* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch.8 Rise of Islam - Miami Beach Senior High School
Islam and war wikipedia , lookup
Islamic feminism wikipedia , lookup
Soviet Orientalist studies in Islam wikipedia , lookup
War against Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam and violence wikipedia , lookup
Islamofascism wikipedia , lookup
Islam and secularism wikipedia , lookup
Schools of Islamic theology wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of Islamism wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Sikhism wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Iran wikipedia , lookup
Islamic democracy wikipedia , lookup
History of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islamic Golden Age wikipedia , lookup
Liberalism and progressivism within Islam wikipedia , lookup
Gender roles in Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Egypt wikipedia , lookup
Spread of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Afghanistan wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Bangladesh wikipedia , lookup
Medieval Muslim Algeria wikipedia , lookup
Islamic ethics wikipedia , lookup
Islamic missionary activity wikipedia , lookup
Islamic socialism wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Somalia wikipedia , lookup
Reception of Islam in Early Modern Europe wikipedia , lookup
Political aspects of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islamic schools and branches wikipedia , lookup
Islam and other religions wikipedia , lookup
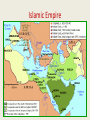
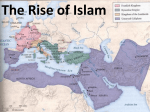
Ch.8 The Rise of Islam 600-1200 Ka’ba in Mecca Main Idea Details Origins •Arabs of 600 CE lived exclusively in the Arabian peninsula and desert fringes of Syria, Jordan, Iraq. •The Sasanids (Persian empire) used Bedouins (nomadic Arabs) to protect their empire from invasion. The Byzantines (Christian Empire) did the same. •The interior Arabs remained isolated and that is where Islam emerged. Technology Notemaking go •Camel saddle contributed to the dominance of caravan cities. Wheels disappeared as pack animals replaced the wheel. Berbers used the camel saddle to cross the Sahara after it was introduced by the Arabs. Bedouin Camel Caravan Main Idea Details Notemaking Politics •After Muhammad’s death in 632, the Arabs conquests gave birth to a dynamic and religious society known as the Islamic Caliphate (empire ruled by a Caliph- political and religious leader) also known as Dar al Islam (house of submission). Stretched from Iberian Peninsula (Spain and Portugal) to the Indus Valley. •Arabs ruled over largely non-Arab, non-Muslim populations. Christians and Jews did not have to convert, but they did have to pay extra taxes. •Umayyad Caliphate fell in 750 (except in Spain). Abbasid Caliphate fell to the Mongols in 1258. Marks the end of Islamic Empires. go Economy •Urban, trade based. •Introduced standard coinage (gold dinars) which spread from Morocco to China. •Spread sugar, cotton and citrus crops. Islamic Empire Main Idea Details Notemaking Society •women lived in seclusion and covered themselves if they left the home. This practice already existed in the Byzantine empire (Christian) and Sasanid Iran. •Men could have sexual relations with as many slave concubine women as he pleased, but could only marry up to 4 women. •Islamic law granted women greater status than Christian or Jewish law. Women could own property, get a cash payment upon divorce and remarry. Could testify in court (but counted half as a man). Still, Koran has misogynist undertones, “I was raised up to heaven and saw that most of its denizens were poor people; I was raised into the hellfire and saw that most its denizens were women.” •Islam allowed slavery but forbade Muslims from enslaving other Muslims (or people of the book-Jews and Christians). •Offspring of slave women and Muslim men were born free. go Alhambra Palace in Andalusia Spain Alhambra Palace in Andalusia Spain Mosaic Tiles Main Idea Details Notemaking Intellectual •Some writers extolled homosexual relationships since male lovers could appear in public and travel. •Madrasas (religious schools) were the first universities. •Arabic language spread across North Africa. •Sufism, mystical form of Islam which tried to create a direct union with God. Known for poetry. •Mosaic tiles and architecture formed basis of Islamic art (not allowed to depict human form). •Major contributions in poetry, math, science, medicine, sea exploration astrolabe, and preservation of Greek and Roman knowledge. go