* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Genetics Unit Guid ANSWERS
Inbreeding avoidance wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
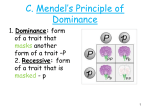
GENETICS UNIT GUIDE Read: Chapters 6.3-6.5 and 7.1-7.2 (www.my.hrw.com username: astudents602 password: n2s7v) Watch (Supplemental Resource): Amoeba sisters (Monohybrids and the punnett square guinea pigs) Bozeman science (Genetics) Listen and Look: Here is a list of key terms you will hear and see during the reading and video. You will be completing a vocabulary activity using these terms. 1. Meiosis = form of nuclear division that divides a diploid cell into haploid cells, important in forming gametes for sexual reproduction. 2. Heredity = passing of traits from parents to offspring. 3. Genome = all an organism’s genetic material. 4. Gene = specific region of DNA that codes for a particular protein. 5. Alleles = any of the alternative forms of a gene that occurs at a specific place on a chromosome. 6. Genotype = collection of all an organism’s genetic information that codes for traits. 7. Phenotype = collection of all of an organism’s physical characteristics. 8. Dominant = allele that is expressed when two different alleles are present in an organism’s genotype. 9. Recessive = allele that is not expressed unless two copies are present in an organism’s genotype. 10. Homozygous = characteristic of having two of the same alleles at the same spot on homologous pairs. 11. Heterozygous = characteristic of having two different alleles that appear at the same spot on homologous pairs. 12. Autosomes = chromosomes that contain genes for characteristics not directly related to the sex of the organism. 13. Sex Chromosome = chromosome that directly controls the development of sexual characteristics. 14. Probability = likelihood that a particular event will happen. 15. Punnett Square = model for predicting all possible genotypes resulting from a mating. 16. Monohybrid cross = mating between organisms that involves only one pair of contrasting traits. 17. Dihybrid cross = mating between organisms involving two pairs of contrasting traits. 18. Incomplete dominance = heterozygous phenotype that is a blend of the two homozygous phenotypes. 19. Codominance = heterozygous genotype that equally expresses the traits from both alleles. 20. Polygenic = trait that is produced by two or more genes. Recall and Review: Use the videos and your textbook to help you answer the following questions in your BILL. Section 6.3 1. State three examples of traits. Hair color, eye color, height 2. Define the term purebred. Homozygous, bred from parents of the same variety Section 6.4 3. Distinguish between the terms allele and locus. An allele is the alternative form of a trait. The locus is the specific point on a chromosome where that allele can be found. 4. Explain the difference between genotype and phenotype. A genotype is the actual DNA of the parent (it is the combination of the two alleles). Phenotype is the way the person looks. It is the actual appearance of the trait. 5. Explain the difference between dominant and recessive. A dominant trait is the one that masks the recessive. If you have one copy of a dominant allele then you will display that trait. The recessive is hidden by the dominant if they are both present. It takes two recessive alleles to actually see the recessive phenotype. 6. Explain how the homozygous condition differs from the heterozygous condition. Homozygous is when both alleles are the same and heterozygous is when one is dominant and the other is recessive. Section 6.5 7. Copy and label the Punnett square at the beginning of this section. (visual vocab). 8. Explain the purpose of a testcross. A testcross allows you to determine the genotype of one parent when you know for sure the other parent is homozygous recessive. You look at the offspring and then work your way backwards. 9. Define probability. is the measure of the likeliness that an event will occur 10. State two similarities and two differences between a monohybrid and a dihybrid Punnett Square. Similar – both display genotypes of parent and then result in genotypes of the offspring; both are probabilities. Different – mono looks at one trait and di looks at two traits; mono can produce only two phenotypes while di can produce four phenotypes. Section 7.1 11. Explain the difference between autosomes and sex chromosomes. Autosomes are the first 22 pairs of chromosomes. They are called the body chromosomes. The 23rd pair of chromosomes are the sex chromosomes. They determine the gender of the individual. 12. What is a “carrier”? A carrier is an individual that is heterozygous for a trait. They carry the recessive allele but do not have the trait. 13. Explain why males are more likely than females to have sex-linked genetic disorders. Because males only have one copy of the x chromosome they are more likely to have the disorder. Because females get two copies of the X chromosome, they need to have to copies of the recessive disorder allele in order to get the disorder. 14. Can a person be a carrier for a dominant genetic disorder? Explain. No because if it is a dominant disorder then you only need one copy to be affected by the disorder. Section 7.2 15. How is incomplete dominance expressed in a phenotype? It is a blend of the two original (P) phenotypes. Ex: Red X White = Pink 16. How is codominance expressed in a phenotype? Both phenotypes are expressed Ex: Black X White = Checkered 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 17. Sample Questions A human with the genotype XX is a. an example of the failure of chromosomes to separate during meiosis b. a female CORRECT c. a male d. a dwarf The scientist who first described the principle of dominance, segregation and independent assortment was a. Charles Darwin b. Albert Einstein c. Louis Pasteur d. Gregor Mendel CORRECT To visualize Mendel's experiments, or any cross in genetics, a simple diagram called a _____ may be used. a. graphing calculator b. Punnett square CORRECT c. probability circle d. genotype The phenotype of a heterozygous brown rabbit is: a. Brown CORRECT b. BB c. bb d. Bb A cross of a white hen with a black rooster produces an offspring that shows a blending or mixing of the genotype. This type of inheritance is known as a. incomplete dominance CORRECT b. polygenic inheritance c. codominance d. multiple allele