* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Proteins are made of chains of amino acids
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Ancestral sequence reconstruction wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Interactome wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptides wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
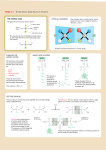
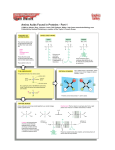
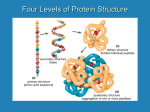
1. What makes an enzyme specific to one type of reaction (in other words, what determines the function of a protein)? – SHAPE determines the function of a protein and makes enzymes specific to one reaction 2. How does heating (boiling) affect the ability of an enzyme to perform its function? – Heating/boiling denatures enzymes (unfolds them) and makes them lose their function What will we learn today? HOW is the shape of a protein determined? WHY does heating/boiling denature enzymes and make them lose their function? Also: • What makes hair straight or curly and how do perms work? • Why is it important to eat different types of food to supply our protein needs? Proteins are made of chains of amino acids What are amino acids? Link to amino acid 3-D models There are 20 different amino acids. All have the same general form. H Amino group H2N C R O Carboxyl group C OH Side chain Non-ionized form Each amino acid has a different side chain. H H3N+ C C H H O – O Glycine (G) Gly H3N+ H O C C – CH3 O Alanine (A) Ala C C – CH O H3C CH3 H3N+ Valine (V) Val H O H O H O O C C – CH2 O CH H3C CH3 H3N+ N+ Leucine (L) Leu Isoleucine (I) Ile Proline (P) Pro H3N+ C C – H2 C C – O O H3C CH H2C CH2 CH2 CH2 CH3 These side chains contain only carbon and/or hydrogen Each amino acid has a different side chain. H H O H3N+ C H3N+ C C CH2 H3N+ C – O H O C O C – CH2 O – O CH2 NH OH Phenylalanine (F) Phe Tyrosine (Y) Tyr Side chains contain ring structures Tryptophan (W) Trp Each amino acid has a different side chain. H H3N+ C H O H3N+ C C O C – – CH2 O CH2 O CH2 SH S CH3 Methionine (M) Met Side chains contain sulfur Cysteine (C) Cys Each amino acid has a different side chain. H H O H3N+ C O H3N+ C C C – – O O CH2 OH Serine (S) Ser CH HO CH3 Threonine (T) Thr Side chains contain hydroxyl [OH] functional groups Each amino acid has a different side chain. H H H3N+ O O C H3N+ C C C – – CH2 O CH2 C H2N CH2 O C H2N Asparagine (N) Asn O Glutamine (Q) Gln Side chains contain amino [NH2] functional groups O Each amino acid has a different side chain. H H3N+ O C H3N+ C H H C CH2 NH +NH H3N+ C C – – O O O CH2 O – CH2 CH2 CH2 CH2 CH2 CH2 NH +NH 3 C C O +NH 2 NH2 Histidine (H) His Lysine (K) Lys Basic side chains Arginine (R) Arg Each amino acid has a different side chain. H H3N+ H O C H3N+ C O C C – – CH2 O CH2 C – O CH2 O C – O Aspartate (D) Asp O Glutamate (E) Glu Acidic side chains O Proteins are chains of amino acids H H2N H O + C C H OH Carboxyl group H2N Amino group C O H2N C CH3 OH H O H H C C N C H Peptide bond O C + OH CH3 C-terminus N-terminus H H2O H H O H H O H H O H H O H H O H H O H H O H H O N C C N C C N C C N C C N C C N C C N C C N C C CH3 H CH2 CH2 OH C CH2 CH H3C OH CH2 CH3 OH CH2 SH O OH N-terminus H2N C-terminus Gly Ala Ser Asp Phe Val Tyr Cys 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 COOH Amino Acid sequence determines the 3-D protein shape • Interactions between amino acids cause folding and bending of the chain Examples: – positive (+) and negative (-) parts of amino acids are attracted to each other. – hydrophobic regions are attracted to each other • Folding http://www.stolaf.edu/people/giannini/flashanimat/proteins/hydrophobic%20force.swf • Structure levels http://www.stolaf.edu/people/giannini/flashanimat/proteins/protein structure.swf Figure 3.11a Interactions that determine the structure of proteins H N C O Hydrogen bond between peptide groups CH2 OH O C Hydrogen bond between side chain and peptide group H CH2 OH CH3 O H3C CH2CH (CH2)4 CHCH2 CH3 H3C NH3+ Ionic bond Hydrophobic interaction O N CH2C H Hydrogen bond between two side chains –O CH2 S S CH2 Disulfide bond CCCH2 Figure 3.11b Tertiary structures are diverse. A tertiary structure composed mostly of a-helices A tertiary structure composed mostly of b-pleated sheets A tertiary structure rich in disulfide bonds Paper polypeptides activity Peptides are chains of amino acids and sometimes used as another word for protein. Follow the instructions of your teacher to build peptides using the paper amino acid models. Straight, curly, and “permed” hair Explain the connection between the order of the amino acids and the shape of the protein. Why did the boiled lactase not work any more? (base your answer on the paper model) ESSENTIAL AMINO ACIDS Essential amino acids and nutrition • Consider why protein is needed and what amino acids and proteins are used for in the body. Describe the symptoms you would expect a person with protein deficiency to have. • Look at Table 1. Which amino acids does corn lack (not have)? Which amino acids do beans and legumes lack (not have)? • Vegans are vegetarians that do not eat any food from animals, including milk and eggs. Why must vegans combine foods from a variety of plant sources to avoid protein deficiency (for example rice and beans instead of only beans)? • A new protein supplement for athletes and weightlifters advertises that it is the best because it is made of “100% natural organic corn protein”. Why would this not be a good product for athletes and weightlifters?