* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 11.1 The Heart - halkuffanatomy
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Saturated fat and cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Remote ischemic conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Congenital heart defect wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
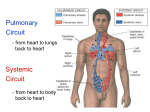
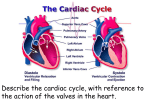
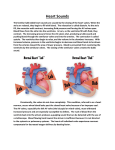
The Heart Objectives: 1. The anatomy of the heart 2. Differentiate between atria & ventricles 3. How valves work 4. Disorders of the heart 5. Heart Sounds Heart Anatomy Base Apex: The pointed tip of the heart that points down toward the left hip. Base: The wider top portion of the heart. Pericardium: The sac that encloses the heart Apex Atria: Top two chambers Ventricles: Bottom two chambers Interventricular Septum: The wall that divides the heart longitudinally Aorta: Largest artery where blood leaves the heart Chordae Tendinae: Heart strings that open and close heart valves. Arteries: Carries oxygenated blood away from the heart & lungs to the rest of the body. (red) Veins: Carries deoxygenated blood from the body back to the heart & lungs. (blue) Valves: Atrioventricular Valves (AV): Found connecting the atria to ventricles. Bicuspid Tricuspid Semilunar Valves: Found in places where blood exits the heart. Pulmonary Semilunar Aortic Semilunar Disorders Angina Pectoris: Chest pains caused by lack of oxygen to the heart. Myocardial Infarction: Heart cells die. Heart attack. Murmurs: Sounds created by improper blood flow. Usually caused by valve problems. Tachycardia: Rapid heartbeat (>100bpm) Bradycardia: Slow heartbeat (<60bpm) Heart Sounds Systole: Contraction of the heart Diastole: Relaxation of the heart Lub: Closing of the AV Valves Dup: Closing of the Semilunar Valves