* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Lymphatic System Immunity
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
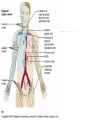
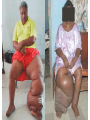
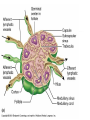
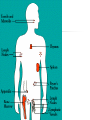
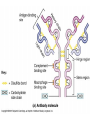
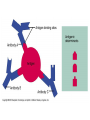
The Lymphatic System and Immunity Lymph, lymph capillaries, ducts, nodes and other lymphoid organs Functions Filter and absorb excess tissue fluid and return it back into circulation Transport of dietary lipids via lacteals Carry out immune responses Lymph and Lymph Capillaries Lymph - clear, watery fluid resembling interstitial fluid Lymph capillaries - begin as blind-ended capillaries consisting of simple squamous epithelium allowing one-way movement of fluid Lymph Vessels Formed from merging capillaries Have thin walls and posses valves Thoracic duct originates as cisterna chyli draining abdomen, extremities, and left side of body Right lymphatic duct - drains lymph from the right arm and upper right side of body Elephantiasis Blockage of the lymphatic system by parasitic worms Transmitted by mosquitos Causes severe swelling Lymph nodes Oval structures clustered along lymphatic vessels that serve to filter lymph Consists of capsule, cortex, and medulla Cortex contains mostly lymphocytes Medulla filled with macrophages Accessory Structures Spleen Thymus Tonsils pharyngeal palatine lingual Spleen Size of a fist Located in left superior abdominal cavity Functions: Lymphocyte storage & surveillance Blood cleansing Recycles blood products Fetal erythrocyte production Stores blood platelets Thymus Located in lower neck, upper thoracic region Secretes hormones, thymosin & thymopoietin Function: T-cell maturation Decreases in size with age Tonsils Form ring around entrance to throat Epithelial surface invaginates to form crypts that trap bacteria & particulate matter Types: Palatine tonsils - visible tonsils Pharyngeal tonsil (adenoids) Lingual tonsil - at base of tongue Tubal tonsils - surround the openings to the auditory tubes Other aggregates of lymphoid tissue Peyer’s patches - nodules located in the ileum portion of the small intestine Appendix Destroy bacteria in the digestive system Belong to MALT (Mucosa-Associated Lymphatic Tissue Disorders of the Lymphatic System Hodgkin’s disease - malignant cancer of the lymph nodes Lymphoma - any tumor of the lymphoid tissue (benign or malignant) Non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma - all cancers of lymphoid tissues except Hodgkin’s disease Tonsilitis - inflammation of the tonsils Mononucleosis - caused by Epstein-barr virus attacking the B-lymphocytes which are in turn attacked by oversized Tlymphocytes. These were misidentified orginally as monocytes. Nonspecific Resistance Mechanical Barriers Skin - epidermis Mucous membranes Cilia - hair, mucus Flushing mechanisms Chemical Protection Lysozymes - in tears & saliva Sebum Gastric juice Body secretions Acid = pH 3-5 Mucus Antimicrobial substances Interferons defend against viruses, suppress tumors and enhance phagocytosis; stimulates production of PKR which interferes with viral replication Complement >20 proteins that attach and “lyse” the cell opsonization (enhances phagocytosis) enhances the inflammatory response Non-specific Immunity Phagocytosis Macrophages, Neutrophils chemotaxis, adherence, ingestion, destroy Natural Killer Cells (NK) Large granular lymphocytes Attach and release “perforins” Inflammation swelling, redness, pain, heat histamines = promote dilation & permeability Phagocyte mobilization Leukocytosis leukocyte production Margination - neutrophils collect inside nearby capillaries Diapedesis - neutrophils squeeze out of capillaries into tissues Chemotaxis - neutrophils are attracted to injury Monocytes follow; become Macrophages Fever Pyrogens released by leukocytes & macrophages raise body temperature Inhibits growth of microorganisms Increases metabolic rate of cells Can denature enzymes Specific Immunity Characteristics: specificity memory self recognition Types of Cells Lymphocytes arise from hemocytoblasts in the bone marrow B cells develop immunocompetence in the bone marrow T cells - mature in thymus Types of Immunity Antibody-mediated immunity humoral immunity involves B cells and the production of antibodies Cell - mediated immunity cellular immunity involves the destruction of intracellular pathogens by T cells Antigens Any substance that can elicit an immune response Immunogenicity - “antibody-generating” Haptens - incomplete antigens (allergens) Major histocompatibility complex antigens (MHC-I, MHC-II) ; “Self”-proteins Class I - found on all cells Class II - found only on certain cells Antibodies = immunoglobulins Highly specific soluble proteins secreted by plasma cells in response to an antigen Structure of an antibody Heavy and light chains Variable and constant regions Up to a Billion different variables Antigen-binding sites Antibodies Five classes of antibodies IgM - first released; can fix complement IgA - usually found in secretions IgD - B-cell receptor IgG - most abundant; crosses placenta; can fix complement IgE - causes allergic reactions Antibody - Mediated Immunity B cells are activated by the presence of a foreign antigen which is taken into the B cell, processed and then displayed in combination with an MHC-II molecule the on the cell’s surface Activated B cells develop into clones of antibody producing plasma cells Plasma cells produce antibodies (2,000/sec) Costimulation by Helper T cells useful Functions of Antibodies Agglutination Precipitation Neutralization Enhanced phagocytosis Complement activation Immunological Memory Primary response - first exposure Secondary response - 2nd, 3rd, 4th, etc. Faster Higher Levels More efficient Active & Passive Immunity Active = caused by encounter with antigens Natural - acquired by infection & disease Artificial - acquired by vaccination Passive = caused by encounter with antibodies Natural - acquired from Mom; antibodies cross placenta Artificial - acquired from immune sera such as: gamma globulin, antivenom, antitoxins Cell - Mediated Immunity T cells recognize and respond only to processed antigen presented by an APC (antigen presenting cell) Binding of T cell to macrophage causes secretion of interleukin-I which helps activate T helper cells (also called CD4 or T4 cells) TH cells secrete IL-2 which enhances B cell activity and costimulates cytotoxic T cells (CD8 or T8 cells) Types of Lymphocytes Helper T cells - TH Cytotoxic (killer)T cells - T8 Stimulates macrophages Suppressor T cells - TS Kills invaded cells, cancer cells, rejects tissue Delayed Hypersensitivity T cells - TDH Stimulates other B & T cells (co-stimulation) Slows or stops B & T cells Memory T cells remain in body for years for secondary response Cytokines Interferons Interleukins Lymphotoxins Macrophage migration inhibitory factor Perforins Supressor factors Complement Immunodeficiencies SCID - Severe Combined Immunodeficiency Syndrome Acquired Immunodeficiencies Disease induced; Hodgkins, Leukemia Chemically induced; immune suppressing drugs AIDS Diagnosed 1981; Began ? AutoImmune Disorders Multiple Sclerosis - affects white matter of CNS Myasthenia Gravis - destroys Ach receptors between nerves & muscles Graves’ Disease - causes hyperthyroidism Type I Juvenile Diabetes - destroys insulinproducing cells Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Rheumatoid Arthritis - attacks joint tissues