* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 2-16-16 Types of Selection Work
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of sexual reproduction wikipedia , lookup
The Selfish Gene wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary landscape wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
The Descent of Man, and Selection in Relation to Sex wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Inclusive fitness wikipedia , lookup
Theistic evolution wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Sexual selection wikipedia , lookup
Saltation (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
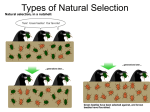
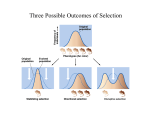
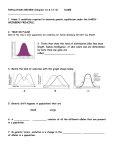
1. Types of Natural Selection Natural Selection is the basis of evolution. Describe the steps that lead to natural selection in an environment. a. b. c. d. e. 2. One of the steps that leads to natural selection (and one that should’ve been listed in your response to #1) is that there is genetic variation. There are 2 major factors that lead to this genetic variation that are listed below. Explain how each ALWAYS results in genetic variation. a. Mutations (Explain how this is the only factor that creates completely new, unique genotypes) b. Sexual reproduction (Explain how each of the following aspects of sexual reproduction lead to variation (although they do not create new alleles). i. Crossing over ii. Segregation of homologous chromosomes iii. Independent assortment of homologous chromosomes iv. Random fertilization 3. In question #2 you explained how genetic variation is created. Now, explain the 5 processes that causes evolution to happen. (Note to remember when answering this question: Evolution is simply a change in allele frequency in a gene pool. Or in other words, evolution is simply 1 genetic variation being favored over another). Hint: The 5 things that can cause evolution to happen will be the OPPOSITE of the 5 rules for Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium. This should make sense because Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium is when a population’s gene pool is not changing while evolution is when a gene pool is changing. a. b. c. d. 4. e. Natural selection can affect a population in many ways. For each of the following types of natural selection, tell what range of phenotype is selected AGAINST? Directional Disruptive Stabilizing 5. For each of the following types of natural selection, tell what range of phenotypes are seen in a population AFTER the selection has occurred? (Hint: For each of these types of selection, you will choose one of the following to indicate what the population’s phenotype looks like AFTER evolution: 1) The majority of the population shows the “normal” phenotype, 2) The majority of the population shows only one of the extreme ends of the phenotypic range, or 3) The majority of the population demonstrates both ends of the phenotypic range but very few show the “normal” phenotype) Directional Disruptive Stabilizing 6. Draw a diagram showing the original population, the new population, and the section of the phenotypic range that was being chosen against for each of the following types of selection. Directional a) b) Disruptive c) Stabilizing For the situations described in questions 7-15 tell whether each of them are directional, disruptive, or stabilizing selection. 7. People that have lived in higher altitudes (i.e. Colorado) have a greater lung capacity than the average U.S. citizen. __________________________________________ 8. The teeth of modern humans are smaller than ancestral humans because our diet has become less coarse (not as tough) over the last few million years. ________________________________ 9. Charles Darwin observed many different species of Finches on the Galapagos Islands. On each of these different islands, Darwin noticed that the Finch species had very different beaks. There were no “average” sized beaks; rather, they were each specialized for the food on their particular island. _____________________________________________ 10. There is a very high incidence of infant mortality for very heavy as well as very light babies. ____ ____________________________ 11. Coho salmon are either very large or very small due to the fact that these respective sizes both pose reproductive benefits. There are very few “normal” sized coho salmon. ______________ _______________________________ 12. In ancient humans, very small men might not be very attractive to women because they can't defend their family as well but large men might have a more difficult time finding enough food. Very large men would tend to be slower and have less endurance. ________________________ 13. Giraffes fight for their mates by swinging their long necks and hitting each other with their heads. This has caused their neck to become longer over time because giraffes with longer necks can swing their necks faster (and thus win the fights for the mate). ________________________ 14. Remember the incidence of peppered moths. White moths had previously been more reproductively successful due to the fact that they blend in with the lichen on the trees. With the recent rise in pollution, the black moths now have more reproductive success because they blend in with trees blackened from pollution. _________________________________________ 15. Dog breeding could be considered disruptive selection because breeders intentionally breed dogs that show extreme phenotypes. Even so, the fact that this form of selection is not natural (it is caused by humans forcing it to happen) means that it is actually what kind of selection? ________________________________________________