously dividing through mitosis. Support of Leaves, Fruits & Flowers Place the leaves in the light Provide a place for the plant to keep its flowers and fruits. Transport of fluids between the roots and the shoots in the xylem and phloem. Site of photosynthesis Chloroplast is the organelle that houses the green pigment chlorophyll Place of Transpiration and Respiration Consists of 2 parts: Blade Petiole basic energy source of cells Transpiration – loss of water through leaves Guard Cells – Change the size of the stomata to control amount of water released. This takes place in STOMATA which is a pore-like opening Take place in CONES Pollen Cones – MALE (produce male gametophyte) Seed Cones – FEMALE (produce female gametophyte) Pollination happens when the pollen is RELEASED from male Fertilization happens when the pollen grains land near ovule Monocots Dicots Seeds Single Cotyledon Two Cotyledon Leaves Parallel Veins Branched Veins Flower Multiples of 3 Multiples of 4 or 5 Stems Vascular – bundled/scattered Vascular – Bundled on ring Roots Fibrous Tap Root Pollination happens when POLLEN lands on STIGMA Fertilization happens when 1 pollen grain divides to make TWO (2) sperm nuclei 1 sperm nuclei = fertilizes the EGG 2nd sperm nuclei = fertilizes with the 2 polar nuclei to make TRIPLOID ENDOSPERM Fruit – any seed that is enclosed within its embryo wall Hormones – control of plants pattern of growth & development & plant response Auxins (3) – stimulate cell elongation Cytokinins (2) – stimulate cell development & growth of lateral buds, cause dormant seeds to sprout Gibberillins (1) –dramatic increase in size, part in stem & fruit Ethylene (1) – stimulate to ripen Gravitropism – response to gravity Phototropism – response to light Thigmotropism – response to touch Photoperiodism – response to light & darkness Winter dormancy – photosynthetic pathway turned off Leaf abscission – losing leaves during colder months Early growth stage of plant embryo Steps: 1. Absorbs water 2. Seeds open from swollen tissue 3. Young root emerges & grows Vegetative Reproduction Includes production of new plants from horizontal stems, from planters & underground roots Benefits: doesn’t involve pollination 2 methods: horizontal stems, planters & underground roots Plant Propagation – horticulturist use cutting, grafting or budding to make identical copies of a plant BENEFITS - produce offspring from seedless plants 3 FORMS – Cutting – cut from plant, place in special soil Grafting – stem out from parent, placed on plant that has stable root for a strong root system Budding – buds used to place on stock 3 ways plants adapt to life in water Seeds that float 2. Grow quick 3. Shoots grow above water 1. Submerged in Water: No Cuticles to Prevent Water Loss Reduced Roots Chloroplasts are restricted to the upper portions Salty Conditions: Specialized cells that pump salt out Desert Plants: Extensive roots Reduced leaves Thick stems Poor Soil: Carnivores Parasites Growth on other plants Shade Tolerance and a way of extracting nutrients Fight Insects Defend themselves against insects attack by manufacturing compounds that have powerful effects on animals