* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 25 Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins
Ancestral sequence reconstruction wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Protein adsorption wikipedia , lookup
Protein (nutrient) wikipedia , lookup
Self-assembling peptide wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptides wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
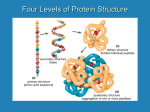
Chapter 25 Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins Review of Concepts Fill in the blanks below. To verify that your answers are correct, look in your textbook at the end of Chapter 25. Each of the sentences below appears verbatim in the section entitled Review of Concepts and Vocabulary. • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Amino acids in which the two functional groups are separated by exactly one carbon atom are called _______ amino acids. Amino acids are coupled together by amide linkages called ____________ bonds. Relatively short chains of amino acids are called ___________. Only twenty amino acids are abundantly found in proteins, all of which are ___ amino acids, except for ____________ which lacks a chirality center. Amino acids exist primarily as _______________ at physiological pH The ___________________ of an amino acid is the pH at which the concentration of the zwitterionic form reaches its maximum value. Peptides are comprised of amino acid _________ joined by peptide bonds. Peptide bonds experience restricted rotation, giving rise to two possible conformations, called _______ and _______. The _______ conformation is more stable. Cysteine residues are uniquely capable of being joined to one another via ______________ bridges. ______ is commonly used to form peptide bonds. In the Merrifield synthesis, a peptide chain is assembled while tethered to __________________________. The primary structure of a protein is the sequence of _____________________. The secondary structure of a protein refers to the ________________________ _____________________ of localized regions of the protein. Two particularly stable arrangements are the ___ helix and ____ pleated sheet. The tertiary structure of a protein refers to its _________________________. Under conditions of mild heating, a protein can unfold, a process called _________________. Quaternary structure arises when a protein consists of two or more folded polypeptide chains, called _____________, that aggregate to form one protein complex. 666 CHAPTER 25 Review of Skills Fill in the blanks and empty boxes below. To verify that your answers are correct, look in your textbook at the end of Chapter 25. The answers appear in the section entitled SkillBuilder Review. 25.1 Determining the Predominant Form of an Amino Acid at a Specific pH CONSIDER THE FOLLOWING AMINO ACID, AND DRAW THE FORM THAT PREDOMINATES AT PHYSIOLOGICAL pH. O H2N OH NH2 25.2 Using the Amidomalonate Synthesis IDENTIFY REAGENTS THAT WILL ACHIEVE THE FOLLOWING TRANSFORMATION: 1) O 2) O O OEt EtO H OH N 3) O 4) N H NH2 25.3 Drawing a Peptide DRAW A BOND-LINE STRUCTURE FOR THE TRIPEPTIDE Phe-Val-Trp. 25.4 Sequencing a Peptide via Enzymatic Cleavage IDENTIFY THE FRAGMENTS OBTAINED FROM ENZYMATIC CLEAVAGE OF THE FOLLOWING PEPTIDE: Ala-Phe-Lys-Pro-Met-Tyr-Gly-Arg-Ser-Trp-Leu-Hist trypsin chymotrypsin CHAPTER 25 667 25.5 Planning the Synthesis of a Dipeptide IDENTIFY ALL REAGENTS NECESSARY TO PREPARE THE DIPEPTIDE Ala-Gly: Ala Boc Gly + Ala Gly Boc OCH3 Ala Gly OCH3 Ala Gly 25.6 Preparing a Peptide using the Merrifield Synthesis IDENTIFY ALL REAGENTS NECESSARY TO PREPARE THE PENTAPEPTIDE Ile-Gly-Leu-Ala-Phe: POLYMER Boc Phe Boc POLYMER Phe Ile Gly Leu Ala Phe Ile Gly Leu Ala Phe Boc POLYMER Ala Phe POLYMER POLYMER Review of Reactions Identify the reagents necessary to achieve each of the following transformations. To verify that your answers are correct, look in your textbook at the end of Chapter 25. The answers appear in the section entitled Review of Reactions. Analysis of Amino Acids O O R O H2O COOH OH + N + OH NH2 O O O CO2 RCHO 668 CHAPTER 25 Synthesis of Amino Acids O R O O R R OH OH Br O O O OH NH2 O O R EtO OEt EtO H N N NH2 H O O O N O R OH OEt R H2 N H R NaCN H2 N C H R O C OH H O OH NHAc O OH NHAc OH NH2 Analysis of Amino Acids Ph O PEPTIDE H PEPTIDE NH2 N N H + NH O H R S N R Synthesis of Peptides O O + OH H2 N N H O O H2N O H N OH OH O R [H+] ROH O H2N O H2N OH R OR R NaOH H2O R