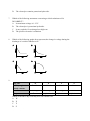
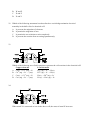
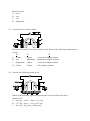
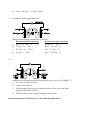
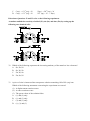
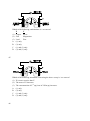
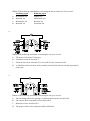
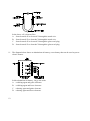
* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
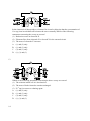
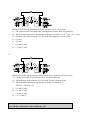
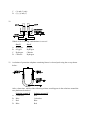
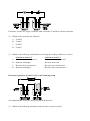
Download Question Bank Topic 5
Patch clamp wikipedia , lookup
Fluorochemical industry wikipedia , lookup
Stoichiometry wikipedia , lookup
Click chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Photoredox catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Chemical reaction wikipedia , lookup
Acid dissociation constant wikipedia , lookup
IsaKidd refining technology wikipedia , lookup
Nucleophilic acyl substitution wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Lewis acid catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Water splitting wikipedia , lookup
Gaseous signaling molecules wikipedia , lookup
Sodium hypochlorite wikipedia , lookup
Multielectrode array wikipedia , lookup
Nanofluidic circuitry wikipedia , lookup
Artificial photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Scanning electrochemical microscopy wikipedia , lookup
Stability constants of complexes wikipedia , lookup
Strychnine total synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Acid–base reaction wikipedia , lookup
Gaseous detection device wikipedia , lookup
History of electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Electrolysis of water wikipedia , lookup
Electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Question Bank Topic 5 Chemical Cells and Electrolysis Name: ___________________________ Mark: ___________ Class: ____________ Class No: __________ Date:______________ Multiple choice questions Unit 18 18.1: Chemical cells in daily life 18.2: Electricity from chemical reactions 18.3: Different types of dry cells 18.4: Characteristics of different types of dry cells 18.5: Choosing a dry cell for a particular use 18.6: The use of dry cells and pollution (CDC guide: Uses of chemical cells in relation to factors such as size, price and life-expectancy) 1 Consider the following simple chemical cell: Which of the following statements concerning the chemical cell is correct? A The magnesium strip is the positive electrode of the cell. B C D A deposit of copper forms on the copper strip. Electrons move freely in the copper(II) sulphate solution. Electrical energy is converted into chemical energy. 2 Which of the following dry cells is a secondary cell? A Zinc-carbon cell B Nickel-cadmium cell C Silver oxide cell D Alkaline manganese cell 3 Which of the following dry cells is the most suitable for a watch? A B C D 4 Which of the following dry cells is most suitable for a mobile telephone? A B C D 5 Zinc-carbon cell Nickel-cadmium cell Silver oxide cell Alkaline manganese cell Which of the following statements concerning a zinc-carbon cell is correct? A The zinc case serves as the positive electrode. B Its voltage remains constant over discharge. C D 6 Silver oxide cell Zinc-carbon cell Alkaline manganese cell Nickel-cadmium cell Chemical energy is converted into electrical energy during discharge. The electrolyte is a moist paste of manganese(IV) oxide. Which of the following statements concerning a silver oxide cell is correct? A The negative electrode is silver oxide. B The positive electrode is zinc. C The cell is rechargeable. D The electrolyte contains potassium hydroxide. 7 Which of the following statements concerning a nickel-cadmium cell is INCORRECT? A Its maximum voltage is 1.25 V. B The electrolyte is potassium hydroxide. C It may explode if overcharged at a high rate. D The positive electrode is cadmium. 8 Which of the following graphs best represents the change in voltage during the discharge of a nickel-cadmium cell? 9 Dry cell W X Y Z Excellent Good Good Poor Service life Long Long Long Short Shape Button Cylindrical Cylindrical Cylindrical Ability to give a steady current Which of the above dry cells may be a zinc-carbon cell? A W B X C Y D Z 10 Which of the following statements concerning zinc-carbon cells are correct? (1) Used zinc-carbon cells can be disposed of in fire. (2) Zinc-carbon cells leak even though they are not in use. (3) The voltage of zinc-carbon cells drops rapidly over discharge. A (1) and (2) only B (1) and (3) only C (2) and (3) only D (1), (2) and (3) 11 Which of the following dry cells are primary cells? (1) Silver oxide cell (2) (3) A B C D 12 Which of the following is / are the advantage(s) of alkaline manganese cells over zinc-carbon cells? (1) Alkaline manganese cells are rechargeable while zinc-carbon cells are not. (2) Alkaline manganese cells can supply a steady current while zinc-carbon cells cannot. (3) Alkaline manganese cells are cheaper than zinc-carbon cells. A (1) only B (2) only C D 13 Nickel-cadmium cell Alkaline manganese cell (1) and (2) only (1) and (3) only (2) and (3) only (1), (2) and (3) (1) and (3) only (2) and (3) only Which of the following is / are the advantage(s) of alkaline manganese cells over nickel-cadmium cells? (1) Alkaline manganese cells are cheaper than nickel-cadmium cells. (2) Alkaline manganese cells do not leak while nickel-cadmium cells do. (3) Alkaline manganese cells can be disposed of in fire while nickel-cadmium A B C D 14 cells cannot. (1) only (2) only (1) and (3) only (2) and (3) only Nickel-cadmium cells are considered more environmental-friendly than alkaline manganese cells because (1) materials in nickel-cadmium cells are non-toxic while materials in alkaline manganese cells are toxic. (2) nickel-cadmium cells are rechargeable while alkaline manganese cells are not. (3) A B C D nickel-cadmium cells has a longer shelf life than alkaline manganese cells. (1) only (2) only (1) and (3) only (2) and (3) only 15 Which of the following dry cells contain the same electrolyte? (1) Silver oxide cell (2) Alkaline manganese cell (3) Nickel-cadmium cell A (1) and (2) only B (1) and (3) only C (2) and (3) only D (1), (2) and (3) 16 Which of the following is / are the advantage(s) of alkaline manganese cells? (1) Leak proof (2) Constant voltage during discharge (3) Rechargeable A (1) only B (2) only C (1) and (3) only D 17 (2) and (3) only Which of the following dry cells are able to supply a large current? (1) Alkaline manganese cell (2) Nickel-cadmium cell (3) Silver oxide cell A (1) and (2) only B (1) and (3) only C (2) and (3) only D (1), (2) and (3) Unit 19 19.1: Reactions in simple chemical cells 19.2: Simple chemical cells made from different metal couples 19.3: The electrochemical series of metals 19.4: Improving simple chemical cells 19.5: The role of a salt bridge 19.6: The Daniell cell (CDC guide: Simple chemical cells: (a) consisting of two metal electrodes and and electrolyte, (b) consisting of metal-metal ion half-cells and salt bridge / porous device; Changes occurring at the electrodes and electron flow in the external circuit; Ionic half-equations and overall cell equations) 1 Electric currents are carried through sodium chloride solution by the movement of A atoms. B C D 2 molecules. ions. electrons. Which of the following substances can make a chemical cell? A Zinc, plastic rod and magnesium chloride solution B Zinc, iron and tetrachloromethane C Magnesium, zinc and sodium nitrate solution D Copper, graphite and water 3 Which of the following metals loses electrons most readily to form ions? A Zinc B Copper C Magnesium D Silver 4 Which of the following statements concerning a chemical cell is correct? A Reduction occurs at the anode. B Oxidation occurs at the negative electrode. C D 5 Which of the following statements concerning a chemical cell is correct? A Electrons flow in the external circuit and the electrolyte in a chemical cell. B Methylbenzene can be used as the electrolyte of a chemical cell. C D 6 7 Electrons move in the salt bridge. An external power source must be present. The electrode at which the ions gain electrons is the positive electrode. A chemical cell converts electrical energy into chemical energy. A chemical cell is made of two different metal electrodes using dilute sodium nitrate solution as the electrolyte. Which of the following combinations concerning the electrodes is correct? A B Cathode Copper Copper Anode Magnesium Silver C D Zinc Zinc Copper Iron Which of the following statements concerning the above chemical cell is correct? A Electrolysis occurs inside the lemon. B The current flows from the copper electrode to the magnesium electrode in C D the electrical wire. The magnesium electrode acts as the positive electrode. The copper electrode acts as the anode. 8 Which of the following statements concerning the above chemical cell is INCORRECT? A The lemon juice acts as an electrolyte. B The ammeter shows a deflection. C The lemon juice contains mobile electrons. D Zinc electrode loses electrons to form zinc ions. 9 Which of the following pairs of metals would give the greatest reading on the ammeter? A Metal X Magnesium Metal Y Silver B C D Copper Silver Iron Zinc Copper Lead 10 Which of the following statements concerning the above set-up is correct? A The copper electrode is the positive electrode. B The mass of the copper electrode decreases. C The mass of metal X increases. D Copper is at a higher position in the electrochemical series than metal X. 11 Which of the following combinations is correct? A Electrode X Electrode Y Zinc Magnesium B C D Copper Iron Copper Lead Zinc Silver 12 Which of the following statements concerning the above chemical cell is correct? A The mass of electrode X increases. B Electrode X is the negative electrode. C Metal Y is more reactive than metal X. D Electrolysis occurs around both electrodes. 13 Which of the following combinations for the set-up is correct after a current has flowed through the external circuit for some time? A Mass of cathode Increases B C D Decreases Increases Decreases Colour intensity of CuSO4(aq) No change No change Decreases Decreases 14 Which of the following changes would lead to an increase in the ammeter reading? A Magnesium is replaced by zinc. B Copper is replaced by iron. C The 1 M magnesium nitrate solution is replaced by 2 M magnesium nitrate solution. D The 1 M magnesium nitrate solution is replaced by 1 M ethanoic acid. 15 Consider the chemical cell shown below: Which of the following changes would lead to an increase in the voltage of the cell? A The zinc electrode is replaced by an iron electrode. B The silver electrode is replaced by a copper electrode. C The zinc electrode is replaced by a magnesium electrode. D 16 The sodium chloride solution is replaced by a sugar solution. Consider the following chemical cells. Which of the following represents the correct order of reactivity of metals X, Y and Z? A X>Y>Z B Y>X>Z C Y>Z>X D Z>X>Y 17 In which of the following chemical cells will the voltmeter give the greatest deflection? 