* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PowerPoint Presentation - Horizon Christian Academy
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Implicit solvation wikipedia , lookup
Circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
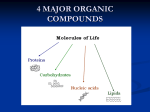
Chapter 2 Main Focus: Organic Compounds organic -we are going to focus on ____________ compounds: C and _____ -always contain ____ H -generally have ____ O as well, but not always **_______ C - H bonds store a lot of energy = when the bonds are ___________ broken, energy is _____________ released _____ 4 major classes of organic compounds Carbohydrates 1. ________________ H and ____ 1:2:1 C ___, -contain __, O in a _________ ratio energy -great source of ________________ 3 major types: Monosaccharide _______________ - 1 sugar molecule Disaccharide - 2 sugar molecules _______________ Polysaccharide _______________ - multiple sugar molecules Monosaccharides simple -__________ sugars -most important energy source in the body is ___________ glucose Disaccharides -2monosaccharides ________________ linked together -also considered ___________ sugars simple Polysaccharides multiple sugars linked together -_________ -sugars are stored in the body in the form of ___________ glycogen Simple vs. complex sugars -simple sugars are the quickest source of energy because they are digested (release energy) ____________ rapidly -complex sugars are made of larger numbers of carbohydrates __________ linked together -generally rich in _________ which fiber slows down rate of digestion _________ -allows for more ____________ sustained levels of energy 2. __________ Lipids -long chains of ____ C and ____ H in a 1:2 ratio ______ -may contain some other elements too fats _____, oils andwaxes - _____, __________ -used for ______-term energy supplies long -about _________% of total body weight 12 - 18 in men and 18 ________% in women - 24 Fatty Acids Saturated vs. Unsaturated -fat molecule is completely covered saturated with hydrogen (___________) solid at room temp. -generally _______ -fat molecule is not entirely covered with hydrogen - _____________ unsaturated -generally liquid at room temp. -most commonly stored in body as triglycerides 3 fatty acids _______________: ___ attached to a _________ glycerol molecule Trans fats (hydrogenated oils) -liquid oils that have been chemically hardened to make them more solid -often used in snack foods because they allow for a long shelf life -Lipids also contain _________, steroids cholesterol ______________, and _______________ hormones phospholipids - main -also form ________________ structure of cell membrane 3. _____________ Proteins -most abundant organic components of the human body 20 of total body weight -about ___% N and H _____, -all contain ___, _____ O C ____, possibly even ______ S -body makes at least __________ 400,000 different proteins **Proteins are chains of _________ amino acids** - anywhere between 1000 - over 100, 000 long Protein Functions: Support 1. __________ - Structural proteins - for cells, tissues, organs Movement 2. _____________ - Contractile proteins muscle contraction and individual cells Transport - carry other substances 3. ___________ in the blood; also inside cells 4. __________ Buffering - help to regulate pH levels Metabolic regulation - enzymes 5. ____________________ control metabolism rates Defense 6. _______________ - antibodies; skin, hair and nails 7. Communication _______________ - affect functions of organs and organ systems shape is critical to the **Protein's _________ function protein's _____________** temp. pH __________, -shape affected by ____, and ___________ composition ionic Nucleic Acid 4. _____________ -large organic molecules H C -composed of _____, _____, ______, O N ______, and _____ P stores and processes -________ ___________ genetic information inside cell 2 kinds: Deoxyribonucleic acid (__________) DNA ____________________ Ribonucleic acid (__________) ____________________ RNA **Nucleic acids are long chains of nucleotides ___________** High Energy Compounds ATP - cellular energy ______