* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Specialized Cells
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
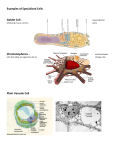
Title: Specialized Cells (on page 43 in your notebook) Generalized Cells – cells that contain all parts of the cell. A generalized cell is a drawing that contains all parts of the cell. In reality, there are many cells that lack one or more parts. A red blood cell, for example, contains cytoplasm and a cell membrane but other parts are missing. Specialized Cells- contain only structures directly connected to its function. In a specialized cell, the structure of the cell is directly connected to its function. http://kerala.skoool.in/id208.htm (The following information is taken from the above site.) Animal Cells All animals are made up of cells. This diagram represents an animal cell. Most cells have: A nucleus that controls the activities of the cell Cytoplasm, where most of the chemical reactions take place. The reactions are controlled by enzymes A cell membrane that controls what enters and leaves the cell Mitochondria in the cytoplasm where respiration takes place to release energy Plant Cells This diagram represents a plant cell. Plant cells also have: A cell wall made of cellulose, which strengthens the cell and provides support They often have: Chloroplasts which contain the green pigment chlorophyll. This absorbs light energy for photosynthesis A permanent vacuole filled with cell sap, which provides support Specialized Cells Different types of cells look different because they are adapted to their function. They are said to be specialized. Similar cells that carry out the same function are grouped together in tissues. Different tissues work together in organs. Different organs are combined together to form organ systems. For example, muscle cells form muscle tissue. The heart contains muscle tissue, nervous tissue and connective tissue. The heart is part of the circulatory system. About skoool | About Supporters | Privacy and Security Copyright © 2009 Intel Corporation http://www.livingscience.co.uk/year7/cells/cells.htm (The following information is taken from the above site.) Cells All plant and animal cells have the following: A Cell Membrane. This controls what goes in and out of the cell Cytoplasm. This has the thickness of wallpaper paste. It is where the chemical reactions take place. A nucleus. This is the 'brain' of the cell. It contains the genetic material (DNA) and tells the cell what to do. Only plant cells contain: A Cell Wall. It support the plant cell and is very strong. It is made out of a substance called cellulose. A Vacuole. This is filled with a liquid called cell sap. It helps the cell to maintain its shape. Chloroplasts. These are green discs that allow the plant to make food by photosynthesis. They contain a chemical called chlorophyll. Plant tissues which contain them appear green. Some cells are adapted to do certain jobs. Examples of these are shown below: + Red Blood Cells Red blood cells are adapted to carry oxygen around the body in blood vessels. A red blood cell has a small size to enable it to fit through capillaries and a biconcave shape (see the picture below - it looks a bit like a Werther's Original sweet). Red blood cells are flexible and contain the chemical hemoglobin which binds to oxygen to carry it around the body. The shape of the red blood cell provides a large surface area to help it take in oxygen and release it rapidly. The flexible shape helps it to fit through narrow capillaries. In the lungs hemoglobin in the red blood cells combines with oxygen to form oxyhemoglobin Oxygen + Hemoglobin Oxyhemoglobin When the red blood cells reach tissues oxyhemoglobin breaks down to release oxygen: Oxyhemoglobin Oxygen + Hemoglobin White Blood Cells White blood cells are bigger than red blood cells and have a flexible shape. White blood cells help to protect our body against disease. The diagrams below show how white blood cells can 'eat' bacteria cells which have entered the body. Palisade Cells Palisade cells contain lots of chloroplasts and are found near to the top surface of the leaf. The chloroplasts absorb light energy and make food (glucose) for the plant using photosynthesis. The chloroplasts give plants their green color. The diagram below shows cells in a plant leaf. The palisade cells can be seen just below the top surface of the leaf. http://www.hyndland-sec.glasgow.sch.uk/PlainText/PlainText.aspx?SectionId=f040c17b-06f9-4f5c-a81c-5acfe1ecccf4 (The following information was taken from the above site.) Specialized cells Animal and plants cells in multi-celluar organisms often become specialized to carry out particular jobs. In this way they can carry these functions out much more efficiently. Here are some examples: The cells of fungi are similar to plant cells. They have a nucleus, cytoplasm, ribosomes and mitochondria. While fungi do have a cell wall, it is made of chitin, a different type of carbohydrate from cellulose. They are however not green – they don’t photosynthesize and so don’t contain chloroplasts. Fungi need to feed on other organisms to obtain their energy source. Fungi are involved in decomposition - recycling nutrients from dead organisms back into the ecosystem. Humans have made great use of fungi, e.g. yeast are fungi and are used to make wine, beer and bread. The primary function of hemoglobin (Hb) is to transport oxygen. Since oxygen is not very soluble in water (the major constituent of blood), an oxygen transport protein must be used to allow oxygen to be 'soluble'. Hemoglobin (Hb) is the oxygen transport protein used in the blood of vertebrates. Below is a wireframe diagram of a hemoglobin molecule. It is composed of 4 polypeptide chains (represented in this diagram by different colors. Each chain contains one heme group (colored orange), each of which contains one iron ion (not shown). The iron is the site of oxygen binding; each iron can bind one O2 molecule thus each hemoglobin molecule is capable of binding a total to four (4) O2 molecules. Specialized Cells Chart Cell Name root hair cell Structure Description large surface area Function to absorb water, Found? roots of plants minerals palisade xylem transport water, hollow tube-like phloem minerals stems, leaves transport food, of plants nutrients Drawing