* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Asepsis - Home | Quincy College
Traveler's diarrhea wikipedia , lookup
Middle East respiratory syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Tuberculosis wikipedia , lookup
Leptospirosis wikipedia , lookup
Toxocariasis wikipedia , lookup
Cryptosporidiosis wikipedia , lookup
Clostridium difficile infection wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Microbicides for sexually transmitted diseases wikipedia , lookup
Carbapenem-resistant enterobacteriaceae wikipedia , lookup
Onchocerciasis wikipedia , lookup
Cross-species transmission wikipedia , lookup
Hookworm infection wikipedia , lookup
Toxoplasmosis wikipedia , lookup
West Nile fever wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Schistosoma mansoni wikipedia , lookup
Trichinosis wikipedia , lookup
Anaerobic infection wikipedia , lookup
Sexually transmitted infection wikipedia , lookup
Herpes simplex wikipedia , lookup
Henipavirus wikipedia , lookup
Dirofilaria immitis wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Herpes simplex virus wikipedia , lookup
Sarcocystis wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis C wikipedia , lookup
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
Coccidioidomycosis wikipedia , lookup
Lymphocytic choriomeningitis wikipedia , lookup
Oesophagostomum wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
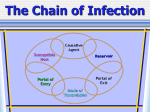
Asepsis Chapter 10 Bethann Davis MSN,NP Quincy College PNU145 Fall2015 Asepsis • Learning objectives: At the end of the chapter, the student will be able to: define microorganisms and pathogens list the six components in the chain of infection name factors to break the chain of infection Asepsis define nosocomial infections differentiate between medical and surgical asepsis list common medical aseptic practices Microorganisms • Living plants, animals visible only with a microscope • Commonly called germs Microorganisms Divided in to 2 groups Pathogens Nonpathogens (normal flora) Microorganisms • Many of these will reside within the body without causing diseases • Some will cause an infection or infectious diseases Types of Pathogens • Pathogens-are micro-organisms or microbes that cause infection • Bacteria (Staphylococcus, E-coli, strep) • Viruses ( HIV, hepatitis, herpes zoster/simplex, ebola) • Fungi Molds and yeasts (Candida albicans, Alpergillus) • Prions Protein particles Pathogens • Parasites Protozoa (malaria, toxoplasmosis) and helminths ( worms) • Virulence is the ability of a pathogen to invade and injure a host Microorganisms • Chain of infection: 1. Infectious agent 2. Reservoir for growth 3. Exit route from reservoir 4. Means of transmission 5. Portal of entry 6. Susceptible host Microorganisms • Chain of infection Microorganisms • Chain of infection 1. infectious agent Bacteria, virus, fungus, prior, parasite 2. reservoir for growth Human, animal, water, soil, insect Chain of infection • 3. Exit route from reservoir • 4. Means of transmission Microorganisms • Chain of infection (cont) 5. Portal of entry 6. Susceptible host Infection Process Chain of infection • Causative agent (bacteria, fungus, parasite) • Reservoir (human, water, soil, insect) • Portal of exit from (means of leaving) the host -Respiratory tract (droplet,airborne) Mycobacterium tuberculosis and strep pn -Gastrointestinal tract Ecoli, hepatitis A, herpes virus Chain of infection • Skin/MM -herpes and varicella Blood/body fluids -HIV,hep B and C Mode of transmission • Contact -direct, indirect, fecal oral Droplet -sneezing, coughing, talking Airborne -sneezing, coughing Vector borne -Animals or insects (ticks, mosquitoes) Portal of entry to the host • May be same as portal or exit • Susceptible host -Compromised defense mechanism (immunocompromised, breaks in skin) leave host more susceptible Immune Defenses • Nonspecific innate immunity -temportary immunity -intact skin -MM, secretions, phagocytic cells, protective protein -inflammatory response Immune Defenses • Specific adaptive immunity -Requires time to react -Provides permanent immunity -Involves B- and T lymphocytes -Produces specific antibodies Infection Control (IC) • An infection occurs when the presence of a pathogen leads to a chain of events. All compartments must be present and intact for the infection to occur. • Nurses use IC practices (medical/surgical asepsis, standard precautions) to break the chain and stop the spread of infection. Microorganisms • Nosocomial infections: an infection acquired while client was in healthcare facility ex. pneumonia, urinary Asepsis • Asepsis: practices that decrease or eliminate infectious agents, their reservoirs, and vehicles for transmission Health care professionals use both medical and surgical asepsis to prevent spread of infections. Asepsis • Medical asepsis: reduces number of organisms measures that interfere with the chain of infection. Infection Process Chain of infection • Causative agent (bacteria, fungus, parasite) • Reservoir (human, water, soil, insect) • Portal of exit from (means of leaving) the host -Respiratory tract (droplet,airborne) Mycobacterium tuberculosis and strep pn -Gastrointestinal tract Ecoli, hepatitis A, herpes virus Stages of an infection • • • • Incubation Prodromal stage Illness stage Convalescence Asepsis • Surgical asepsis: measures that make supplies and equipment totally free of organisms practices to avoid contaminating sterile items Asepsis • Surgical asepsis practices: sterilization using sterile gloves creating sterile fields following rules of sterile fields/objects Asepsis • Surgical asepsis practices: General considerations • Older clients more susceptible to infections. • Maintain intact skin, proper aseptic techniques, personal hygiene, and thorough hand washing. • Sick health care workers should take sick leave rather than expose susceptible clients to infectious organisms.