* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP)
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
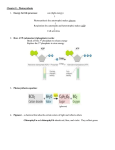
Photosynthesis Standard 1f –Usable energy is captured from sunlight by chloroplasts and is stored through the synthesis of sugar (glucose) from carbon dioxide 1i – In the mitochondria and chloroplasts energy from electrons is stored for ATP production (Chemiosmosis) – complex process by which visible sunlight is converted into chemical energy in carbohydrate molecules Reactants Products light 6CO2 + 6H2O ▬► C6H12O6 + 6O2 – light-absorbing molecules – green pigment (plants reflect green light and look green) Chloroplast -the organelle that captures energy from sunlight for photosynthesis • thylakoids – saclike photosynthetic membranes • grana – thylakoid stacks • photosystems – light-collecting units • stroma – region outside the thylakoid membranes Photosystems II & I (light-dependent reactions) O2 H2O • produce oxygen gas • occurs in the thylakoid membranes - light-independent rxn., occurs in the stroma, produces sugars Photosynthesis 5 Essential Questions 1. Write the equation for photosynthesis. 2. In photosynthesis, light energy is converted into ___________ energy. This is called ___________________. 3. In what organelle does photosynthesis occur? 4. On what part of the chloroplast does the light dependant reaction take place? What are the four products of the reaction? 5. What is another name for the light independent reaction? Where in the chloroplast does is take place? What does it produce? Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) - one of the main chemical compounds cells use to store and release energy - adenine - 5-carbon sugar - three phosphate groups - light-independent rxn., occurs in the stroma, produces sugars CO2 + ATP + NADPH phosphoglyceraldehyde (PGAL) high-energy sugars (glucose), sometimes lipids and amino acids Photosystems II & I O2 (light-dependent reactions) ADP NADP + ATP NADPH • produce oxygen gas • convert ADP and NADP+ into the energy carriers ATP and NADPH • occurs in the thylakoid membranes ATP Used to power: 1. active transport (Na+ K+ pump) 2. protein synthesis 3. muscle contractions (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate) electron • high energy electron carrier • NADP+ + 2e- = NADPH (electron transport) • pigment absorbs light, electrons’ energy increases and pass down the electron transport chain • H20 is oxidized to replace the 2e-, releasing O2 & H+ • uses energy from electrons to move more H+ inside • uses energy from light to reenergize the electrons • NADP + electrons + H+ ions = NADPH (outside the membrane) • more H+ pumped into membrane creating a chemiosmotic gradient • H+ pass through ATP synthase producing ATP • CHEMIOSMOSIS – coupling energy from the electrons to create a gradient and make ATP