* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Knuffke Prezi- Macromolecules
Rosetta@home wikipedia , lookup
Protein design wikipedia , lookup
Structural alignment wikipedia , lookup
Bimolecular fluorescence complementation wikipedia , lookup
Protein purification wikipedia , lookup
Homology modeling wikipedia , lookup
Protein domain wikipedia , lookup
Protein folding wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Protein mass spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Intrinsically disordered proteins wikipedia , lookup
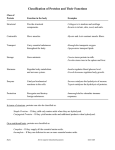
Organic Compounds Substances which contain Carbon. All living things contain Carbon, it is known as the backbone of life. Proteins 21 Amino Acids Amino Acids • Alpha C • H atom • Amino group • Carboxyl group • R side chain • • • • • 21 aa found in proteins 8 are essential, we can’t make them Form peptide bonds to make proteins Some are hydrophilic, hydrophobic and electrically charged The R group determines the 3 dimensional shape of protein Protein formation • Primary structure - the linear sequence of amino acids • Secondary structure • alpha-helix - (called alpha b/c 1st to be discovered) • a- keratins are hard • nails, hooves, and horns • soft=hair, wool (the difference is the amount of cystine) • b-pleated sheet - cross-linked by H • b-keratins are silk, spider webs, feathers, scales, claws, beaks of reptiles and birds • collagen - most abundant protein in body; found in bones, tendons, ligaments, and cartilage; boiled for Jello • Tertiary structure - most functional proteins • Secondary structure + random coiled subunits + S-S bonds • Caused by interactions of R groups • Globular or cigar shaped • Quaternary structure • Tertiary + tertiary + tertiary, etc. • Hemoglobin = 4 tertiaries Nucleic Acids ATP ATP + H2O ADP + Pi + free energy