18 Which of the following represents the correct order of reactivity of metals W, X, Y and Z? A X>Y>Z>W B W>Z>Y>X C D 19 Y>Z>W>X X>W>Z>Y Which of the following combinations would produce the largest current flowing from metal Y to metal X in the external circuit? Metal X Mg Zn Cu Ag A B C D Metal Y Ag Al Fe Mg Directions: Questions 20 and 21 refer to the following set-up which was used to investigate the tendency of four metals W, X, Y and Z to lose electrons. The voltmeter reading for each metal strip was recorded in the following table: Metal strip under test Direction of electron flow in the external circuit Voltage recorded (V) W W to Cu +0.46 X Cu to X -0.38 Y Y to Cu +1.21 Z Z to Cu +0.32 20 Which of the following represents the ascending order of tendency of metals W, X, Y and Z to lose electrons? A Z<W<Y<X B C D 21 Y<W<Z<X X<Z<W<Y Y<X<W<Z Which of the following pairs of metals will give the greatest voltage when they are connected in a chemical cell? A W and Y 22 B W and Z C D X and Z X and Y Which of the following statements best describes how a salt bridge maintains electrical neutrality in the half-cells of a chemical cell? A It prevents the migration of electrons. B It permits the migration of ions. C It permits the two solutions to mix completely. D It prevents the reaction from occurring spontaneously. 23 Which of the following sets of half-equations represents the cell reactions in the chemical cell? A B C D Copper electrode Cu(s) → Cu2+(aq) + 2eCu2+(aq) + 2e- → Cu(s) Cu(s) → Cu2+(aq) + 2eCu2+(aq) + 2e- → Cu(s) Lead electrode Pb2+(aq) + 2e- → Pb(s) Pb2+(aq) + 2e- → Pb(s) Pb(s) → Pb2+(aq) + 2ePb (s) → Pb2+(aq) + 2e- 24 When metal X is connected to iron in the above cell, the mass of metal X increases. Metal X may be A B C D 25 silver. zinc. iron. magnesium. Consider the set-up shown below: Electrons flow from X to Y in the external circuit. Which of the following combinations is correct? 26 A B C X Carbon Iron Magnesium Y Copper Magnesium Carbon Z Copper(II) sulphate solution Magnesium sulphate solution Copper(II) sulphate solution D Carbon Carbon Zinc sulphate solution Consider the following chemical cell. Which of the following equations represents the overall reaction in the above chemical cell? A Zn2+(aq) + Cu(s) → Zn(s) + Cu2+(aq) B Cu2+(aq) + Zn(s)→ Cu(s) + Zn2+(aq) C Zn2+(aq) + SO42-(aq)→ ZnSO4(aq) D 27 Cu(s) + 2K+(aq) → Cu2+(aq) + 2K(s) Consider the following chemical cell. Which of the following combinations is correct? A Reaction at positive electrode W(s) → W2+(aq) + 2e- Reaction at negative electrode X+(aq) + e- → X(s) B C D X2+(aq) + 2e-→ X(s) W2+(aq) + 2e- → W(s) X+(aq) + e-→ X(s) W(s) → W2+(aq) + 2eX(s)→ X2+(aq) + 2eW(s) → W2+(aq) + 2e- 28 Which of the following statements concerning the above set-up is INCORRECT? A Zinc is the negative electrode. B Copper is the cathode. C D The salt bridge can be made by soaking a piece of filter paper with dilute potassium hydroxide solution. The blue colour of the copper(II) sulphate solution fades. Directions: Questions 29 and 30 refer to the following chemical cell. 29 Which of the following statements is correct? A Metal X is the negative electrode. B Oxidation takes place at metal Y. C D 30 Metal Y forms ions more readily than metal X. The salt bridge allows electrons to flow between the two half-cells. Which of the following combinations is correct? A B C D X Cu Ag Fe Zn Y Cu Cu Zn Ag 31 Which of the following sets of ionic half-equations represents the cell reactions of the chemical cell shown above? A B Copper container Cu2+(aq) + 2e-→ Cu(s) Cu2+(aq) + 2e- → Cu(s) Zinc strip Zn(s) → Zn2+(aq) + 2eZn2+(aq) + 2e- → Zn(s) C Cu(s) → Cu2+(aq) + 2e- Zn(s) → Zn2+(aq) + 2e- D Cu(s) → Cu2+(aq) + 2e- Zn2+(aq) + 2e- → Zn(s) Directions: Questions 32 and 33 refer to the following experiment. A student studied the reactivity of nickel (Ni), tin (Sn) and zinc (Zn) by setting up the following two chemical cells. 32 Which of the following represents the increasing tendency of the metals to lose electrons? A Sn, Zn, Ni B Sn, Ni, Zn C Zn, Ni, Sn D Zn, Sn, Ni 33 A piece of zinc is immersed into an aqueous solution containing 1M of Ni2+(aq) ions. Which of the following statements concerning the experiment are correct? (1) (2) (3) A B C D A displacement reaction occurs. A redox reaction occurs. The green colour of the solution fades. (1) and (2) only (1) and (3) only (2) and (3) only (1), (2) and (3) 34 Which of the following statements concerning a chemical cell are correct? (1) Electrons flow from the negative electrode to the positive electrode through the conducting wires. (2) Reduction occurs at the positive electrode. (3) It is a device for bringing out chemical changes by electricity. A (1) and (2) only B (1) and (3) only C (2) and (3) only D (1), (2) and (3) 35 Which of the following statements concerning a chemical cell is / are correct? (1) Oxidation occurs at the anode. (2) (3) A B C D Reduction occurs at the negative electrode. Electrons flow through the electrolyte. (1) only (2) only (1) and (3) only (2) and (3) only 36 Which of the following statements concerning the above chemical cell are correct? (1) The mass of copper electrode decreases. (2) The mass of silver electrode increases. (3) The colour of the solution remains unchanged. A (1) and (2) only B (1) and (3) only C (2) and (3) only D (1), (2) and (3) 37 Which of the following solutions can be used as the electrolyte in the above chemical cell? (1) Sodium nitrate solution (2) Ammonium nitrate solution (3) Orange juice A (1) and (2) only B C D (1) and (3) only (2) and (3) only (1), (2) and (3) 38 Which of the following metals will dissolve if they are connected to silver in the above set-up? (1) Copper (2) Zinc (3) A B C D Iron (1) and (2) only (1) and (3) only (2) and (3) only (1), (2) and (3) Directions: Questions 39 and 40 refer to the following set-up: 39 40 What will be observed at the metal electrodes when the circuit is opened? (1) Gas bubbles are given off at the magnesium electrode. (2) Metal deposits on the silver electrode. (3) The magnesium electrode dissolves. A B C (1) only (2) only (1) and (3) only D (2) and (3) only What will happen when the circuit is closed? (1) Gas bubbles are given off at the magnesium electrode. (2) Electrons flow from magnesium to silver through the external circuit. (3) The concentration of hydrogen ions in the acid decreases. A B C D (1) and (2) only (1) and (3) only (2) and (3) only (1), (2) and (3) 41 Which of the following metals can be metal X? (1) Magnesium (2) Silver (3) Zinc A (1) only B (2) only 42 C (1) and (3) only D (2) and (3) only Which of the following is / are the function(s) of a salt bridge in a chemical cell? (1) To complete the circuit by allowing electrons to move between the two half-cells. (2) To balance the charges in the two half-cells. (3) To prevent direct reactions of the solutions in the two half-cells. A (1) only B (2) only C (1) and (3) only D (2) and (3) only 43 Which of the following solutions can be used to make the salt bridge of the above chemical cell? (1) Potassium nitrate solution (2) Potassium chloride solution (3) Potassium hydroxide solution A (1) only B (2) only C (1) and (3) only D 44 (2) and (3) only Which of the following combinations is / are correct? X (1) Copper (2) Zinc Y Silver Magnesium (3) Lead Zinc A (1) only B (2) only C D (1) and (3) only (2) and (3) only 45 Which of the following statements concerning the above set-up is / are correct? (1) X is more reactive than Y. (2) The mass of X increases. (3) The concentration of Y2+(aq) ions in YSO4(aq) increases. A B C D 46 (1) only (2) only (1) and (3) only (2) and (3) only Which of the following are correct for the two half-cells? (1) The colour of the solution in half-cell A fades. (2) A brown solid deposits on the copper electrode. (3) The reaction that occurs at the magnesium electrode is Mg(s) → Mg2+(aq) + 2e- 47 A B (1) and (2) only (1) and (3) only C D (2) and (3) only (1), (2) and (3) Consider the set-up shown below: Which of the following statements concerning the set-up are correct? (1) Electrons flow from the zinc electrode to the carbon electrode. (2) The zinc electrode is the anode. (3) The mass of the carbon electrode increases. A B C D 48 (1) and (2) only (1) and (3) only (2) and (3) only (1), (2) and (3) Consider the set-up shown below: Which of the following statements are correct? (1) Chromium forms ions more readily than silver. (2) The silver electrode is the anode. (3) The concentration of Ag+(aq) ions in the silver nitrate solution decreases. 49 A B C (1) and (2) only (1) and (3) only (2) and (3) only D (1), (2) and (3) Lithium iodine button cells are widely used in pacemakers. Which of the following statements concerning the dry cell are correct? (1) The lithium electrode is the anode. (2) Reduction occurs at the iodine electrode. (3) Its voltage remains steady over discharge. A (1) and (2) only B (1) and (3) only C (2) and (3) only D 50 (1), (2) and (3) Which of the following statements concerning a chemical cell are correct? (1) Oxidation occurs at the negative electrode. (2) Electrons flow from the anode to the cathode through the conducting wires. (3) It is a device for generating electricity from chemical reactions. A (1) and (2) only B (1) and (3) only C D (2) and (3) only (1), (2) and (3) Unit 20 20.1: The nature of oxidation and reduction processes 20.2: Oxidizing agent and reducing agent 20.3: Oxidation and reduction in terms of electron transfer 20.5: Ionic half-equations 20.6: The reducing power of metals 20.8: The oxidizing power of non-metals 20.9: Chemical changes of common oxidizing and reducing agents 20.10: Oxidation numbers 20.11: Using oxidation numbers to identify redox reactions (CDC guide: Oxidation and reduction; Oxidizing agents (e.g. MnO4-(aq) / H+(aq), Cr2O72-(aq) / H+(aq), Fe3+(aq), Cl2(aq)); Reducing agents (e.g. SO32-(aq), I-(aq), Fe2+(aq), Zn(s)); Oxidation numbers) 1 Reduction involves A an increase in atomic number. B a decrease in number of electrons. C an increase in mass number. D a decrease in oxidation number. 2 Oxidation involves A a decrease in oxidation number. B C D 3 an increase in oxidation number. a decrease in number of protons. an increase in number of protons. Which of the following statements is INCORRECT? A Oxidation and reduction occur at the same time. B If a substance is reduced, its oxidation number decreases. C All oxidations involve loss of electrons. D If oxygen is added to a substance, the substance is oxidized. 4 When zinc forms zinc oxide, zinc A gains electrons and is oxidized. B loses electrons and is oxidized. C gains electrons and is reduced. D loses electrons and is reduced. 5 Which of the following statements concerning an oxidizing agent is INCORRECT? A An oxidizing agent is oxidized in a redox reaction. B An oxidizing agent can oxidize other species in a redox reaction. C D 6 Which of the following elements in the third period of the periodic table is the strongest reducing agent? A Aluminium B C D 7 Chlorine Magnesium Sodium Which of the following is NOT a common reducing agent? A Sulphur dioxide gas B Iodide ions C Iron(III) ions D 8 An oxidizing agent is an electron acceptor. The oxidation number of an oxidizing agent decreases in a redox reaction. Carbon Which of the following is the strongest reducing agent? A Calcium B Potassium C Bromine D Sulphur 9 Which of the following is the strongest oxidizing agent? A Chlorine B Bromine C Chloride ions D Bromide ions 10 Which of the following Group VII elements is the strongest oxidizing agent? A Fluorine B C D 11 Chlorine Bromine Iodine Consider the following table. Element P Q R S Atomic number 8 11 17 18 Which of the above elements is likely to be a reducing agent? A B C D 12 P Q R S Consider the following table. Element W X Y Z Atomic number 3 8 17 18 Which of the above elements is likely to have an oxidation number of -1 in its compounds? A W B X C Y D Z 13 Consider the following table. Element W X Y Z Atomic number 3 7 9 18 Which of the above elements is likely to be a reducing agent? A W B X C Y D Z 14 The oxidation number of vanadium in V2O5 is A +3. B C D 15 +4. +5. +6. The oxidation number of oxygen in H2O2 is A -1. B -2. C +1. D +2. 