* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download C - bellevuebiology
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Catalytic triad wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptides wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
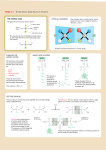
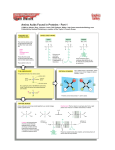
Welcome Back! February 27, 2012 • Sit in any seat for today. You will have assigned seats tomorrow • Were you absent before the break? Plan on coming to tutorial today or tomorrow to makeup the test (from Thursday), it must be completed by Tuesday in tutorial. Open Logbook…do you have an entry from Friday before break? • Entry10: Proteins Beginning Ideas Make an entryEntry 11. Proteins: Amino Acids in 3 D2/27/12 2 Types of Proteins 1) Structural – proteins that form physical parts. Examples – -keratin (hair and nails) -actin (muscle) -microtubules (cell membrane skeletons) - gelatin - collagen 2) Functional – Proteins that have activity Examples-Hormones – used for signaling -Defensive – antibodies that recognize foreign invaders -Transport – Carrier proteins!!! -Enzymes – used for chemical reaction - Hemoglobin – found on RBC and carry oxygen Protein Shape Determines Function Example – Fibrous proteins are long and thin, and are used for structure What will we learn today? HOW is the shape of a protein determined? Proteins are made of chains of amino acids What are amino acids? Link to amino acid 3-D models There are 20 different amino acids. All have the same general form. H Amino group H2N C R O Carboxyl group C OH Side chain Non-ionized form Each amino acid has a different side chain. H H3N+ C C H H O – O Glycine (G) Gly H3N+ H O C C – CH3 O Alanine (A) Ala C C – CH O H3C CH3 H3N+ Valine (V) Val H O H O H O O C C – CH2 O CH H3C CH3 H3N+ N+ Leucine (L) Leu Isoleucine (I) Ile Proline (P) Pro H3N+ C C – H2 C C – O O H3C CH H2C CH2 CH2 CH2 CH3 Side chains contain carbon and/or hydrogen Each amino acid has a different side chain. H H O H3N+ C H3N+ C C CH2 H3N+ C – O H O C O C – CH2 O – O CH2 NH OH Phenylalanine (F) Phe Tyrosine (Y) Tyr Side chains contain ring structures Tryptophan (W) Trp Each amino acid has a different side chain. H H3N+ C H O H3N+ C C O C – – CH2 O CH2 O CH2 SH S CH3 Methionine (M) Met Side chains contain sulfur Cysteine (C) Cys Each amino acid has a different side chain. H H O H3N+ C O H3N+ C C C – – O O CH2 OH Serine (S) Ser CH HO CH3 Threonine (T) Thr Side chains contain hydroxyl functional groups Each amino acid has a different side chain. H H H3N+ O O C H3N+ C C C – – CH2 O CH2 C H2N CH2 O C H2N Asparagine (N) Asn O Glutamine (Q) Gln Side chains contain amino functional groups O Each amino acid has a different side chain. H H3N+ O C H3N+ C H H C CH2 NH +NH H3N+ C C – – O O O CH2 O – CH2 CH2 CH2 CH2 CH2 CH2 NH +NH 3 C C O +NH 2 NH2 Histidine (H) His Lysine (K) Lys Basic side chains Arginine (R) Arg Each amino acid has a different side chain. H H3N+ H O C H3N+ C O C C – – CH2 O CH2 C – O CH2 O C – O Aspartate (D) Asp O Glutamate (E) Glu Acidic side chains O Proteins are chains of amino acids H H2N H O + C C H OH Carboxyl group H2N Amino group C O H2N C CH3 OH H O H H C C N C H Peptide bond O C + OH CH3 C-terminus N-terminus H H2O H H O H H O H H O H H O H H O H H O H H O H H O N C C N C C N C C N C C N C C N C C N C C N C C CH3 H CH2 CH2 OH C CH2 CH H3C OH CH2 CH3 OH CH2 SH O OH N-terminus H2N C-terminus Gly Ala Ser Asp Phe Val Tyr Cys 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 COOH Amino Acids Model activity Peptides are chains of amino acids and sometimes used as another word for protein. Follow the instructions of your teacher to build peptides using the paper amino acid models for questions #1-4. Then join your chain with another groups chain to form an 8 amino acid chain for #5