* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Design of specific peptide Inhibitors of Phospholipase A2
Survey
Document related concepts
X-ray crystallography wikipedia , lookup
Protein domain wikipedia , lookup
Degradomics wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Implicit solvation wikipedia , lookup
Cooperative binding wikipedia , lookup
Protein mass spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Alpha helix wikipedia , lookup
Ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptides wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
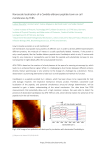
Design of specific peptide Inhibitors of Phospholipase A2: Crystal structure of a complex formed between Russell's viper Phospholipase A2 and a designed Peptide V. Chandra1, J. Jasti1, P. Kaur1, S. Dey1, A. Srinivasan1, Ch. Betzel2 and T. P. Singh1 1Department 2Institute of Biophysics, All India Institute of Medical sciences, New Delhi-110029, India of Medical Biochemistry and Molecularbiology, University Hospital Hamburg Eppendorf, c/o DESY, Build. 22a, Notkestr. 85, 22603 Hamburg Phospholipase A2 (E.C. 3.1.1.4) is a key enzyme of the cascade mechanism involved in the production of proinflammatory compounds known as eicosanoids [1]. Specific inhibitor design is therefore of highest interest [2,3]. The binding of phospholipase A2 to membrane surfaces and hydrolysis of phospholipids are thought to involve the formation of a hydrophobic channel into which a single substrate molecule diffuses before cleavage. In order to regulate the production of proinflammatory compounds, a specific peptide inhibitor of PLA2, Leu-Ala-Ile-Tyr-Ser has been designed. Phospholipase A2 from Daboia russelli pulchella (DPLA2) and peptide Leu-Ala-Ile-Tyr-Ser (LAIYS) have been co-crystallized. Diffraction data were collected at the beam line X13. The structure of the complex has been determined and refined to 2.0 Å resolution. The structure contains two crystallographically independent molecules of DPLA2 with one molecule of peptide specifically bound to one of them, as shown in figure 1. The overall conformations of two molecules are essentially similar except in three regions, namely, the calcium binding loop including Trp31 (residues: 25-34), the b-wing consisting of two antiparallel b-strands (residues: 74-85) and the Cterminal region (residues: 119-133). Out of these, the most striking difference pertains to the orientation of Trp31 in the two molecules. The conformation of Trp31 in molecule A was suitable and allowed the binding of peptide LAIYS while that in molecule B prevented the entry of the ligand into the hydrophobic channel. The structure of the complex clearly showed that the OH group of Tyr of the inhibitor formed hydrogen bonds with both His48 Nd and Asp49 Od1 while OgH of Ser was involved in a hydrogen bond with Trp31. Other peptide backbone atoms interact with protein through water molecules while Leu, Ala and Ile form strong hydrophobic interactions with the residues of the hydrophobic channel. Figure 1 showing the specific peptide bound to the active site region References [1] Silhammer, J.J., Pruzanski, W., Vadas. P., Plant, S., Miller, J.A., Kloss, J. and Johnson, L.K., J. Biol. Chem. 264, 5335-5341 (1989) [2] Chandra, V., Jasti, J., Kaur, P., Betzel, Ch., Srinivasan, A. and Singh, T. P. J. Mol. Biol. 320, 215222 (2002) [3] Chandra V., Jasti J., Kaur P., Srinivasan, A., Betzel, Ch. and T. P. Singh, Biochemistry 41, 1091410919 (2002)