16 The oxidation number of manganese in MnO4- is A +7. B +6. C +5. D +4. 17 The oxidation number of nitrogen in NH4Cl is A -1. B -3. C +1. D +3. 18 The oxidation number of zinc in Zn(NH3)42+ is A -2. B C D 0. +2. +4. 19 The oxidation number of chlorine in ClO4-is A -1. B +1. C +3. D +7. 20 The oxidation number of phosphorus in Na3PO4 is A B C D 21 +1. +3. +5. +7. Titanium (Ti) is manufactured from ilmenite which contains iron(II) titanate (FeTiO3). What is the oxidation number of titanium in this compound? A +2 B +3 C +4 D +5 22 When dichromate ion (Cr2O72-) becomes chromium(III) ion (Cr3+), the oxidation number of chromium decreases by A B C D 23 3. 4. 5. 6. In which of the following substances does sulphur have the smallest oxidation number? A S8 B H2S C D Na2S2O3 H2SO3 24 Oxygen has an oxidation number of -1 in A Cr2O72-. B BrO3-. C CO2. D H2O2. 25 Consider the reaction represented by the following ionic equation. Zn(s) + Cu2+(aq) → Zn2+(aq) + Cu(s) The above reaction A is a redox reaction. B occurs in dry cells. C takes in heat energy. D is used in the extraction of copper from its ores. 26 In the following changes, which underlined element has the greatest change in oxidation number? A S(s) → SO2(g) B NO3-(aq) → NO2(g) C Cr2O72-(aq) → 2Cr3+(aq) D MnO4-(aq) → Mn2+(aq) 27 In the following changes, which underlined element has the smallest change in oxidation number? A Cl2(g) → Cl-(aq) B SO2(g) → SO42-(aq) C VO2+(aq) → V3+(aq) D H2S(aq) → S(s) 28 Which of the following changes involves an increase in oxidation number of the underlined element? A Cl2(g) → ClO3-(aq) B SO2(g) → SO32-(aq) C NO3-(aq) → NO2(g) D O2(g) → H2O(l) 29 Consider the following reaction. SO32-(aq) → SO42-(aq) The oxidation number of S A increases by 4. B C D 30 increases by 2. decreases by 2. decreases by 4. A constituent of wood preservative is manufactured by heating the ore chromite (FeCr2O4) with sodium carbonate in the air. 4FeCr2O4(s) + 8Na2CO3(s) + 7O2(g) → 8Na2CrO4(s) + 2Fe2O3(s) + 8CO2(g) In this reaction, the oxidation number of chromium (Cr) changes from A +2 to +3. B C D 31 +3 to +6. +2 to +6. +3 to +2. The following equation represents the oxidation of ammonia in an industrial process: 4NH3(g) + 5O2(g) → 4NO(g) + 6H2O(l) In the process, the oxidation number of nitrogen changes from A -3 to +2. B C D 32 -3 to +4. +3 to +2. +3 to +4. Which of the following is NOT a redox reaction? A Zn(s) + 2HCl(aq) → ZnCl2(aq) + H2(g) B CuO(s) + H2SO4(aq) → CuSO4(aq) + H2O(l) C 2NO(g) + O2(g) → 2NO2(g) D 2H2S(g) + SO2(g) → 2H2O(l) + 3S(s) 33 Which of the following is a redox reaction? A Na2CO3(s) + 2HCl(aq) → 2NaCl(aq) + CO2(g) + H2O(l) B Cu(OH)2(s) + 4NH3(aq) → [Cu(NH3)4](OH)2(aq) C MnO2(s) + 4HCl(aq) → MnCl2(aq) + Cl2(g) + 2H2O(l) D Ca(OH)2(aq) + CO2(g) → CaCO3(s) + H2O(l) 34 The equation shows what happens when hydrated copper(II) sulphate is heated. CuSO45H2O(s) ⇌ CuSO4(s) + 5H2O(g) What can be deduced from the equation? A B C D The hydrated copper(II) sulphate is oxidized. The hydrated copper(II) sulphate is reduced. The reaction is reversible. There is no colour change. 35 Which of the following changes is a redox reaction? A BaCl2(aq) + Na2CrO4(aq) → BaCrO4(s) + 2NaCl(aq) B Fe2(SO4)3(aq) + H2S(g) → 2FeSO4(aq) + S(s)+ H2SO4(aq) C CH3COOH(aq) + NaOH(aq) → CH3COONa(aq) + H2O(l) D Al(OH)3(s) + NaOH(aq) → NaAl(OH)4(aq) 36 Which of the following is NOT a redox reaction? A NH4NO3(s) → N2O(g) + 2H2O(l) B Cl2(g) + 2NaI(aq) → 2NaCl(aq) + I2(aq) C D 37 N2O4(g) + H2O(l) → HNO2(aq) + HNO3(aq) PCl3(l) + 3H2O(l) → H3PO3(aq) + 3HCl(aq) Which of the following reactions involves a reduction? A H+(aq) + OH-(aq) → H2O(l) B Ca2+(aq) + CO32-(aq) → CaCO3(s) C Cu(s) → Cu2+(aq) + 2e- D Cu2+(aq) + 2e- → Cu(s) 38 Which of the following conversions is NOT a reduction? A Al2O3(s) → Al(s) B CaO(s) → Ca(OH)2(s) C MnO2(s) → Mn(OH)2(s) D HNO3(aq) → NO2(g) 39 In which of the following reactions is sulphur reduced? A SO2(g) + Cl2(aq) + 2H2O(l) →SO42-(aq) + 4H+(aq) + 2Cl-(aq) B SO3(g) + H2O(l) → H2SO4(aq) C 2Mg(s) + SO2(g) → 2MgO(s) + S(s) D 40 2MnO4-(aq) + 6H+(aq) + 5SO32-(aq) → 2Mn2+(aq) + 5SO42-(aq) +3H2O(l) In which of the following reactions is the underlined substance oxidized? A 2CuO(s) + C(s) → CO2(g) + 2Cu(s) B 3H2(g) + N2(g) → 2NH3(g) C Mg(s) + ZnSO4(aq) → MgSO4(aq) + Zn(s) D CaCO3(s) + 2HCl(aq) → CaCl2(aq) + CO2(g) + H2O(l) 41 In which of the following reactions is the underlined substance reduced? A H2S2O7(l) + H2O(l) → 2H2SO4(l) B 2Fe2+(aq) + Cl2(aq) → 2Fe3+(aq) + 2Cl-(aq) C Al(OH)3(s) + OH-(aq) → Al(OH)4-(aq) D C(s) + O2(g) → CO2(g) 42 Which of the following underlined reactants is NOT a reducing agent in the reactions indicated? A PbO(s) + CO(g) → Pb(s) + CO2(g) B Zn(s) + 2Ag+(aq) → Zn2+(aq) + 2Ag(s) C Br2(aq) + 2I-(aq) → 2Br-(aq) + I2(aq) D SO2(g) + H2O(l) → H2SO3(aq) 43 In which of the following pairs of sulphur compounds does sulphur exist in the same oxidation state? A SCl2, H2S B FeS, SO2 C SO2, H2SO3 D Na2S2O3, Na2SO4 44 In which of the following pairs of substances are the oxidation numbers of sulphur and nitrogen the same? 45 A B C H2SO4 and HNO3 H2SO3 and NO2 Na2S and NO D FeS and NH4Cl In which of the following pairs of substances are the oxidation numbers of chlorine and nitrogen the same? A HCl, NaNO3 B HClO, NO2 C D 46 In which of the following compounds does vanadium (V) exhibit the highest oxidation number? A VO2+ B V2O3 C VO3D 47 NaClO3, Ca(NO3)2 SCl2, NO VO2 The atomic number of element X is 19. In its compound, this element is likely to have an oxidation number of A -1. B -2. C +1. D +2. 48 In the presence of sodium chloride and dilute sulphuric acid, MnO4-(aq) ions can be reduced to A MnO2(s)。 B MnO42-(aq) ions。 C Mn2+(aq) ions。 D Mn(s)。 49 Identify the reducing agent in the following reaction: Zn(s) + 2MnO2(s) + 2H2O(l) → Zn(OH)2(s) + 2MnO(OH)(s) 50 A Zn B C D H2O MnO2 Zn(OH)2 A simple carbon monoxide detector for a gas heater consists of a patch containing palladium(II) chloride (PdCl2). When carbon monoxide is present, palladium(II) chloride turns from orange to black as the following reaction takes place. CO(g) + PdCl2(aq) + H2O(l) → CO2(g) + Pd(s) + 2HCl(aq) orange Which species is reduced in the reaction? A Carbon monoxide B Hydrogen chloride C Palladium(II) chloride D Water 51 black Sodium sulphite is added to chlorine water. Which of the following combinations concerning the reaction is correct? A B C D Oxidizing agent Cl-(aq) SO32-(aq) Cl2(aq) SO32-(aq) Reducing agent SO32-(aq) Cl2(aq) SO32-(aq) Cl-(aq) 52 Which of the following combinations concerning the reaction between potassium iodide solution and iron(III) sulphate solution is correct? A B C D 53 Oxidizing agent Iodide ion Iron(III) ion Iron(III) ion Iodide ion Reducing agent Sulphate ion Iodide ion Potassium ion Iron(III) ion heat (NH4)2Cr2O7(s) → N2(g) + 4H2O(l) + Cr2O3(s) The above equation represents the reaction occurs when ammonium dichromate is heated. Which of the following combinations about the reaction is correct? A B C D 54 Oxidation number of nitrogen Increases Increases Decreases Decreases Oxidation number of chromium Decreases Increases Decreases Increases The equation below shows how hydrogen sulphide (H2S) could be produced from sulphuric acid in a redox reaction. 9H2SO4(aq) + 8KI(s) → H2S(g) + 8KHSO4(aq) + 4H2O(l) +4I2(s) Which species is oxidized in the reaction and which is reduced? A B C D 55 Species being reduced H2S I2 H2SO4 KI Species being oxidized I2 H2S KI H2SO4 2CrO42-(aq) + 2H+(aq) → Cr2O72-(aq) + H2O(l) Which of the following statements concerning the above reaction is correct? A The reaction is a redox reaction. B H+(aq) ions are oxidized. C CrO42-(aq) ions act as an oxidizing agent. D The solution changes from yellow to orange. 56 Which of the following statements concerning the reaction between sulphur dioxide and iron(III) sulphate solution is correct? A Sulphur dioxide acts as a reducing agent. B Iron(III) ions are oxidized. C Sulphur dioxide is oxidized to sulphide ions. D The colour of the solution changes from green to yellow. 57 When excess sodium sulphite solution is added to acidified potassium permanganate solution, the resulting solution is colourless. Which of the following is the best explanation for such a phenomenon? A Sodium sulphite acts as a bleaching agent. B Permanganate ions are reduced to colourless manganese(II) ions. C Both sodium sulphite solution and acidified potassium permanganate solution are colourless. D Sulphite ions are oxidized to sulphate ions. 58 Iron(II) sulphate solution is added to acidified potassium permanganate solution. The colour of the solution gradually changes from purple to yellow. Which of the following statements concerning the reaction is correct? A The yellow colour is due to the formation of Mn2+(aq) ions. B Sulphate ions take part in the reaction. C The oxidation number of potassium does not change in the reaction. D Iron(II) ions are reduced to iron(III) ions. 59 Which of the following statements concerning magnesium is INCORRECT? A Magnesium is a stronger reducing agent than silver. B Magnesium forms ions more readily than silver. C Magnesium ion is a stronger oxidizing agent than silver ion. D Magnesium donates electrons more readily than silver. 60 Which of the following statements concerning potassium is correct? 61 A Potassium is a hard solid at room conditions. B C D Potassium is a stronger reducing agent than sodium. Potassium reacts with chlorine to form a covalent compound. Potassium is less reactive than lithium. Which of the following statements is INCORRECT? A Sodium ion is a stronger oxidizing agent than magnesium ion. B The reaction between sodium and water is a redox reaction. C When sodium sulphite solution is added to bromine water, bromine water is decolourized. D Acidified potassium dichromate solution is a common oxidizing agent. 62 Which of the following statements concerning a calcium atom and a calcium ion is correct? A The formation of a calcium ion from a calcium atom is a reduction. B They have different nuclear charges. C They have different number of occupied electron shells. D They have the same reducing ability. 63 Which of the following statements concerning elements in Period 3 of the periodic table is INCORRECT? A Their ability to gain electrons increases from Group I to Group VII. B The outermost shell of an argon atom has an octet structure. C Chlorine is an oxidizing agent. D Melting points of the elements increase from left to right. 64 Element X can form an anion X2- which has an electronic arrangement of 2, 8. Which of the following statements concerning X is correct? A X has a giant covalent structure. B X is in Period 2 of the periodic table. C X is a common reducing agent. D X has a high melting point. 