* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download LIFE OVER TIME
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Objections to evolution wikipedia , lookup
Sociocultural evolution wikipedia , lookup
Hindu views on evolution wikipedia , lookup
Evolving digital ecological networks wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Creation and evolution in public education in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Unilineal evolution wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Punctuated equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Acceptance of evolution by religious groups wikipedia , lookup
Creation and evolution in public education wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Catholic Church and evolution wikipedia , lookup
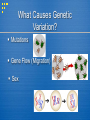
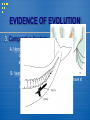
LIFE OVER TIME What processes have created diverse species & adaptations throughout history? Theories of Evolution began when scientists began asking these questions… What is a Scientific Theory? Fact: An observation that has been repeatedly confirmed with not dispute. For example, there are 23 pairs of chromosomes in human cells. Law: A descriptive generalization about how some aspect of the natural world behaves under stated circumstances. For example, one of Newton's laws of motion that states that for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. Hypothesis: A testable statement about the natural world that explains why something occurs. Theory: A well-supported explanation of some aspect of the natural world that can incorporate facts, laws, and tested hypotheses. For example, the cell theory states that cells are the basic unit of all living organisms and that all new cells arise from the division of pre-existing cells. What is Evolution? Evolution = a series of gradual or rapid changes in living & nonliving things through time Evolution of Stars Evolution of the Earth System (water, landforms, atmosphere) Evolution of Living Things Evolution of Scientific ideas Theories of Evolution Theories of Evolution are… • attempts to explain changes & diversity in living things through time • supported by a great deal of research & study Theories of Evolution are Not… • attempts to explain the origins & purpose of life! • a religion or belief system Early Theories of Evolution Jean-Baptiste de Lamarck (1744-1829) • Law of Use & Disuse - organisms respond to changes in their environment by developing new organs or changing the structure/function of old organs. . . . • Theory of Inheritance of Acquired Characteristics these acquired characteristics were then passed on to the organism's offspring. . . . Giraffes Long Necks The Basis for Modern Theories of Evolution Charles Darwin (1809-1882) • Artificial Selection - selective breeding in pigeons • Natural Selection - organisms with certain variations survive, reproduce & pass on these traits to their offspring Galapagos Island Animal Species An Intro to Modern Theory http://evolution.berkeley.edu/evosite/evo 101/IIntro.shtml How Does Evolution Happen? Fundamental to the process of evolution is genetic variation within populations upon which selective forces can act in order for long term change to occur. Genetic Drift (Random) Genetic Variation Natural Selec tion (Non-random) Change in Populations (Evo lution) What Causes Genetic Variation? Mutations Gene Flow (Migration) Sex Genetic Drift Change in the genetic makeup of a population by chance events (random!) It does NOT work to produce adaptations! Examples: 1. Ellis-van Creveld syndrome in Amish 2. Stepping on a bug! 3. A bird left on an island - Galapagos Natural Selection 1. There is Genetic Variation 2. There is Selective Pressure environmental conditions 3. There is Survival of Some 4. There is Reproduction by the Survivors 5. Adaptations Show How Do New Species Form? Species = Group of similar organisms that can interbreed & produce fertile offspring Speciation = Evolution of a new species Causes of Speciation 1. Geographic Isolation = when a physical barrier divides a population Each population adapts to its environment thru natural selection & develops its own gene pool. Over time the separate groups become so different they can no longer interbreed! (Galapagos Animals) 2. Reproductive Isolation = when organisms no longer mate & produce fertile offspring Mating times change to different parts of the year for groups in different areas (Tree frogs) Mutations in chromosomes occur to make breeding difficult (Plants - crops) How Fast is Speciation? 1. Gradualism = species originate through a gradual change in adaptations (10,000+ yrs) Fossils show camels evolved slowly & steadily over time (pg 408) 2. Punctuated Equilibrium = species originate in rapid bursts (10,000 yrs or less) with long periods of equilibrium in between Fossils show that higher temps & competitive species caused rapid changes in isolated populations elephants! EVIDENCE OF EVOLUTION 1. Adaptations - a structure or behavior that helps an organism better survive in its environment (arose from Natural Selection) A. Mimicry B. Camo C. Physiological - antibiotic resistance in bacteria = superbugs EVIDENCE OF EVOLUTION 2. Fossil Record A. Give clues to what ancient organisms looked like B. Compare to organisms today to see relationships C. A link to show change over time EVIDENCE OF EVOLUTION 3. Comparative Anatomy A. Homologous Structures = body structures on diff. organisms that are similar in structure/function evidence of common ancestor B. Vestigial Structures = body structures in an organism that no longer serve a purpose but may have in an ancestor - show what used to be EVIDENCE OF EVOLUTION 4. Embryos = all vertebrates look similar as embryos - suggests all related EVIDENCE OF EVOLUTION 5. DNA Similarities EVIDENCE OF EVOLUTION Examples of Recent Evolution (Change): 1. Natural Selection in Action - Peppered Moths 2. Artificial Selection - Crops, Dogs - People? The End QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture.