* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Seed Plants
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Verbascum thapsus wikipedia , lookup
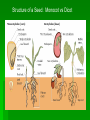
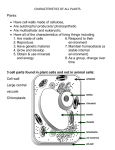
The Plant Kingdom Chapter 5:1,2,3,4 Seed Plants Part 1 of 2 Characteristics of All Seed Plants Vascular tissue Xylem Phloem Use Pollen and seeds to reproduce Vascular tissue Functions to provide support for the plant to grow tall and to help transport food, water and nutrients throughout the plant Vascular Tissue Xylem Water and minerals go UP from the roots to the stems and leaves Phloem Moves food, made from photosynthesis Pollen and Seeds Pollen: carries sperm cells to the eggs Seeds: contains a young plant inside a protective covering Seed Structure 3 Main parts Seed coat – protects the embryo for a long time Embryo – baby plant Stored food (cotyledon) Structure of a Seed: Monocot vs Dicot How are seeds dispersed? Dispersal is the scattering of seeds by: Wind Water Animal Ejection by the plant Germination When the embryo begins to grow out of the seed The seed must first absorb water from the environment Roots 3 main functions Anchor plants to the ground Absorb water and nutrients from the soil Store food (that we sometimes eat) Carrots, onions, parsnips, Beets, potatoes, radishes Types of Roots Tap root One long, thick main root with smaller branch roots Fibrous root Many similar sized roots in a dense mass Root Structures Root hairs Increase absorptive area Vascular system Xylem and phloem Root Cap Protects root as it grows through dirt What has to happen for germination to occur? What are thestore 3 functions of Anchor, absorb, food roots? What do root hairs do? What does the root cap do? Stems Functions Transportation Provides support for plant and holds leaves up Some store food Rhubarb, broccoli, asparagus, celery Types of Stems Herbaceous Soft stems that contain no wood flowers Woody Hard, rigid stems that contain several layers (bark, living phloem, cambium, xylem trees Stem structures Annual Rings Made of xylem Light and dark rings represent 1 year together Leaves Function Carry out photosynthesis Some store food Structures of the leaf Cuticle – waterproof covering to protect from water loss (transpiration) Stomata for gas exchange Chloroplasts for photosynthesis Vascular system