65 The atomic number of element X is 7. Which of the following statements concerning X is correct? A B C D 66 The oxidation number of sulphur remains unchanged when A zinc is added to concentrated sulphuric acid. B sulphur dioxide is added to water. C sodium sulphite solution is added to acidified potassium dichromate solution. D 67 (1), (2) and (3) Which of the following substances are common oxidizing agents? (1) Aqueous chlorine (2) Acidified potassium permanganate solution (3) Iron(III) sulphate solution A (1) and (2) only B (1) and (3) only C D 69 sulphur is heated in air. An oxidation may involve (1) an addition of oxygen to a substance. (2) a removal of electrons from a substance. (3) an increase in oxidation number. A (1) and (2) only B (1) and (3) only C (2) and (3) only D 68 X is a solid at room temperature and pressure. In the compound formed between X and lithium, X has an oxidation number of -3. The oxide of X gives an alkaline solution when dissolved in water. X belongs to Group VII of the periodic table. (2) and (3) only (1), (2) and (3) Which of the following substances are common reducing agents? (1) Calcium (2) Concentrated sulphuric acid (3) Potassium iodide solution 70 A (1) and (2) only B C D (1) and (3) only (2) and (3) only (1), (2) and (3) Which of the following gases can act as reducing agents? (1) Carbon monoxide (2) Hydrogen (3) Fluorine A (1) and (2) only B C D 71 Which of the following statements concerning a reducing agent are correct? (1) A reducing agent undergoes reduction in a redox reaction. (2) A reducing agent may lose electrons in a redox reaction. (3) The oxidation number of a reducing agent increases in a redox reaction. A (1) and (2) only B C D 72 (1) and (3) only (2) and (3) only (1), (2) and (3) Which of the following statements concerning a reducing agent is / are correct? (1) A reducing agent must donate electrons in a redox reaction. (2) A reducing agent is oxidized in a redox reaction. (3) Zinc acts as a reducing agent when it reacts with dilute sulphuric acid. A B C D 73 (1) and (3) only (2) and (3) only (1), (2) and (3) (1) only (2) only (1) and (3) only (2) and (3) only Which of the following underlined species have the same oxidation number? (1) NO2 (2) P4 (3) A B C D 74 H2SO3 (1) and (2) only (1) and (3) only (2) and (3) only (1), (2) and (3) Which of the following underlined species have the same oxidation number? (1) CrO42(2) Cr2O72(3) NaClO3 A (1) and (2) only B (1) and (3) only C D 75 Which of the following underlined species have an oxidation number of -1? (1) LiCl (2) NaH (3) A B C D 76 (2) and (3) only (1), (2) and (3) NH2OH (1) and (2) only (1) and (3) only (2) and (3) only (1), (2) and (3) Which of the following underlined species have an oxidation number of +2? (1) Pb(OH)42(2) (3) A B C D Cu(NH3)42+ MnCl2 (1) and (2) only (1) and (3) only (2) and (3) only (1), (2) and (3) 77 Which of the following are redox reactions? (1) 4HNO3(aq) → 2H2O(l) + 4NO2(g) + O2(g) (2) CaCO3(s) + 2HCl(aq)→ CaCl2(aq) + H2O(l) + CO2(g) (3) Zn(s) + CuSO4(aq) → ZnSO4(aq) + Cu(s) A B C D 78 (1) and (2) only (1) and (3) only (2) and (3) only (1), (2) and (3) Which of the following are redox reactions? (1) H2S(g) + Cl2(g) → 2HCl(g) + S(s) (2) PbS(s) + 4H2O2(aq) → PbSO4(s) + 4H2O(l) (3) NH3(aq) + HNO3(aq) → NH4NO3(aq) A B C D (1) and (2) only (1) and (3) only (2) and (3) only (1), (2) and (3) 79 In which of the following reactions do the underlined substances act as oxidizing agents? (1) 2Fe3+(aq) + SO2(aq) + 2H2O(l) → 2Fe2+(aq) + 4H+(aq) + SO42-(aq) (2) Cr2O72-(aq) + 6Fe2+(aq) + 14H+(aq) → 6Fe3+(aq) + 2Cr3+(aq) + 7H2O(l) (3) Cl2(g) + 2Br-(aq) → 2Cl-(aq) + Br2(aq) A B C D 80 (1) and (2) only (1) and (3) only (2) and (3) only (1), (2) and (3) Which of the following changes involve a decrease in oxidation number of the underlined elements? (1) N2(g) + 3H2(g) → 2NH3(g) (2) NO3-(aq) → NO(g) (3) SO42-(aq) → SO2(g) A B C (1) and (2) only (1) and (3) only (2) and (3) only D 81 (1), (2) and (3) Consider the following equation. 5K2C2O4(aq) + 2KMnO4(aq) + 16HCl(aq) → 10CO2(g) + 2MnCl2(aq) + 12KCl(aq) + 8H2O(l) Which of the following elements undergo(es) a change in oxidation number? (1) C (2) O (3) H A (1) only B (2) only C D 82 When a small piece of sodium is put into a trough of water, a reaction occurs. Which of the following statements concerning this reaction are correct? (1) It is an exothermic reaction. (2) It is a redox reaction. (3) An alkaline solution is formed. A (1) and (2) only B C D 83 (1) and (3) only (2) and (3) only (1), (2) and (3) Which of the following statements concerning the reaction between magnesium and nickel(II) sulphate solution are correct? (1) The reaction is a redox reaction. (2) Magnesium acts as a reducing agent. (3) A B C D 84 (1) and (3) only (2) and (3) only The green colour of the solution fades. (1) and (2) only (1) and (3) only (2) and (3) only (1), (2) and (3) Excess sodium iodide solution is added to acidified potassium permanganate solution. Which of the following statements concerning the reaction are correct? (1) (2) (3) A B C D 85 The solution changes from purple to colourless. Iodide ions are oxidized. The oxidation number of manganese decreases from +7 to +2. (1) and (2) only (1) and (3) only (2) and (3) only (1), (2) and (3) Which of the following statements concerning the reaction between acidified potassium permanganate solution and sodium sulphite solution is / are correct? (1) The oxidation number of sulphur changes from +4 to +6. (2) Sodium sulphite acts as an oxidizing agent. (3) A B C D The oxidation number of potassium remains unchanged. (1) only (2) only (1) and (3) only (2) and (3) only 86 Which of the following statements concerning the reaction between iron(II) sulphate solution and acidified potassium dichromate solution are correct? (1) Iron(II) sulphate acts as a reducing agent. (2) Dichromate ions lose electrons. (3) The colour of the mixture changes from orange to yellowish green. A (1) and (2) only B (1) and (3) only C (2) and (3) only D (1), (2) and (3) 87 If iron(III) sulphate solution and potassium iodide solution are mixed directly, (1) chemical energy will be converted to heat energy. (2) a redox reaction will occur. (3) iodide ions will lose electrons. A (1) and (2) only B (1) and (3) only 88 C (2) and (3) only D (1), (2) and (3) When hydrogen peroxide is added to acidified potassium dichromate solution, the following reaction occurs. Cr2O72-(aq) + 3H2O2(aq) + 8H+(aq) → 2Cr3+(aq) + 3O2(g) + 7H2O(l) Which of the following statements concerning the reaction are correct? (1) Hydrogen peroxide acts as a reducing agent. (2) The colour of acidified potassium dichromate solution changes from orange to green. (3) The oxidation number of chromium remains unchanged. A B C (1) and (2) only (1) and (3) only (2) and (3) only D (1), (2) and (3) 89 Which of the following will occur when sodium carbonate is added to dilute hydrochloric acid? (1) Effervescence (2) Neutralization (3) Redox reaction A B C D 90 (1) only (2) only (1) and (3) only (2) and (3) only Which of the following gases can decolourize acidified potassium permanganate solution? (1) Carbon dioxide (2) (3) A B C D Sulphur dioxide Chlorine (1) only (2) only (1) and (3) only (2) and (3) only 91 Which of the following statements concerning acidified potassium permanganate solution are correct? (1) It is purple in colour. (2) It should be stored in brown bottles. (3) It is a common reducing agent. A (1) and (2) only B (1) and (3) only C (2) and (3) only D (1), (2) and (3) 92 Which of the following statements are correct? (1) Reactive metals undergo oxidation more readily than less reactive metals. (2) A displacement reaction is a redox reaction. (3) A B C D Oxidation and reduction always occur at the same time. (1) and (2) only (1) and (3) only (2) and (3) only (1), (2) and (3) 93 Which of the following statements concerning sodium to chlorine in Period 3 of the periodic table is / are correct? (1) Their oxides change from acidic to basic. (2) The reducing power of sodium is higher than that of magnesium. (3) The atomic size of the elements decreases from left to right. A (1) only B (2) only C (1) and (3) only D (2) and (3) only 94 Rubidium is a Group I element below potassium in the periodic table. Which of the following statements about rubidium are correct? (1) Rubidium is a stronger reducing agent than potassium. (2) Rubidium forms a basic oxide. (3) The chloride of rubidium conducts electricity in molten state. A (1) and (2) only 95 B (1) and (3) only C D (2) and (3) only (1), (2) and (3) Permanganate ions can be reduced to manganese(IV) oxide under alkaline medium. MnO4-(aq) → MnO2(s) Which of the following statements concerning the process is / are correct? (1) The oxidation number of manganese decreases by 3. (2) MnO4-(aq) ion is a reducing agent. (3) The above process is an oxidation. 96 A B C (1) only (2) only (1) and (3) only D (2) and (3) only Consider the following reaction. Cl2(g) + 2NaOH(aq) → NaCl(aq) + NaOCl(aq) + H2O(l) Which of the following statements concerning the reaction are correct? (1) The oxidation number of chlorine decreases. (2) (3) A B C D 97 The oxidation number of chlorine increases. Sodium hydroxide acts as an oxidizing agent. (1) and (2) only (1) and (3) only (2) and (3) only (1), (2) and (3) Consider the following chemical equation. 2NH3(g) + 3CuO(s) → N2(g) + 3Cu(s) + 3H2O(l) Which of the following statements concerning the reaction are correct? (1) The oxidation number of oxygen remains unchanged. (2) The oxidation number of nitrogen changes from -3 to 0. (3) Ammonia acts as a reducing agent. A (1) and (2) only B (1) and (3) only C (2) and (3) only D 98 (1), (2) and (3) The following equation represents the decomposition that occurs when potassium chlorate KClO3 is heated. 2KClO3(s) → 2KCl(s) + 3O2(g) Which of the following statements concerning the decomposition are correct? (1) The oxidation number of chlorine decreases. (2) The oxidation number of potassium increases. (3) The oxidation number of oxygen changes from -2 to 0. A (1) and (2) only B C D 99 (1) and (3) only (2) and (3) only (1), (2) and (3) Which of the following reagents can be used to distinguish between iron(II) sulphate solution and iron(III) sulphate solution? (1) Acidified potassium permanganate solution (2) Ammonia solution (3) Sulphur dioxide A B C D (1) and (2) only (1) and (3) only (2) and (3) only (1), (2) and (3) 20.13:Balancing redox equations using ionic half-equations 20.14:Balancing redox equations using oxidation number method (CDC guide: Balancing redox equations by using ionic half-equations or by oxidation numbers) 1 The reaction between dilute nitric acid and copper can be represented by the following equation. 3Cu(s) + wNO3-(aq) + xH+(aq) → 3Cu2+(aq) + yNO(g) + zH2O(l) Which of the following sets of values of w, x, y and z is correct? A B C D 2 w 2 3 2 3 x 2 8 8 2 y 2 3 2 3 z 1 4 4 1 The reaction between concentrated nitric acid and silver can be represented by the following equation. Ag(s) + xHNO3(aq) → AgNO3(aq) + yNO2(g) + zH2O(l) Which of the following sets of values of x, y and z is correct? 