* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Study Notes
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
The Selfish Gene wikipedia , lookup
Group selection wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
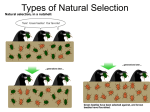
Name: ____________________________________ Distribution Date: 4/10/12 Pd: ___ Summary Notes & Study Guide for Chapter 11 Keep this Copy of notes in your binder!! The Evolution of Populations 11.1 Genetic Variation within Populations Georgia Standards: SB2.c; SB2.d (refer to pg. 328 in the text) Based on the standards listed above, write a 2-4 sentences summary that describes what tasks or concepts you should be able to complete, explain, or perform at the end of this section _________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________ Vocabulary Review (define the vocabulary listed below, you know these words from a previous unit) Genotype: ____________________________________________ Phenotype: ____________________________________________ Allele: _______________________________________________ Where is genetic variation stored in a population? ___________________ An _________ _____________ is a measure of how common a certain allele is in a gene pool. Using figure 11.1 on pg. 329 in your text, practice the steps to calculating allele frequencies: 1. Count the number of times an allele occurs in the gene pool. 2. Then divide that number by total number of ALL ALLELES. 7 G’s in the gene pool; 5 g’s in the gene pool; 12 total alleles What is the allele frequency for recessive alleles? Show the fraction ______ What is the allele frequency for dominant alleles? Show the fraction ______ 1 Consider a population of flowers that may be white or shaded. Look at the figure below for the ALLELE FREQUENCY in the population. ss Ss SS ss ss SS SS Ss What is the total number of alleles shown? _____ What is the allele frequency for recessive alleles? Show the fraction _____ What is the allele frequency for dominant alleles? Show the fraction _____ Use the diagram below to list the two main sources of genetic variation. Include a description of those two sources. Genetic Variation (has two main sources) 2 11.2 Natural Selection in Populations Georgia Standards: SB5.d (refer to pg. 330 in the text) Based on the standards listed above, write a 1-2 sentence(s) summary that describes what tasks or concepts you should be able to complete, explain, or perform at the end of this section _________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________ Vocabulary Review (define the vocabulary listed below, you know these words from a previous unit or another subject area) Mean: _______________________________________________ Natural selection: ______________________________________ Read the section on page 330 with the following heading NATURAL SELECTION ACTS ON DISTRIBUTIONS OF TRAITS In a crowd of 100,000 people, would you expect the mean height to be short, medium, or tall? _____________ In _____________ ________________ natural selection favors individuals with the average phenotype. Use figure 11.2 on page 330 to draw a graph of the BELL SHAPED curve that results from this type of distribution; include the labels. 3 Natural Selection can change the distribution of traits in three ways. What are they? 1. __________________________ 2. __________________________ 3. __________________________ ____________________ Selection (page 331) It favors what type of phenotype? (circle your answer) a. 1 extreme/rare phenotype b. intermediate/average phenotype c. 2 extreme/rare phenotypes Use figure 11.3 on page 331 to draw a graph of the SHIFTING curve that results from this type of distribution; include the labels. What does the dashed line represent? _______________________ What does the solid represent? ____________________________ **You will notice the dashed line and solid line on the graphs in the next examples** Review the example of this type of selection in your textbook. What organism is involved? _______________________________ Describe what happens in this example: _______________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________ 4 ___________________ Selection (page 332) It favors what type of phenotype? (circle your answer) a. intermediate/average phenotype b. 2 extreme/rare phenotypes c. 1 extreme/rare phenotype Use figure 11.5 on page 332 to draw a graph of the SHRINKING curve that results from this type of distribution; include the labels. Review the example of this type of selection in your textbook. What 3 organisms are involved? ______________________________________________________ Describe what happens in this example: _______________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________ What is the effect that this selection has on genetic diversity? _________________________________________________________ 5 ___________________ Selection (page 333) It favors what type of phenotype? (circle your answer) a. 1 extreme/rare phenotype b. 2 extreme/rare phenotypes c. intermediate/average phenotype Use figure 11.6 on page 333 to draw a graph of the WAVE curve that results from this type of distribution; include the labels. Review the example of this type of selection in your textbook. What organism is involved? ___________________________________ What two phenotypes are selected? 1. _______________________________ 2. _______________________________ Describe what happens in this example: _______________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________ What is the intermediate phenotype? ____________________________ What happens to the intermediate phenotype? _________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________ 6