* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Changes in Traits
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Dual inheritance theory wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Selective breeding wikipedia , lookup
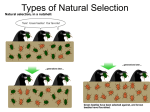
Changes in Traits Background Information CSCOPE – Lesson 06 Unit 02 Natural Selection Also called Natural occurrence. The process by which favorable traits that are heritable become more common in successive generations of a population of reproducing organisms, and unfavorable traits that are heritable become less common. Acts on the phenotype, or the observable characteristics of an organism, such as individuals with favorable phenotypes are more likely to survive and reproduce than those with less favorable phenotypes. If these phenotypes have a genetic basis, then the genotype associated with the favorable phenotype will increase in frequency in the next generation. Over time, this process can result in specialized adaptations for particular ecological niches and may eventually result in the emergence of new species. One example of a favorable phenotype in natural selection is camouflage, also known as cryptic coloration or concealing coloration. Camouflage allows an otherwise visible organism or object to remain indiscernible from the surrounding environment. Camouflage is a form of deception. Selective Breeding Has produced new types of plants and animals. It allows desirable traits to be passed when animals or plants with the desirable trait are allowed to breed. These genes that produce desirable traits are passed to the next generation.