* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Types of Natural Selection
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
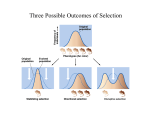
Types of Natural Selection Natural Selection and Genetic Equilibrium • Synthetic Theory of Evolution: Darwin’s ideas about natural selection plus our modern understanding of genetics. • According to the Synthetic Theory of Evolution, natural selection disturbs genetic equilibrium. • As a result, allele frequencies will change. • In this way, natural selection determines which adaptations are beneficial to a species. • There are three main types of natural selection Directional Selection • Directional Selection: An extreme phenotype (very long or very short etc.) is a favorable adaptation. • Ex. Neck length in giraffes, very long necks are favorable. • Selects in the direction of one extreme phenotype Stabilizing Selection • Stabilizing Selection: Average phenotype is a favorable adaptation. Extreme phenotypes are unfavorable. • Operates most of the time in populations • Ex. Mouse size: too big use too much energy to keep warm; too small can’t burrow. Average is just right • Limits evolution by keeping allele frequencies relatively constant Disruptive Selection • Disruptive Selection: Most rare type of natural selection. Two opposite extreme phenotypes are favorable over average phenotype • Ex. Some crabs show a continuous range of color from light tan to dark brown. The light tan provides camouflage in the sand. Dark brown provide camouflage in mud. Colors in between – no camouflage • Over time this could lead to speciation Summary