* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Sunni and Shiite
War against Islam wikipedia , lookup
Muslim world wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Sikhism wikipedia , lookup
Islam in South Africa wikipedia , lookup
Reception of Islam in Early Modern Europe wikipedia , lookup
Islam and secularism wikipedia , lookup
Islamic missionary activity wikipedia , lookup
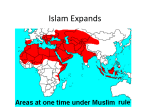
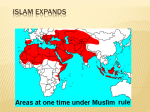
Spread of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Political aspects of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam and war wikipedia , lookup
Islam and modernity wikipedia , lookup
Islam in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Islamic Golden Age wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Indonesia wikipedia , lookup
History of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Origin of Shia Islam wikipedia , lookup
Schools of Islamic theology wikipedia , lookup
Islamic schools and branches wikipedia , lookup
Islamic culture wikipedia , lookup
Sunni and Shiite Shiite Sunni Follow custom of community (sunna). Believe inspiration comes from example of Muhammad 90% of Muslims True descendants are of Ali and Fatima’s children Live in Iran, Lebanon, Iraq and Yemen After Muhammad No successor named after Muhammad died Abu Bakr-Muhammad’s father-in-law and 1st caliph. Reunited Muslims and converted last Arab tribe to Islam After Ali died a Meccan clan set up Ummayyad (caliphate). Dynasty of Sunni caliphs ruled Muslim empire until 750. Factors for Success Weakened Byzantine and Persian empires Welcomed Arabs as liberators Fighting method-Bedouin camel and horse cavalry-mobile and aggressive Tax on non-Muslims in conquered areas Many converted- equality, simple, no Fall of Umayyads and Rise of Abbasids Umayyads Abbasids While conquests wealth Abu al-Abbas founder went to Umayyads. When they stopped tensions built between wealthy Arabs and those who had less Criticized and wanted ways of early caliphs Considered illegitimate rulers of Islamic community Captured Damascus 750 and dynasty lasted until 1258 Had member of Umayyad family killed. All but one escaped and went to Spain where they were more tolerant and thrived The Crusades 900-Seljuk Turks came from Central Asia to Middle East 1055-Suljuk sultan controlled Baghdad and kept caliph as figurehead 1095-Pushed into Asia Minor and prevented Christians from going to Jerusalem. Muslim Golden Era Muslim scholars reintroduced knowledge of Greco-Roman civilization to later Europeans. United diverse cultures-translated Greek, Hindu and Buddhist text Social Mobility Up, slavery common but Islamic law encouraged freeing slaves as act of charity. Religion shaped arts and literature; banned idol worship and artists could not portray God or human figures in religious art Muslim Golden Era Architecture-domed mosques, adopted from Byzantine buildings; symbolic of Muslim architecture Artists skilled in calligraphy-decorated on buildings Poetry- oral tradition, wrote about desert journeys, battles, joy of clans, chivalry and romance of nomadic life Muslim Golden Era Mathematics- al-Khwarizmi pioneered study of algebra. 800s-wrote book that was translated into Latin. Became standard textbook in Europe. Medicine-Based knowledge on Ancient Greeks. Physicians and pharmacists had to pass test. Set up hospitals India Muslims mingled with Indians and each civilization absorbed elements from each other. 550-Gupta empire fell and India split, princes battled for control 1000-Muslim Turks and Afghans moved to India Low caste Hindus converted to Islam Muslims in India 1200s-scholars and adventurers fled Baghdad to India. Brought Persian and Greek knowledge 1398- Tamerlane invades India, enslaved thousand artisans to build capital @ Samarkand Delhi slowly recovered. Sultans no longer controlled empire and India split. Rival Hindu and Muslim states Hindus and Muslims in India Hinduism-ancient religion evolved over thousand years. Sacred texts, prayed before statues representing gods/goddess. Caste system; celebrated with music and dance Islam-newer faith with single sacred text; monotheistic. No religious hierarchy. Did not celebrate with music and dance. Taj Mahal Over time Delhi sultans grew more tolerant of Hindu subjects. Allowed to practice, paid a poll tax. Shah Jahan built Taj Mahal as tomb for her when she died. Greatest monument of Mughal empire.