3 A B x 1 2 y 2 2 z 2 2 C D 1 2 1 1 1 1 Chlorine can be prepared from concentrated hydrochloric acid and potassium permanganate according to the following equation: 2KMnO4(s) + xHCl(aq) → 2KCl(aq) + 2MnCl2(aq) + yH2O(l) + zCl2(g) Which of the following combinations is correct? A B C D 4 x 8 8 16 16 y 4 2 8 5 z 2 4 5 8 The reaction between concentrated sulphuric acid and zinc can be represented by the following equation. Zn(s) + wH+(aq) + xSO42-(aq) → Zn2+(aq) + yH2O(l) + zSO2(g) Which of the following sets of values of w, x, y and z is correct? A B C D w 2 4 2 4 x 1 1 2 2 y 1 2 1 1 z 1 1 2 2 5 Consider the following ionic half-equation. MnO4-(aq) + xH+(aq) + ye- → Mn2+(aq) + zH2O(l) Which of the following sets of values of x, y and z is correct? A B C D 6 x 8 4 8 4 y 5 5 3 3 z 4 2 4 2 Consider the following ionic equation. xCl2(g) + yOH-(aq) → zCl-(aq) + ClO3-(aq) + 3H2O(l) Which of the following sets of values of x, y and z is correct? A B C D 7 y 2 3 6 7 z 1 3 5 8 What is the value of n in the following ionic half-equation? SO32-(aq) + H2O(l) → SO42-(aq) + nH+(aq) + neA B C D 8 x 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 Hydrogen peroxide is oxidized by acidified potassium permanganate solution according to the following ionic half-equations. H2O2(l) → O2(g) + 2H+(aq) + 2eMnO4-(aq) + 8H+(aq) + 5e- →Mn2+(aq) + 4H2O(l) How many moles of KMnO4 will react completely with one mole of H2O2? A 0.4 B 2.0 C 2.5 D 9 5.0 The tarnish on silverware, silver sulphide (Ag2S), can be removed by placing the articles in an aluminium pan and covering them with a warm dilute sodium hydroxide solution. The following ionic half-equations explain how this method is effective: Ag2S(s) + 2e-→2Ag(s) + S2-(aq) Al(s) + 3OH-(aq) → Al(OH)3(s) + 3eHow many moles of Al will react completely with one mole of Ag2S? 10 A 1 2 B 2 3 C 2 D 3 In which of the following ionic half-equations do n have a value of 3? (1) NO3-(aq) + 4H+(aq) + ne-→ NO(g) + 2H2O(l) (2) CrO42-(aq) + 8H+(aq) + ne-→ Cr3+(aq) + 4H2O(l) (3) MnO4-(aq) + 8H+(aq) + ne-→ Mn2+(aq) + 4H2O(l) A B C D 11 (1) and (2) only (1) and (3) only (2) and (3) only (1), (2) and (3) Consider the following equation. xFe2+(aq) + Cr2O72-(aq) + 14H+(aq) → xFe3+(aq) + 2Cr3+(aq) + 7H2O(l) Which of the following statements concerning the above equation are correct? (1) (2) (3) A B C D The value of x is 6. Cr2O72-(aq) ion is the oxidizing agent. Fe2+(aq) ions lose electrons. (1) and (2) only (1) and (3) only (2) and (3) only (1), (2) and (3) 12 Consider the following equation. wCl2(g) + xFe2+(aq) → yCl-(aq) + zFe3+(aq) Which of the following statements concerning the equation are correct? (1) The value of x is 2. (2) The solution changes from green to yellow. (3) The equation represents a redox reaction. A (1) and (2) only B (1) and (3) only C (2) and (3) only D (1), (2) and (3) 20.15: Nitric acid of different concentrations as oxidizing agent (CDC guide: Nitric acid of different concentrations as oxidizing agent to give NO and NO2) 1 Concentrated nitric acid reacts with copper because of its A B C D 2 Which of the following statements concerning concentrated nitric acid and concentrated hydrochloric acid is INCORRECT? A They are corrosive. B They are strong acids. C D 3 acidic property. dehydrating property. oxidizing property. reducing property. They react with ammonia solution to give ammonium salts. They react with zinc to give hydrogen. When copper is added to concentrated nitric acid, which of the following substances will NOT be produced? A Nitrogen monoxide B Nitrogen dioxide C Copper(II) nitrate D Water 4 Which of the following substances / instrument CANNOT be used to distinguish between very dilute nitric acid and dilute nitric acid? A pH meter B Copper C Sodium hydroxide solution D Zinc 5 Which of the following experiments can be used to show that concentrated nitric acid is an oxidizing agent? A B C D 6 Which of the following statements concerning dilute nitric acid is correct? A B C D 7 Dilute nitric acid does not react with copper. Dilute nitric acid reacts with zinc to give hydrogen. Dilute nitric acid can act as an oxidizing agent. Dilute nitric acid is a weak acid. Zinc does NOT liberate hydrogen from a 6 M nitric acid because A there is no reaction between zinc and 6 M nitric acid. B 6 M nitric acid is a strong acid. C D 8 Adding it to iron(III) hydroxide Adding it to sugar Adding it to sulphur Adding it to calcium carbonate 6 M nitric acid acts as an oxidizing agent. insoluble zinc nitrate forms on the surface of zinc and prevents further reaction. When magnesium is added to concentrated nitric acid, a gas is given off. Which of the following statements concerning the gas is INCORRECT? A It is coloured. B It is toxic. C D It has a pungent smell. It is neutral. 9 A colourless solution X turns moist blue litmus paper red. It reacts with zinc to give a brown gas. Solution X may be A concentrated hydrochloric acid. B concentrated nitric acid. C dilute sulphuric acid. D concentrated sulphuric acid. 10 When dilute nitric acid reacts with silver, the oxidation number of nitrogen in nitric acid A B C D 11 increases by 1. increases by 3. decreases by 1. decreases by 3. An alloy contains 60% copper and 40% silver. When the alloy is heated with excess concentrated nitric acid, which of the following will be observed? A Part of the alloy dissolves, leaving a reddish brown substance behind. B Part of the alloy dissolves, leaving a silvery substance behind. C The alloy dissolves completely to form a colourless solution. D The alloy dissolves completely to form a blue solution. 12 Which of the following processes would produce hydrogen gas? A Adding lead to water B C D 13 Adding zinc to dilute nitric acid Adding magnesium to concentrated hydrochloric acid Adding sodium hydroxide to dilute sulphuric acid Which of the following statements about dilute nitric acid is INCORRECT? A It turns moist blue litmus paper red. B It reacts with sodium hydrogencarbonate to give carbon dioxide. 14 C It reacts with carbon to give carbon dioxide. D It is a dehydrating agent. Consider the following flow diagram: Reactant A Reactant B CuCl2(aq) Cu(s) Cu2+(aq) Which of the following combinations is correct? A B Reactant A Fe(s) Zn(s) C D C(s) H2(g) Reactant B Concentrated HCl Dilute HNO3 Dilute HCl Concentrated HNO3 15 Which of the following is a suitable method for preparing the substance mentioned? A Preparing copper from sodium and copper(II) sulphate solution B Preparing nitrogen dioxide from copper and very dilute nitric acid C Preparing hydrogen from calcium and dilute sulphuric acid D Preparing carbon dioxide from calcium carbonate and dilute nitric acid 16 Which of the following are the reduction products of nitric acid? (1) NO3-(aq) (2) NO(g) (3) NO2(g) A (1) and (2) only B (1) and (3) only C (2) and (3) only D (1), (2) and (3) 17 Consider the following redox reaction: 3Cu(s) + 2NO3-(aq) + 8H+(aq) → 3Cu2+(aq) + 2NO(g) + 4H2O(l) Which of the following statements concerning the above reaction is / are correct? (1) Copper is the reducing agent. (2) Nitrate ions are oxidized to nitrogen monoxide. (3) The oxidation number of hydrogen changes from +1 to 0. 18 19 A (1) only B C D (2) only (1) and (3) only (2) and (3) only In an experiment, hot concentrated nitric acid is added to carbon. Which of the following statements concerning the experiment is / are correct? (1) Carbon monoxide is produced. (2) Nitrogen dioxide is produced. (3) Carbon is reduced. A B C (1) only (2) only (1) and (3) only D (2) and (3) only In an experiment, concentrated nitric acid is added to a solution containing Fe2+(aq) ions. Which of the following statements concerning the experiment are correct? (1) Nitrogen monoxide is produced. (2) Concentrated nitric acid acts as an oxidizing agent. (3) A B C D 20 The colour of the solution changes from green to yellow. (1) and (2) only (1) and (3) only (2) and (3) only (1), (2) and (3) Which of the following statements concerning nitrogen dioxide are correct? (1) The oxidation number of nitrogen in nitrogen dioxide is +4. (2) (3) A B C D Nitrogen dioxide can be produced by adding copper to concentrated nitric acid. Nitrogen dioxide has a simple molecular structure. (1) and (2) only (1) and (3) only (2) and (3) only (1), (2) and (3) 21 Which of the following substances is / are the product(s) of the reaction between dilute nitric acid and silver? (1) Hydrogen (2) Silver nitrate (3) Water A (1) only B (2) only C (1) and (3) only D (2) and (3) only 22 Which of the following are the products of the reaction between silver oxide and dilute nitric acid? (1) Water (2) (3) A B C D Silver nitrate Nitrogen monoxide (1) and (2) only (1) and (3) only (2) and (3) only (1), (2) and (3) 23 Which of the following substances can react with concentrated nitric acid? (1) Sulphur (2) Zinc (3) Magnesium hydroxide A (1) and (2) only B (1) and (3) only C (2) and (3) only D (1), (2) and (3) 24 Which of the following substances can be used to obtain copper powder from a mixture of zinc and copper powder? (1) Dilute hydrochloric acid (2) Dilute nitric acid (3) Water A (1) only 25 B (2) only C D (1) and (3) only (2) and (3) only A mixture contains only copper and copper(II) hydroxide. Which of the following methods can be used to separate copper from the mixture? (1) Add dilute sulphuric acid to the mixture and then filter. (2) Add dilute nitric acid to the mixture and then filter. (3) Add water to the mixture and then filter. A (1) only B C D 26 Which of the following reagents can be used to distinguish between dilute nitric acid and dilute sulphuric acid? (1) Ammonia solution (2) Copper (3) Lead(II) nitrate solution A B C D 27 (2) only (1) and (3) only (2) and (3) only (1) only (2) only (1) and (3) only (2) and (3) only Which of the following will be observed when copper is added to dilute nitric acid in a test tube? (1) The solution turns blue. (2) (3) A B C D Copper dissolves. Brown gas is observed at the mouth of the test tube. (1) and (2) only (1) and (3) only (2) and (3) only (1), (2) and (3) 28 Which of the following acids can be stored in a tank made of copper? (1) (2) (3) A B C D 29 Dilute hydrochloric acid Dilute nitric acid Dilute ethanoic acid (1) and (2) only (1) and (3) only (2) and (3) only (1), (2) and (3) Which of the following statements concerning nitric acid are correct? (1) In the laboratory, concentrated nitric acid is commonly stored in brown bottles. (2) Nitric acid can be used as a fertilizer. (3) The corrosiveness of concentrated nitric acid is due to its oxidizing property. A B C D 30 (1) and (2) only (1) and (3) only (2) and (3) only (1), (2) and (3) Which of the following statements concerning the reaction of copper(II) hydroxide with 12 M nitric acid is / are correct? (1) The nitric acid acts as an oxidizing agent. (2) The nitric acid acts as an acid. (3) The reaction is a redox reaction. A (1) only B (2) only C (1) and (3) only D (2) and (3) only 31 Which of the following acids, when heated with copper, would produce a gas? (1) Concentrated nitric acid (2) Dilute ethanoic acid (3) Dilute nitric acid A (1) only B (2) only C (1) and (3) only D 32 Which of the following statements concerning the reaction of lead(II) carbonate with 8 M nitric acid is / are correct? (1) Nitric acid acts as an acid. (2) Nitric acid acts as an oxidizing agent. (3) The reaction is a neutralization reaction. A (1) only B (2) only C (1) and (3) only D 33 (2) and (3) only (2) and (3) only A counterfeit gold coin is made from an alloy of copper and zinc. Which of the following methods can be used to distinguish this gold coin from a pure gold coin? (1) Comparing their electrical conductivities (2) Treating them with dilute nitric acid (3) Treating them with dilute sulphuric acid A (1) and (2) only B (1) and (3) only C D (2) and (3) only (1), (2) and (3) 20.16: Redox reactions in simple chemical cells with inert electrodes (CDC guide: Reactions in chemical cells consisting of half-cell(s) other than metal-metal ion systems) 1 Which of the following statements concerning the above set-up is INCORRECT? A Electrons flow from half-cell B to half-cell A through the external circuit. B The solution in half-cell A becomes brown in colour after some time. C The colour of the solution in half-cell B changes from yellow to green. D Oxidation occurs in half-cell A. 2 Which of the following combinations concerning the above chemical cell is correct? A B C D 3 At cathode 2I-(aq) → I2(aq) + 2eFe3+(aq) + e- → Fe2+(aq) I2(aq) + 2e- → 2I-(aq) Fe2+(aq) → Fe3+(aq) + e- At anode Fe3+(aq) + e- → Fe2+(aq) 2I-(aq) → I2(aq) + 2eFe2+(aq) → Fe3+(aq) + eI2(aq) + 2e- → 2I-(aq) Which of the following combinations concerning the above chemical cell is correct? A B C D Oxidizing agent Dichromate ion Bromide ion Dichromate ion Bromide ion Reducing agent Sodium ion Dichromate ion Bromide ion Potassium ion 4 Which of the following statements concerning the set-up is correct? A The mass of electrode X increases. B Oxidation occurs at electrode Y. C Electrons flow from electrode Y to electrode X in the external circuit. D A dark blue colour develops in the solution in half-cell A after the cell has operated for some time. 5 Which of the following statements concerning the set-up is correct? A The salt bridge allows the passage of electrons between the two half-cells. B The current flows from half-cell A to half-cell B. C Reduction occurs in half-cell A. D The purple colour of the solution in half-cell B fades. 