* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Heart
Saturated fat and cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Remote ischemic conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Congenital heart defect wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
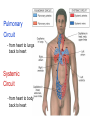
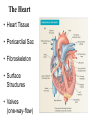
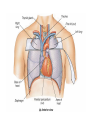
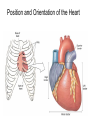
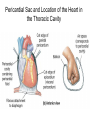
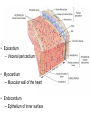
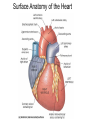
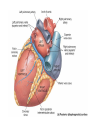
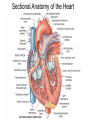
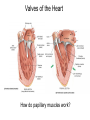
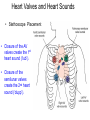
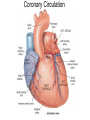
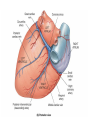
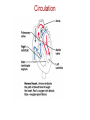
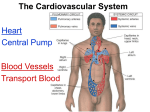
Pulmonary Circuit - from heart to lungs back to heart Systemic Circuit - from heart to body back to heart The Heart • Heart Tissue • Pericardial Sac • Fibroskeleton • Surface Structures • Valves (one-way-flow) Position and Orientation of the Heart Pericardial Sac and Location of the Heart in the Thoracic Cavity • Epicardium – Visceral pericardium • Myocardium – Muscular wall of the heart • Endocardium – Epithelium of inner surface The Fibrous Skeleton Is an internal connective tissue of the heart 1. Provides attachment for heart’s valves 2. Evenly distributes the force of contraction 3. Electrically isolates atria from ventricles Surface Anatomy of the Heart Sectional Anatomy of the Heart The Atria • Right Atrium receives blood from systemic circuit: 1) Superior vena cava 2) Inferior vena cava 3) Coronary Sinus • Left Atrium receives blood from pulmonary circuit: From L and R Pulmonary veins. • Walls of both Atria have Pectinate muscles. • Foramen ovale open in utero – closes to become the Fossa ovalis after birth. The Ventricles • Blood comes from atria through atroventricular (AV) valves: – Tricuspid AV valve (Rt) and Bicuspid AV valve (Lt) • Chordae Tendineae • Papillary Muscles • Trabeculae Carneae • Blood leaves via pulmonary truck (Rt) and aorta (Lt) – Pulmonary semilunar valve – Aortic semilunar valve Valves of the Heart How do papillary muscles work? Heart Valves and Heart Sounds • Stethoscope Placement • Closure of the AV valves create the 1st heart sound (‘lub’). • Closure of the semilunar valves create the 2nd heart sound (‘dupp’). Coronary Circulation Circulation Fetal Circulation