* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cells and HBS
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Somatic cell nuclear transfer wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal lineage marker wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Symbiogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
Cell (biology) wikipedia , lookup
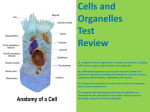
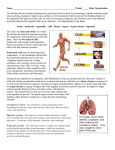
Bell Work: 4/13/16 •Read pg. 19. Answer 1&3 on pg. 20. Cell Organelles SPI 0707.1.1 Identify and describe the function of the major plant and animal cell organelles. •Cell Structures • A few major Organelles: • Nucleus- Control Center • Cell Membrane- controls what enters and leaves the cell • Ribosome- Makes proteins • Endoplasmic Reticulum- Smooth and Rough; packages and transports proteins • Cytoskeleton- web of proteins that provides structure. • Cytoplasm- thick fluid that hold organelles • Vacuole- packages and sends materials to other cells • Mitochondria- creates energy for the cell (Cellular Respiration) • Chloropasts- only in plant cells. Makes food for the cell (Photosynthesis) • Cell Wall- Only in plant cells. Gives extra support for the cell. • • • • • ER: passageway, rough has ribosomes (protein) Vacuole: helps digestion, stores waste Lysosome: digests food, waste, cell parts Mitochondria: makes energy (ATP) & breaks down food Plants have cell wall, chloroplasts, & 1 large vacuole Study Guide KP! 1.1 Organelles Review Game- Cell Organelles • Which of these correctly identifies a cell organelle and its function? • • • • a.The nucleus temporarily stores materials. b.The ribosome makes proteins. c.The vacuole performs cellular respiration. d.The Golgi complex converts light energy into chemical energy. • Look at this diagram of an animal cell. • • • • • The arrow is pointing to a.the endoplasmic reticulum b.the Golgi apparatus c.a mitochondrion d.a ribosome Mitosis vs. Meiosis SPI 0707.1.4 Sequence a series of diagrams that depict chromosome movement during plant cell division. •Mitosis • Stages of the Cell Cycle • Interphase- the cell is growing and DNA is copying. • Mitosis • Prophase- DNA condenses into chromosomes • Metaphase- Chromosomes line up in the middle. • Anaphase- Chromosomes split and are pulled to opposite sides of the cell. • Telophase- Two new nuclei form and DNA decondenses. • Cytokinesis- The cell has divided and begins to grow. • • • • • During this phase of mitosis, new chromosomes stretch out, a new nucleus forms around each set of chromosomes, and a new cell membrane begins to form: A Prophase B Metaphase C Anaphase D Telophase • • Interphase, Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase, Cytokinesis • Chromosomes copy, condense, align, separate, unwind, new nuclear membrane, 2 identical cells Study Guide KP! 1.4 Cell Division Bell Work: 4/14/16 •Read pg. 21. Answer 1-2 on pg. 22. •Read pg. 23. Answer 1-3 on pg. 24. Levels of Organization SPI 0707.1.2 Interpret a chart to explain the integrated relationships that exist among cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems. •Cellular Organization (neuron grey matter brain nervous system human) • cell tissue organ organ system organism Study Guide KP! 1.2 Levels of Organization • A group of cells that work together is a(n): • A B C D organism tissue organ system organ Human Body Systems SPI 0707.1.3 Explain the basic functions of a major organ system. • Amoeba Sisters Human Body Systems • Cardiovascular: carries oxygen-rich blood through body (to and from heart) • Nervous: receives & sends electrical messages from surroundings (brain) • Lymphatic/ immune: protect against bacteria, viruses, invaders • Respiratory: includes lungs, take in O2 and release CO2 • Skeletal/ muscular: work together to protect organs, create movement Study Guide KP! 1.3 Human Body Systems • Which is not a major function of the circulatory system? • • A delivering oxygen and nutrients to cells • B carrying carbon dioxide away from cells • C removing solid waste from the body • D pumping blood throughout the body • What is the function of this organ system? • A transporting oxygen and nutrients to cells B breaking food down into nutrients that cells can use C producing offspring D removing wastes from the body • Which two organ systems work together to get nutrients to body cells? • • • • A B C D circulatory and digestive circulatory and respiratory digestive and immune excretory and digestive • The primary function of the muscular system is: A B C D to provide strength and movement in an organism taking oxygen into the lungs giving structure and protection to the body to help your body grow • Which of the following is necessary in order to move our skeletal system: • A B C D eyes muscles skin hands • The diagram best illustrates: • A B C D frontal cortex central nervous system neurons peripheral nervous system • Which organ system is responsible for sending signals to the brain? • • • • A B C D nervous system excretory system muscular system integumentary system • Which of the following organ systems is matched to its correct function? • A skeletal; protects your internal organs from damage B respiratory; pumps blood through your body C cardiovascular; takes in oxygen and removes carbon dioxide D muscular; provides structure and support