* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Function of VHL and
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
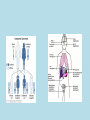
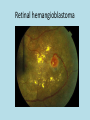
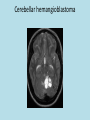
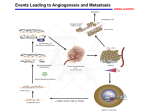
The Function of VHL and pVHL Protein • VHL is a tumor suppressor gene on chromosome 3 • Helps to regulate and destroy the alpha subunit of hypoxia-inducible factor or HIF-1 • HIF-1 is a transcription factor that has a myriad of target genes • Products are involved in angiogenesis, erythropoiesis, energy metabolism, glucose transport Different Results in Different Conditions Normoxia • pVHL helps to degrade the alpha subunit of HIF-1 • HIF-1α unit is created and degraded very rapidly in “futile cycle” • So full HIF-1 transcription factor remains inactive Hypoxia • HIF-1α does not occur, so its levels increase • Can now combine with HIF1β to form full HIF-1 • Target genes are promoted and proteins synthesized • These proteins help cell survive condition • Esp proteins that attract new vessels Results of Activation of HIF-1 • Important in Angiogenic Response • Induces genes encoding: – Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) – Platelet-Derived Growth Factor (PDGF) – Transforming Growth Factor-α (TGF-α) The Disease • • • • 1/36,000 individuals Usually appears in young adulthood Autosomal dominant 20% of the time the altered gene is new mutation uninherited • 2 copies needed for tumor and cyst formation – Caused by knockout of function – Leads to over recruitment of vessels creation of tumors • Prognosis – Untreated can result in blindness or permanent brain damage – With treatment and early detection better off – Usually a 50 year life-span – Death usually occurs due to complications with kidney cancer and pheochromocytoma • Treatment – Surgery to remove tumors, especially before they get big enough to cause serious problems – Focused radiation for cancerous growths Variety of Disease Results • Mainly kidney cancer known as clear-cell Renal Cell Carcinoma or ccRCC – Main cause of disease related death (70%) • Less frequently cancers in – Pancreas – Adernal gland – testes • Hemangioblastomas – In CNS – Usually non-cancerous, but issue with where they develop pressure on spinal cord, eyes, brain Retinal hemangioblastoma Cerebellar hemangioblastoma Model Organisms • Mouse, drosphilia, C. Elegens, and Zebrafish have all been studied • Generally, models have shown that VHL is important in angiogenesis • Double mutants are lethal embryonically References • Davis, S. & Uwaydat, S. (n.d.). Diagnosis and treatment of von hippel– lindau syndrome. Retrieved from http://www.aao.org/publications/eyenet/201005/pearls.cfm • Hsu, Y. (2012). Complex cellular functions of the von hippel–lindau tumor suppressor gene: insights from model organisms. Oncogene, 31, 22472257. • National Library of Medicine. (2011, November 14). Genetics home reference. Retrieved from http://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/condition/von-hippellindau-syndrome • Stanford medicine cancer institute. (2013). Retrieved from http://cancer.stanford.edu/information/geneticsAndCancer/types/vhl.htm l • Weinberg, R. A. (2007). The biology of cancer. New York: Garland Pub. • William G. Kaelin Jr. (2010, october 26). National institute of neurological disorders and stroke. Retrieved from http://www.ninds.nih.gov/disorders/von_hippel_lindau