6 Which of the following statements concerning the above chemical cell is correct? A B C Oxidation occurs at electrode X. The mass of electrode Y increases. Sulphite ions migrate into the salt bridge. D The solution around electrode X turns yellow. 7 Which of the following statements concerning the above set-up is correct? A Dichromate ions are oxidized and iodide ions are reduced. B Dichromate ions are oxidized and sodium ions are reduced. C Iodide ions are oxidized and dichromate ions are reduced. D Iodide ions are oxidized and potassium ions are reduced. 8 Gas bubbles of hydrogen are given off at the graphite electrode because A the graphite electrode reacts with dilute sulphuric acid to form hydrogen gas. B NO3-(aq) ions supply electrons to hydrogen ions. C D hydrogen ions are reduced by sulphate ions. hydrogen ions accept electrons released from the zinc electrode. 9 Which of the following statements about the chemical cell is correct? A Potassium ion is being reduced. B Electrons flow from electrode Y to electrode X in the external circuit. C The mass of electrode X increases. D The mass of electrode Y decreases. 10 In the chemical cell shown below, electrons flow in such a direction that the concentration of Ni2+(aq) ions in each arm becomes the same eventually. In the above cell, electrons flow A from electrode X to electrode Y through the metal wire. B C D 11 from electrode Y to electrode X through the metal wire. from electrode X to electrode Y through the glass wool plug. from electrode Y to electrode X through the glass wool plug. The diagram below shows an aluminium-air battery, a new battery that can be used to power electric motors. In this aluminium-air battery, O2(g) acts as the A oxidizing agent and gains electrons. B oxidizing agent and loses electrons. C D 12 reducing agent and gains electrons. reducing agent and loses electrons. In the chemical cell shown above, electrons flow in such a direction that the concentration of Cu2+(aq) ions in each half-cell becomes the same eventually. Which of the following statements concerning the set-up are correct? (1) Reduction occurs at electrode X. (2) Electrons flow from electrode Y to electrode X in the external circuit. (3) The mass of electrode Y increases. A (1) and (2) only B C D (1) and (3) only (2) and (3) only (1), (2) and (3) 13 Which of the following statements concerning the above set-up are correct? (1) The solution in half-cell A is decolourized. (2) The mass of both electrodes remains unchanged. (3) A B C D 14 Fe2+(aq) ion acts as a reducing agent. (1) and (2) only (1) and (3) only (2) and (3) only (1), (2) and (3) Which of the following statements concerning the above chemical cell are correct? (1) Oxidation occurs at the anode. (2) Sulphate ion acts as an oxidizing agent. (3) A dark blue colour develops in the solution in half-cell B after the cell has operated for some time. A (1) and (2) only B C D (1) and (3) only (2) and (3) only (1), (2) and (3) 15 What may solution Z be so that electrons flow in the direction as indicated in the diagram? (1) Acidified KMnO4(aq) (2) KI(aq) (3) A B C D 16 Na2SO3(aq) (1) only (2) only (1) and (3) only (2) and (3) only Which of the following statements about the chemical cell is / are correct? (1) The purple colour of the potassium permanganate solution fades out gradually. (2) The ionic half-equation for the change occurring at electrode X is Fe2+(aq) + 2e-→ Fe(s). (3) Electrons flow from electrode Y to electrode X through the external circuit. A B C (1) only (2) only (1) and (3) only D (2) and (3) only 17 Which of the following statements concerning the above chemical cell are correct? (1) Carbon electrodes are used because they are chemically inert. (2) Electrons flow from electrode Y to electrode X in the external circuit. (3) The ionic half-equation for the change occurring at electrode Y is 2Br-(aq) → Br2(aq) + 2eA B C D (1) and (2) only (1) and (3) only (2) and (3) only (1), (2) and (3) 20.17: Redox reactions in a zinc-carbon dry cell (CDC guide: Reactions in a zinc-carbon cell) 1 Which of the following substances acts as the anode in a zinc-carbon cell? A Ammonium chloride B Zinc case C Carbon rod D Manganese(IV) oxide 2 Which of the following substances is used to oxidize the hydrogen produced in a zinc-carbon cell? A Carbon powder B Carbon rod C D 3 Manganese(IV) oxide Ammonium chloride Which of the following is the electrolyte in a zinc-carbon cell? A Manganese(IV) oxide B C D Ammonium chloride Sulphuric acid Potassium hydroxide 4 Which of the following statements concerning a zinc-carbon cell is correct? A Electrons flow from the carbon rod to the zinc case in the external circuit. B Manganese(IV) oxide acts as an oxidizing agent. C The zinc case becomes thicker when the dry cell has been used for a long time. D The carbon powder increases the internal resistance of the dry cell. 5 Which of the following statements concerning a zinc-carbon cell is correct? A Manganese(IV) oxide acts as a reducing agent to remove hydrogen. B Oxidation occurs at the zinc case. C It is rechargeable. D Its maximum voltage is 1.25 V. 6 Which of the following statements concerning the above set-up is correct? A Electrons flow from the zinc case to the carbon rod in the external circuit. B C D Zinc acts as an oxidizing agent. Ammonium chloride acts as a reducing agent. Manganese(IV) oxide is oxidized. 7 Which of the following reactions occurs at the anode in a zinc-carbon cell? A Zn(s) → Zn2+(aq) + 2eB Zn2+(aq) + 2e- → Zn(s) C 2NH4+(aq) + 2e- → 2NH3(aq) + H2(g) D 2MnO2(s) + H2(g) → Mn2O3(s) + H2O(l) 8 Which of the following reactions occurs at the cathode of a zinc-carbon cell? A Zn2+(aq) + 2e-→ Zn(s) B 2NH4+(aq) + 2e- → 2NH3(aq) + H2(g) C Mn2O3(s) + H2O(l) → 2MnO2(s) + H2(g) D Zn(NH3)2Cl2(s) → Zn2+(aq) + 2NH3(aq) + 2Cl-(aq) 9 Which of the following reactions does NOT occur in a zinc-carbon cell? A Zn(s) → Zn2+(aq) + 2eB C(s) + 2H2(g) → CH4(g) C 2NH4+(aq) + 2e-→ 2NH3(aq) + H2(g) D 2MnO2(s) + H2(g) → Mn2O3(s) + H2O(l) 10 When a zinc-carbon cell has been used for a long time, its voltage drops rapidly. It is due to the presence of A B C D hydrogen. zinc ions. manganese(III) oxide. ammonium chloride. 11 Which of the following statements concerning the above set-up are correct? (1) An electric current flows from the zinc case to the carbon rod in the external circuit. (2) The zinc case becomes thinner after some time. (3) Reduction occurs at the cathode. A (1) and (2) only B (1) and (3) only C D 12 Which of the following statements concerning the manganese(IV) oxide in zinc-carbon cells are correct? (1) Manganese(IV) oxide acts as an oxidizing agent. (2) The oxidation number of manganese in manganese(IV) oxide changes from +4 to +2 over discharge. (3) A B C D 13 (2) and (3) only (1), (2) and (3) Manganese(IV) oxide is used to remove the hydrogen produced in the cells. (1) and (2) only (1) and (3) only (2) and (3) only (1), (2) and (3) Which of the following statements concerning a zinc-carbon cell are correct? (1) It is a primary cell. (2) (3) A B C D 14 Its zinc case acts as the anode. It has a short shelf life. (1) and (2) only (1) and (3) only (2) and (3) only (1), (2) and (3) Which of the following statements concerning a zinc-carbon cell are correct? (1) A zinc-carbon cell has a steady voltage over discharge. (2) Hydrogen will be produced inside the dry cell over discharge. (3) The carbon rod is the cathode. A (1) and (2) only B C D 15 (1) and (3) only (2) and (3) only (1), (2) and (3) Which of the following statements concerning a zinc-carbon cell are correct? (1) It may explode if disposed of in fire. (2) (3) A B C D Its voltage falls rapidly over discharge. Potassium hydroxide acts as an electrolyte. (1) and (2) only (1) and (3) only (2) and (3) only (1), (2) and (3) Unit 21 21.1:Electrolysis: chemical reactions from electricity 21.2 :Comparing a chemical cell and an electrolytic cell 21.3 :Electrolysis of molten sodium chloride using carbon electrodes 21.4 :Some knowledge related to aqueous electrolytes 21.5 :Electrolysis of aqueous solutions of ionic compounds 21.6 :Factors affecting the electrolysis of aqueous solutions (CDC guide: Electrolysis as the decomposition of substances by electricity as exemplified by electrolysis of (a) dilute sulphuric acid, (b) sodium chloride solutions of different concentrations, (c) copper(II) sulphate solution; Anodic and cathodic reactions; Preferential discharge of ions in relation to the electrochemical series, concentration of ions and nature of electrodes.) 1 Which of the following statements is correct? A In a chemical cell, oxidation occurs at the positive electrode. B All redox reactions involve electron transfer. C Sodium oxide is a non-electrolyte. D A direct current should be used in electrolysis. 2 Which of the following statements is correct? A B C D In an electrolytic cell, oxidation takes place at the anode. In an electrolytic cell, reduction takes place at the anode. In a chemical cell, oxidation takes place at the cathode. In a chemical cell, reduction takes place at the anode. 3 Which of the following statements concerning electrolysis is INCORRECT? A During electrolysis, chemical energy is converted into electrical energy. B Electrolysis involves the decomposition of an electrolyte. C An energy supply is required for electrolysis. D Graphite is commonly used as the inert electrodes in electrolysis. 4 Which of the following is NOT an essential component of the set-up for electrolysis? A An electrolyte B Electrodes C D 5 An ammeter An energy supply Which of the following substances would NOT be decomposed by electricity? A Molten silver B Dilute sulphuric acid C Concentrated sodium chloride solution D Silver nitrate solution 6 Which of the following ions are reduced during the electrolysis of molten silver chloride? A Silver ions B Chloride ions C Hydrogen ions D Hydroxide ions 7 Fluorine is NOT readily obtained as a product of electrolysis because 8 9 10 A B C fluoride ion has a small size. fluoride ion is readily oxidized in contact with air. fluoride ion is not readily oxidized. D fluoride compounds have extremely high melting points. Which of the following changes would occur at the electrodes during the electrolysis of dilute copper(II) chloride solution using copper electrodes? A Anode Copper dissolves Cathode Copper deposits B C D Copper deposits Chlorine given off Chlorine given off Copper dissolves Copper deposits Hydrogen given off In the electrolysis of a dilute copper(II) sulphate solution, carbon is used as the anode and copper as the cathode. Which of the following changes will occur at the electrodes? A Anode Copper dissolves Cathode Copper deposits B C D Copper dissolves Oxygen given off Oxygen given off Hydrogen given off Copper deposits Hydrogen given off Which of the following combinations concerning the electrolysis of dilute sulphuric acid is correct? Positive electrode Negative electrode 11 A 2H+(aq) + 2e-→ H2(g) 4OH-(aq) → 2H2O(l) + O2(g) + 4e- B C D 2H+(aq) + 2e- → H2(g) 4OH-(aq) → 2H2O(l) + O2(g) + 4e4H+(aq) + SO42-(aq) + 2e→ SO2(g) + 2H2O(l) 4H+(aq) + SO42-(aq) + 2e- → SO2(g) + 2H2O(l) 2H+(aq) + 2e- →H2(g) 2H+(aq) + 2e- →H2(g) Which of the following sets of changes would occur during the electrolysis of dilute sulphuric acid using platinum electrodes? A B C D 12 C D 14 Hydrogen Oxygen Hydrogen Product at anode Hydrogen Oxygen Hydrogen Oxygen Concentration of sulphuric acid Increases Increases Decreases Decreases Which of the following combinations concerning the electrolysis of a 2 M copper(II) chloride solution using carbon electrodes is correct? A B 13 Product at cathode Oxygen Product at cathode Copper Copper Hydrogen Hydrogen Product at anode Oxygen Chlorine Colour of electrolyte Remains unchanged Fades Chlorine Oxygen Fades Remains unchanged Which of the following sets of changes would occur to silver nitrate solution during the electrolysis using graphite electrodes? A Number of moles of Ag+(aq) Decreases Number of moles of NO3-(aq) Decreases pH value of the solution Remains unchanged B C D Decreases Remains unchanged Remains unchanged Remains unchanged Remains unchanged Decreases Decreases Decreases Remains unchanged In an experiment, concentrated sodium iodide solution is electrolyzed using carbon electrodes. Which of the following combinations concerning the changes in the experiment is correct? Product at cathode Product at anode Resulting solution 15 A Hydrogen Iodine More concentrated NaI(aq) B C D Sodium Hydrogen Hydrogen Oxygen Oxygen Iodine More concentrated NaI(aq) NaOH(aq) NaOH(aq) Consider the following set-up. Which of the following combinations is correct? A Reaction at cathode Cu2+(aq) + 2e- → Reaction at anode 4OH-(aq) → B Cu(s) 2H+(aq) + 2e-→ 2H2O(l) + O2(g) + 4e4OH-(aq) → C D 16 2H2O(l) + O2 + 4e Cu2+(aq) + 2e- → No change Cu(s) Cu(s) → No change 2+ - Cu (aq) + 2e In the electrolysis of a copper(II) sulphate solution, carbon is used as the anode and copper as the cathode. Which of the following statements concerning this experiment is correct? A B C D 17 - Cu (aq) + 2e Cu2+(aq) + 2e- → Cu(s) Becomes more concentrated - H2(g) Cu(s) → 2+ Change in electrolyte Becomes H2SO4(aq) The blue colour of the solution remains unchanged. The concentration of H+(aq) ions in the solution increases. Cu2+(aq) ions are produced at the anode. H2(g) is liberated at the cathode. The following diagram shows the set-up for the electrolysis of concentrated sodium chloride solution. Which of the following combinations is correct? A Product at cathode Sodium Product at anode Chlorine B C D Sodium Hydrogen Hydrogen Oxygen Oxygen Hydrogen 18 Which of the following statements concerning the above set-up is INCORRECT? A Only hydroxide ions migrate to the anode. B The negative electrode is the cathode. C Gas A is oxygen. D 19 The electrodes can be made of platinum. Which of the following diagrams concerning the electrolysis of dilute sulphuric acid is correct? Directions: Questions 20 and 21 refer to the following experiment. 20 The gases collected at electrodes X and Y respectively are in the volume ratio of A 1 : 1. B 1 : 2. C 2 : 1. D 1 : 4. 21 Which of the following statements concerning the above experiment are correct? (1) The concentration of magnesium ions around electrode Y increases. (2) The pH value of magnesium sulphate solution remains unchanged after electrolysis. (3) The products obtained at both electrodes remain unchanged if dilute magnesium sulphate solution is used instead of concentrated magnesium sulphate solution. A (1) and (2) only B (1) and (3) only C (2) and (3) only D (1), (2) and (3) 22 Which of the following combinations is correct? A B C D 23 Gas X Hydrogen Oxygen Hydrogen Chlorine Gas Y Oxygen Hydrogen Chlorine Hydrogen A solution of potassium sulphate containing litmus is electrolyzed using the set-up shown below: After a short time, which of the following colours would appear in the solutions around the two platinum electrodes? A B C D Solution around X Colourless Blue Red Blue Solution around Y Red Colourless Blue Red Directions: Questions 24 and 25 refer to the following set-up. 24 What is the function of the rheostat? A To measure the electric current. B C D 25 Which of the following substances is most suitable for making electrodes for the electrolysis of molten sodium chloride? A B C D 26 To supply energy. To increase the electrical conductivity of the conducting wire. To vary the electric current. Zinc Platinum Graphite Calcium A solution of potassium hydroxide was electrolyzed using graphite electrodes. Which of the following graphs correctly represents the change in mass of cathode with time? 27 Which of the following solutions, when electrolyzed using platinum electrodes, will liberate only one gaseous product? A Mg(NO3)2(aq) B KOH(aq) C FeCl2(aq) D CuCl2(aq) 28 The products of the electrolysis of dilute magnesium iodide solution using carbon electrodes are A hydrogen and iodine. B hydrogen and oxygen. C magnesium and iodine. D magnesium and oxygen. 29 Which of the following substances, when electrolyzed using graphite electrodes, will liberate gaseous products at both electrodes? A Molten sodium chloride B Concentrated sodium bromide solution C Sodium sulphate solution D Silver nitrate solution 30 Which of the following methods can produce hydrogen gas? A B C D 31 Which of the following processes will NOT produce a gas at the anode? A Electrolysis of silver nitrate solution using silver electrodes B Electrolysis of dilute sulphuric acid using platinum electrodes C Electrolysis of very dilute sodium chloride solution using carbon electrodes D 32 33 Addition of zinc to concentrated nitric acid Electrolysis of sodium hydroxide solution Addition of sodium oxide to water Addition of copper to concentrated sulphuric acid Electrolysis of concentrated sodium chloride solution using mercury cathode and carbon anode In which of the following combinations will oxygen be the major product at the anode during electrolysis? A B C Electrolyte 0.1 M NaCl(aq) 0.1 M CuCl2(aq) 5 M NaCl(aq) Cathode Carbon Carbon Carbon Anode Carbon Copper Carbon D 5 M CuCl2(aq) Carbon Copper In which of the following combinations will hydrogen be the major product at the cathode during electrolysis? A B C Electrolyte 5 M NaCl 2 M CuCl2 2 M CuCl2 Cathode Mercury Carbon Copper Anode Carbon Carbon Copper D 5 M HCl Platinum Platinum Directions: Questions 34 and 35 refer to the following set-up. Electrodes E and F are copper electrodes while electrodes G and H are carbon electrodes. 34 35 Which of the electrodes are cathodes? A B C E and H E and G F and H D F and G Which of the following combinations concerning the resulting solutions is correct? A B Solution in beaker X Becomes more concentrated Remains unchanged Solution in beaker Y Becomes more concentrated Becomes nitric acid C D Becomes less concentrated Remains unchanged Becomes less concentrated Becomes more concentrated Directions: Questions 36 and 37 refer to the following set-up. On completing the circuit, the mass of electrode B increases. 36 Which of the following statements about the above set-up is correct? 37 A X is the positive terminal of the battery. B C D Electrode A is the cathode. Oxidation occurs at electrode B. The colour of the copper(II) sulphate solution fades. Which of the following ionic half-equations represents the reaction at electrode C? A 2H+(aq) + 2e-→ H2(g) B Na+(aq) + e- → Na(s) C 4OH-(aq) → O2(g) + 2H2O(l) + 4eD 38 NO3-(aq) + 4H+(aq) + 3e- → NO(g) + 2H2O(l) Hydrogen ions instead of sodium ions are preferentially discharged at the cathode in the electrolysis of dilute sodium chloride solution using carbon electrodes because A sodium is reactive while hydrogen is not. B hydrogen ion is a stronger reducing agent than sodium ion. C hydrogen ion is a stronger oxidizing agent than sodium ion. D the concentration of hydrogen ions is higher than that of sodium ions. 39 Which of the following substances will NOT be produced in the electrolysis of brine using carbon electrodes? A Hydrogen B Chlorine C Sodium D Sodium hydroxide solution 40 In the electrolysis of a copper(II) sulphate solution, copper is used as the anode and carbon as the cathode. Which of the following ionic half-equations represents the reaction at the anode? A Cu2+(aq) + 2e- → Cu(s) B Cu(s) → Cu2+(aq) + 2eC 2H+(aq) + 2e- → H2(g) D 4OH-(aq) → 2H2O(l) + O2(g) + 4e- 41 In the electrolysis of dilute copper(II) sulphate solution using copper electrodes, copper instead of hydroxide ions loses electrons at the anode because A the position of copper is higher than that of hydroxide ion in the electrochemical series. B the concentration of copper(II) ions is higher than that of hydroxide ions. C copper gains electrons more readily than hydroxide ions. D copper(II) ions gain electrons more readily than hydroxide ions. 42 Which of the following are the advantages of using graphite electrodes in the electrolysis of concentrated sodium chloride solution? (1) Graphite can conduct electricity. (2) Graphite is inert. (3) Graphite is cheap. A B C D 43 (1) and (2) only (1) and (3) only (2) and (3) only (1), (2) and (3) Which of the following is / are the disadvantage(s) of using platinum electrodes for the electrolysis of concentrated sodium chloride solution? (1) Platinum is not a good electrical conductor. (2) Platinum is readily attacked by chlorine gas given off. (3) Platinum is an oxidizing agent. A (1) only B (2) only C (1) and (3) only D (2) and (3) only 44 Which of the following ions migrate(s) to the cathode during the electrolysis of molten lead(II) bromide? (1) Lead(II) ions (2) Hydrogen ions (3) Bromide ions A (1) only B (2) only C (1) and (3) only D (2) and (3) only 45 Which of the following statements concerning the above set-up are correct? (1) Lead(II) ions are reduced. (2) The experiment should be performed in a fume cupboard. (3) A reddish-brown gas is given off at the anode. A (1) and (2) only B (1) and (3) only C (2) and (3) only D (1), (2) and (3) 46 Which of the following substances will increase the electrical conductivity of the distilled water in the above set-up? (1) Sugar (2) Anhydrous copper(II) sulphate (3) Silver nitrate solution A (1) and (2) only 47 B (1) and (3) only C D (2) and (3) only (1), (2) and (3) Electrolysis of water in the presence of sulphuric acid can be carried out in the set-up shown below. Which of the following statements concerning the experiment is / are correct? (1) The sulphuric acid acts as a catalyst. (2) Platinum electrodes can be used. (3) After some time, volume ratio of gases collected at anode and cathode is 2 : 1. A (1) only B C D 48 Which of the following statements concerning the electrolysis of 2 M copper(II) chloride solution using carbon electrodes are correct? (1) Chlorine is liberated at the anode. (2) Copper(II) ions are reduced at the cathode. (3) A B C D 49 (2) only (1) and (3) only (2) and (3) only The solution becomes more dilute. (1) and (2) only (1) and (3) only (2) and (3) only (1), (2) and (3) Consider the following set-up. Which of the following statements concerning the above set-up is / are correct? (1) Oxygen is given off at the anode. (2) The reaction at the cathode is Cu(s) → Cu2+(aq) + 2e-. (3) Finally, the solution becomes sulphuric acid. 50 A B C (1) only (2) only (1) and (3) only D (2) and (3) only Which of the following statements concerning electrolysis are correct? (1) Oxidation occurs at the anode. (2) Reduction occurs at the negative electrode. (3) The electrolyte is decomposed during electrolysis. A B C D 51 Which of the following statements concerning electrolysis are correct? (1) The negative electrode is the cathode. (2) Electrolysis involves chemical changes. (3) A B C D 52 (1) and (2) only (1) and (3) only (2) and (3) only (1), (2) and (3) Electrons flow from the anode to the cathode in the electrolyte. (1) and (2) only (1) and (3) only (2) and (3) only (1), (2) and (3) Which of the following substances are produced at