* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Acetylcholine (ACh)
Biochemical cascade wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Paracrine signalling wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Lipid signaling wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
NMDA receptor wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
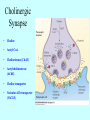
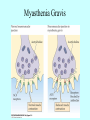
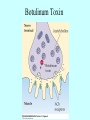
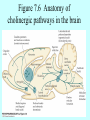
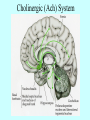
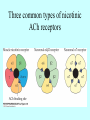
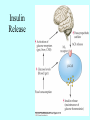
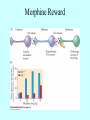
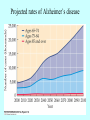
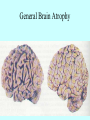
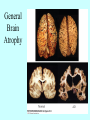
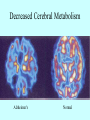
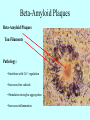
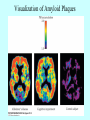
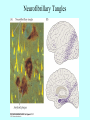
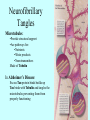
Neurotransmitters •Neuropeptides •Amines •Quaternary amines •Acetylcholine (ACh) •Monoamines •Catecholamines •Epinephrine (EPI) •Norepinephrine (NE) •Dopamine (DA) •Indoleamines •Serotonin (5-HT) •Melatonin •Amino acids •Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) •Glutamate (GLU) •Glycine •Histamine (HIST) •Opioid peptides •Enkephalins (ENK) •Endorphins (END) •Peptide Hormones •Oxytocin (Oxy) •Substance P •Cholecystokinin (CCK) •Vasopressin (ADH) •Neuropeptide Y (NPY) •Brain-derived Neurotrophic factor •Hypothalamic Releasing Hormones •GnRH •TRH •CRH •Lipids •Anandamide •Gases •Nitric Oxide (NO) Acetylcholine Synthesis Breakdown Cholinergic Synapse • Choline • Acetyl CoA • Cholinesterase (ChAT) • Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) • Choline transporter • Vesicular ACh transporter (VAChT) Myasthenia Gravis Botulinum Toxin Autonomic Nervous System Figure 7.6 Anatomy of cholinergic pathways in the brain Cholinergic (Ach) System Cholinergic Receptors • Nicotinic receptors • Muscle Type • • • • CNS Type Muscarinic receptors • M1 • • Iontotropic • • Blood vessels Lungs Exocrine Glands M4 • • Heart M3 • • • metabotropic CNS Autonomic ganglia M2 • • CNS M5 • Nicotinic ACh Receptor Neuromuscular junction Autonomic ganglia CNS Structure of the nicotinic ACh receptor Three common types of nicotinic ACh receptors Insulin Release Attentional Processing Morphine Reward Deadly nightshade (Atropa belladonna) Alzheimer’s Disease • • • • Chronic Progressive Dementia disorder Cases are expected to increase Projected rates of Alzheimer’s disease Disease Progression • • • • • • • • • • • • mild cognitive impairment (MCI) general forgetfulness progressive loss of memory issues with emotional behavior, personality, language, perception, thinking, and judgment anhedonia ability to name familiar objects or people is impaired problems with misplacing items or getting lost on familiar routes increase in frequency physiological problems such as disrupted sleep, incontinence, and difficulty swallowing psychiatric symptoms such as delusions, hallucinations, depressed mood, and agitation (including violent outbursts) may occur. communication skills are diminished loss of personal episodic memories leads to withdrawal from social contact Loss of the ability to use language, interact, and recognize loved ones Risk Factors • • • • • • • • • • • • Advancing Age Family History Obesity Untreated Hypertension High Cholesterol Stress Sedentary Lifestyle Head Trauma Hypoxic Brain Injury Depression Bipolar Disorder PTSD Alzheimer's: Biology • chromosomes 1, 14, 19, and 21 • general brain atrophy • neuronal degeneration • decreased cerebral metabolism • general decay of acetylcholine system – especially in the basal forebrain • neurofibrillary tangles • beta-amyloid plaques General Brain Atrophy General Brain Atrophy Neuronal Degeneration Normal Alzheimer’s Decreased Cerebral Metabolism Alzheimer's Normal Beta-Amyloid Plaques Beta-Amyloid Plaques Tau Filaments Pathology: •Interferes with Ca2+ regulation •Increases free radicals •Stimulates microglia aggregation •Increases inflammation Beta-Amyloid Plaque Formation Key enzymes: •Alpha-secretase •Beta-secretase •Gamma-secretase Protein fragments: p3 alpha and gamma harmless 40 amino acid string beta and gamma harmless 42 amino acid string beta and gamma TOXIC Beta-Amyloid Precursor Protein (BAPP) is cut or cleaved by these enzymes three different protein fragments form Visualization of Amyloid Plaques Neurofibrillary Tangles Neurofibrillary Tangles Microtubules: •Provide structural support •Are pathways for: •Nutrients •Waste products •Neurotransmitters Made of Tubulin In Alzheimer’s Disease: Excess Tau protein binds builds up Tau binds with Tubulin and tangles the microtubules preventing them from properly functioning Treatment • Cholinesterase inhibitors: improve cognition by increasing acetylcholine in the synapse by reducing its breakdown. • NMDA glutamate receptor antagonist memantine (Namenda): prevents the drastic increase in cell firing that leads to excitotoxicity, without significant side effects.