* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Bell Work: What is the difference between a haploid and diploid cell?
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
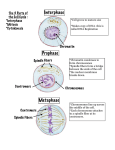
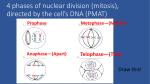
meiosisnotes.notebook November 14, 2013 Thursday, November 21 Bell Work: What is the difference between a haploid and diploid cell? 1 meiosisnotes.notebook November 14, 2013 Review Mitosis: 2 meiosisnotes.notebook November 14, 2013 3 meiosisnotes.notebook November 14, 2013 Prophase I DNA coils into chromosomes Spindle fibers form Nuclear membrane breaks down Centrioles move to opposite sides of the cell. Crossing over occurs here. Homologous chromosomes line up gene to gene in a fourpart structure called a tetrad. Tetrad is made up of 2 homologous chromosomes, with 2 sister chromatids. Sex chromosomes also pair up with one another 4 meiosisnotes.notebook November 14, 2013 Crossing Over The exchange of chromosome segments between homologous chromosomes during prophase I of meiosis. Exchange of genetic material creates more genetic diversity. Results in a new combination of alleles, called genetic recombination. Can occur at any location on a chromosome and in several locations at the same time. Draw a detailed picture using colored pencils to show crossing over occuring. pg 190 In humans approximately 23 crossovers for each pair of homologous chromosomes. 5 meiosisnotes.notebook November 14, 2013 Linked Genes or (genetic linkage) genes that are close together on the same chromosome are more likely to be inherited together (linked together) the farther apart two genes are located, the more likely they are to be separated when crossing over. 6 meiosisnotes.notebook November 14, 2013 7 meiosisnotes.notebook November 14, 2013 Metaphase I Centromere attaches to spindle fibers Homologous chromosomes are lined up side by side in the middle as tetrads. **Remember: In mitosis they were a single file line** 8 meiosisnotes.notebook November 14, 2013 Anaphase I: Homologous chromosomes separate and move to opposite ends of the cell. Centromere does NOT split, sister chromatids stay together. Ensures that each new cell will only have 1 chromosome from each homologous pair. 9 meiosisnotes.notebook November 14, 2013 Telophase I: Nuclear membrane forms again. Spindle fibers break down Cytoplasm divides We end up with 2 cells with a unique combination of 23 duplicated chromosomes coming from both parents. Note: Still contains doubled chromosomes. Therefore, a second cell division is necessary to separate the doubled chromsomes 10 meiosisnotes.notebook November 14, 2013 11 meiosisnotes.notebook November 14, 2013 Meiosis II: Exactly like mitosis. It divides sister chromatids resulting in undoubled chromosomes. The process described below relates to both cells. Note: DNA is NOT copied again between the two stages. Directions: Use pages 174175 to describe what occurs during each phase and complete a detailed picture of each stage. Prophase II The nuclear membrane breaks down Centrioles move to opposite sides of the cell. Spindle fibers form 12 meiosisnotes.notebook November 14, 2013 Metaphase II Spindle fibers align the 23 chromosomes at the cell equator (in the middle). Anaphase II Sister chromatids are pulled apart from each other and move to opposite sides of the cell. 13 meiosisnotes.notebook November 14, 2013 Telophase II: Nuclear membranes form around each set of chromosomes at opposite ends of the cell. Spindle fibers break apart. cell undergoes cytokinesis END RESULT OF MEIOSIS Four haploid cells with a combination of chromosomes from mom and dad. Haploid cells become gametes transferring the genes they contain to the offspring. 14 meiosisnotes.notebook November 14, 2013 15 meiosisnotes.notebook November 14, 2013 16