the electrodes during the electrolysis of dilute sulphuric acid using graphite electrodes? (1) (2) (3) A B C D 53 Hydrogen Sulphur dioxide Oxygen (1) and (2) only (1) and (3) only (2) and (3) only (1), (2) and (3) For the electrolysis of dilute sodium bromide solution using carbon electrodes, which of the following statements is / are correct? (1) A brown colour develops near the cathode. (2) Oxidation occurs at the anode. (3) A B C D The solution in the electrolytic cell becomes more acidic. (1) only (2) only (1) and (3) only (2) and (3) only 54 Which of the following substances will be produced during the electrolysis of molten sodium chloride using graphite electrodes? (1) Sodium (2) Chlorine (3) Oxygen A (1) and (2) only B (1) and (3) only C (2) and (3) only D (1), (2) and (3) 55 Which of the following is / are electrolyte(s)? (1) Alcohol (2) Lead(II) bromide (3) Zinc A (1) only B (2) only 56 C (1) and (3) only D (2) and (3) only Which of the following statements concerning a chemical cell and an electrolytic cell are correct? (1) Chemical energy is converted to electrical energy in a chemical cell while electrical energy is converted to chemical energy in an electrolytic cell. (2) In an electrolytic cell, oxidation occurs at the positive electrode. (3) In a chemical cell, reduction occurs at the cathode. A (1) and (2) only B C D 57 In which of the following electrolytic processes will the solution in the electrolytic cell become alkaline? (1) Electrolysis of dilute sodium iodide solution using carbon electrodes (2) Electrolysis of dilute magnesium sulphate solution using platinum electrodes (3) Electrolysis of dilute copper(II) nitrate solution using copper electrodes A B C D 58 (1) and (3) only (2) and (3) only (1), (2) and (3) (1) only (2) only (1) and (3) only (2) and (3) only In which of the following electrolytic processes will the solution in the electrolytic cell become more acidic? (1) Electrolysis of dilute hydrochloric acid using carbon electrodes (2) (3) A B C D Electrolysis of dilute nitric acid using platinum electrodes Electrolysis of dilute silver nitrate solution using carbon electrodes (1) only (2) only (1) and (3) only (2) and (3) only 59 When very dilute sodium chloride solution is electrolyzed using carbon electrodes, (1) (2) (3) A B C D 60 both chloride ions and hydroxide ions migrate to the anode. hydrogen is given off at the cathode. the resulting solution becomes more concentrated sodium chloride solution. (1) and (2) only (1) and (3) only (2) and (3) only (1), (2) and (3) During the electrolysis of dilute silver nitrate solution using platinum anode and silver cathode, which of the following will occur? (1) Hydrogen ion is preferentially discharged at the silver cathode. (2) Hydroxide ion is preferentially discharged at the platinum anode. (3) A B C D 61 The concentration of Ag+(aq) ions in the electrolyte increases. (1) only (2) only (1) and (3) only (2) and (3) only Which of the following statements concerning the electrolysis of concentrated sodium chloride solution using carbon electrodes are correct? (1) Hydrogen ions are preferentially discharged at the cathode because the concentration of hydrogen ions in the solution is higher than that of sodium ions. (2) Chloride ions are preferentially discharged at the anode because the concentration of chloride ions in the solution is higher than that of hydroxide ions. (3) The resulting solution is sodium hydroxide solution. A (1) and (2) only B (1) and (3) only C D (2) and (3) only (1), (2) and (3) 62 In the electrolysis of a copper(II) sulphate solution, copper is used as the anode and carbon as the cathode. Which of the following statements concerning this experiment are correct? (1) Copper deposits on the cathode. (2) Oxygen is liberated at the anode. (3) A B C D 63 The concentration of copper(II) ions in the solution remains unchanged. (1) and (2) only (1) and (3) only (2) and (3) only (1), (2) and (3) In which of the following processes will a metal be produced at the cathode? (1) Electrolysis of molten lead(II) bromide using graphite electrodes (2) Electrolysis of silver nitrate solution using carbon electrodes (3) Electrolysis of concentrated sodium chloride solution using mercury cathode and carbon anode A (1) and (2) only B C D 64 In which of the following processes will the solution in the electrolytic cell become more concentrated? (1) (2) (3) A B C D 65 (1) and (3) only (2) and (3) only (1), (2) and (3) Electrolysis of dilute magnesium sulphate solution using carbon electrodes Electrolysis of very dilute sodium chloride solution using carbon electrodes Electrolysis of copper(II) sulphate solution using copper electrodes (1) and (2) only (1) and (3) only (2) and (3) only (1), (2) and (3) In which of the following processes will hydrogen be produced? (1) Addition of zinc granules to dilute nitric acid (2) Electrolysis of dilute sodium nitrate solution using carbon electrodes (3) Electrolysis of concentrated sodium chloride solution using mercury cathode and carbon anode A (1) only B (2) only C (1) and (3) only D 66 (2) and (3) only In which of the following combinations will oxygen be the major product at the anode during electrolysis? Electrolyte (1) 0.1 M CuCl2(aq) (2) 2 M NaCl(aq) (3) 0.1 M CuCl2(aq) A (1) only B (2) only C D 67 Anode Carbon Platinum Copper (1) and (3) only (2) and (3) only Which of the following ions would migrate to the negative electrode during the electrolysis of molten sodium chloride? (1) Chloride ions (2) Sodium ions (3) Hydrogen ions A (1) only B C D 68 Cathode Copper Platinum Copper (2) only (1) and (3) only (2) and (3) only In which of the following processes will the solution in the electrolytic cell become more acidic? (1) Electrolysis of dilute sulphuric acid using platinum electrodes (2) Electrolysis of concentrated hydrochloric acid using carbon electrodes (3) A B C D Electrolysis of dilute copper(II) sulphate solution using carbon electrodes (1) only (2) only (1) and (3) only (2) and (3) only 21.7 :Industrial uses of electrolysis (CDC guide: Industrial applications of electrolysis :(a) electroplating) 1 Which of the following set-ups can be used to plate a layer of copper on the key? 2 Which diagram shows the correct set-up for coating the iron ring with zinc? 3 A student wanted to electroplate a copper knob with nickel using the following set-up. Which of the following combinations is correct? A B Cathode Nickel rod Copper knob Anode Copper knob Nickel rod Electrolyte NiSO4(aq) NiSO4(aq) C D Nickel rod Copper knob Copper knob Nickel rod CuSO4(aq) CuSO4(aq) 4 Which of the following ionic half-equations represents the change at the negative electrode when electroplating an iron object with nickel? A Fe2+(aq) + 2e- → Fe(s) B Fe(s) → Fe2+(aq) + 2eC Ni2+(aq) + 2e- → Ni(s) D Ni(s) → Ni2+(aq) + 2e- 5 The set-up below can be used to coat an object with nickel. Which of the following statements concerning the set-up is correct? A Nickel(II) ions move towards the nickel electrode. B Oxidation occurs at the nickel electrode. C Electrons flow through the solution. D The process is an example of anodization. 6 The diagram shows an electroplating experiment using metals X and Y electrodes. One of the metals becomes coated with copper after some time. Which metal becomes coated and which aqueous solution is used? 7 A B C Metal X X Y D Y Aqueous solution CrCl3(aq) CuCl2(aq) CrCl3(aq) CuCl2(aq) The following set-up is used to purify copper. Which of the following combinations is correct? 8 A B Anode Impure copper rod Pure copper rod Cathode Pure copper rod Impure copper rod Electrolyte Sodium chloride solution Sodium chloride solution C D Impure copper rod Pure copper rod Pure copper rod Impure copper rod Copper(II) sulphate solution Copper(II) sulphate solution Which of the following substances is NOT a product from the industrial electrolysis of brine? A Sodium hydroxide B Bleaching solution C Hydrochloric acid D Mercury 9 Which of the following is NOT an application of electrolysis? A Extraction of reactive metals from their ores B Electroplating C Removal of metal ions from sewage D Anodization 10 The following set-up is used to refine impure copper containing iron and silver. Which of the following statements about the above set-up is INCORRECT? A The impure copper electrode is the anode. B The iron in the impure copper loses electrons. C D 11 The silver in the impure copper settles at the bottom of the container. The pure copper electrode is connected to the positive terminal of the d.c. power supply. Brass is an alloy containing mainly of copper and zinc. The electric circuit shown below was set up. What reactions would occur on turning on the switch? A B At anode Copper dissolves preferentially. Copper dissolves preferentially. At cathode Copper is deposited. Hydrogen is evolved. 12 C Zinc dissolves preferentially. Copper is deposited. D Zinc dissolves preferentially. Hydrogen is evolved. Electrolysis is used in the extraction of (1) copper. (2) sodium. (3) aluminium. A (1) and (2) only B (1) and (3) only C (2) and (3) only D 13 To coat a layer of chromium on a copper ring, (1) the ring to be electroplated should be the cathode. (2) the electrolyte should be dilute sulphuric acid. (3) the anode should be made of chromium. A (1) and (2) only B (1) and (3) only C (2) and (3) only D 14 (1), (2) and (3) (1), (2) and (3) The following set-up is used to electroplate a layer of silver on an iron key. When a current has passed through the circuit for some time, which of the following would occur? (1) Silver ions migrate to the iron key. (2) The mass of the silver rod decreases. (3) The concentration of silver ions in the solution increases. A (1) and (2) only B (1) and (3) only 15 C (2) and (3) only D (1), (2) and (3) Which of the following substances are commonly found in the sewage produced by the electroplating industry? (1) Acids (2) Alkalis (3) Heavy metal ions A (1) and (2) only B (1) and (3) only C D 16 (2) and (3) only (1), (2) and (3) Consider the following set-up. Which of the following statements is / are correct? (1) The mass of the pure copper rod increases after some time. (2) The process increases the strength of copper. (3) Concentration of the copper(II) sulphate solution remains unchanged. A (1) only B (2) only C (1) and (3) only D 17 (2) and (3) only Which of the following are applications of electrolysis? (1) Electroplating (2) Anodization (3) Production of chlorine A (1) and (2) only 18 B (1) and (3) only C D (2) and (3) only (1), (2) and (3) Which of the following is / are the industrial use(s) of electrolysis? (1) Purification of copper (2) Extraction of copper (3) Silver-plating A (1) only B (2) only C D (1) and (3) only (2) and (3) only Directions: Questions 19 to 21 refer to the following flow diagram. The flow diagram below shows the stages involved in the extraction of zinc from zinc blende. 19 The reaction in Stage I gives a gaseous product. This gaseous product is A oxygen. B carbon dioxide. C nitrogen dioxide. D sulphur dioxide. 20 In Stage II, zinc sulphate solution can be obtained by adding zinc oxide to dilute sulphuric acid. Which of the following statements concerning the reaction are correct? (1) A neutralization reaction occurs. (2) A redox reaction occurs. (3) Effervescence occurs. A (1) only 21 B (2) only C D (1) and (3) only (2) and (3) only Which of the following statements concerning the electrolysis of zinc sulphate solution in Stage III are correct? (1) Zinc metal is produced at the cathode. (2) Hydrogen is produced at the anode. (3) Oxidation occurs at the anode. A (1) and (2) only B C D (1) and (3) only (2) and (3) only (1), (2) and (3)