* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Byond Particle Physics
String theory wikipedia , lookup
Double-slit experiment wikipedia , lookup
Quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear structure wikipedia , lookup
Spin (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Bell's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Relational approach to quantum physics wikipedia , lookup
Quantum gravity wikipedia , lookup
Electron scattering wikipedia , lookup
Canonical quantization wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Search for the Higgs boson wikipedia , lookup
Peter Kalmus wikipedia , lookup
Symmetry in quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Atomic nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Quantum chromodynamics wikipedia , lookup
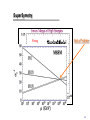
Renormalization wikipedia , lookup
Higgs mechanism wikipedia , lookup
ATLAS experiment wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization group wikipedia , lookup
Technicolor (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Identical particles wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Compact Muon Solenoid wikipedia , lookup
History of quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
Weakly-interacting massive particles wikipedia , lookup
Future Circular Collider wikipedia , lookup
An Exceptionally Simple Theory of Everything wikipedia , lookup
Mathematical formulation of the Standard Model wikipedia , lookup
Minimal Supersymmetric Standard Model wikipedia , lookup
Theory of everything wikipedia , lookup
Grand Unified Theory wikipedia , lookup
Elementary particle wikipedia , lookup
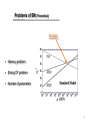
Physics Beyond the Standard Model I think I finally understand atoms Democritus 460–370 BC I. II. III. I. Nestoras L. Zimmerman S. Anderl 1 General Outline Part I (I. Nestoras) • SuperSymmetry (SUSY) Part II (L. Zimmerman) • Dark Matter Part III (S. Anderl) • String Theory 2 I think I finally understand atoms Democritus 460–370 BC 3 Particle Physics - Intro • Particle Physics is the study individual particles (protons, neutrons, electrons muons, kaons, pions, lambdas,quarks,…) • And the forces between them. (gravity, electromagnetism, strong force, weak force). 4 Particle Physics - Intro Question: how many cuts are required? Answer: only 84 times! A nucleus with orbiting electrons nanometre 5 Particle Physics - Intro The forces of nature Unified? 6 History of Unification Planets Apple Electric Gravity Mechanics Magnetism Electromagnetism Atoms Quantum mechanics g-decay QED Weak force GR Special relativity String theory? a-decay Electroweak theory Strong force SM b-decay SM SUSY - Grand Unification? 7 Problems of SM (Experimental) • Gravity • Dark matter and dark energy • Neutrino masses • Matter–antimatter asymmetry 8 Problems of SM (Theoretical) Problem • Hierarcy problem • Strong CP problem • Number of parameters 9 Problems of SM (Predictions not observed) In the “Standard Model” the origin of mass is addressed using a mechanism named after the British physicist Peter Higgs. This predicts a new particle: the Higgs boson. 10 11 What about Supersymmetry? 12 Beyond SM Super-symmetry OR SUSY 13 Brief history of Supersymmetry • First proposed by Hironari Miyazawa in 1966 • Supersymmetry was revealed in two-dimensional string models in 1971 by Ramond, Neveu, Schwarz, Gervais and Sakita The history of supersymmetry is exceptional. In the past, virtually all major conceptual breakthroughs have occurred because physicists were trying to understand some established aspect of nature. In contrast, the discovery of supersymmetry in the early 1970s was a purely intellectual achievement, driven by the logic of theoretical development rather than by the pressure of existing data. 14 What is Supersymmetry ? There are two types of particles in nature: fermions and bosons. Fermions have half units of spin, and tend to shy away from each other, like people who always stay in single rooms at the fermion motel. Bosons have zero or integer units of spin, and like to be with each other, like people who stay in shared dormitories at the boson inn. Supersymmetry says that for every fermion in Nature there must be a boson and vice-versa. Super-symmetric particles have not been observed (yet) so they must be heavier - SUSY must be broken by some mechanism 15 SuperSymetry d s b e e The Generations of Matter Squarks u c t SPIN 0 BOSONS Sleptons Leptons Quarks SPIN ½ FERMIONS u c t d s b e e The Generations of Smatter 16 SuperSymetry BOSO NS FERMIONS Gravitino W W Z0 Photino Gluino 17 17 SuperSymetry 18 19 SuperSymetry Strong Strong Not a Problem Weak Weak Electromagnetic Electromagnetic 20 Quote from Ed Witten in preface of Gordon Kane’s book “Super-symmetry” “Super-symmetry, if it holds in nature, is part of the quantum structure of space and time… Discovery of super-symmetry would be one of the real milestones in physics… Indeed, super-symmetry is one of the basic requirements of string theory… Discovery of super-symmetry would surely give string theory an enormous boost… The search for super-symmetry is one of the great dramas in present day physics.” 21 SuperSymetry SUSY provides an excellent candidate for dark matter. In SUSY we TRUST!!! 22 Welcome Lisa for dark matters (applause) 23