* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CHEMISTRY – UNITS 3 and 4 REVIEW PACKET Name Date
Photoelectric effect wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Degenerate matter wikipedia , lookup
Chemical bond wikipedia , lookup
Mössbauer spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Molecular Hamiltonian wikipedia , lookup
Marcus theory wikipedia , lookup
X-ray fluorescence wikipedia , lookup
Auger electron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Electron scattering wikipedia , lookup
Heat transfer physics wikipedia , lookup
Isotopic labeling wikipedia , lookup
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Atomic orbital wikipedia , lookup
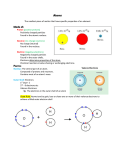
CHEMISTRY – UNITS 3 and 4 REVIEW PACKET Name _______________________________________________________ Date ________________________________ ATOMIC STRUCTURE Draw a picture of each model of an atom. Write the main/key point of each atom. Name of model Rutherford’s Gold Foil (hard sphere model) Picture of model Key point of the model Bohr model – Electron shell diagrams Wavemechanical model Label the following parts of the picture: proton, neutron, electron, nucleus, orbital, valence electron. What is the total mass of the nucleus of the atom? ____________________________________ What is the total mass of the atom (including electrons)? ____________________________ Complete the table Subatomic Particle Mass Charge Location in atom Use the two pictures to answer the questions. 1) How many protons does each atom have? Atom 1: ___________ Atom 2: _____________ 2) What kind of element is each atom? Atom 1: _______________ Atom 2: _______________ 3) How many neutrons does each atom have? Atom 1: ___________ Atom 2: ____________ 4) What is the word that describes two atoms that have the same # of protons but different numbers of neutrons? _____________________________ 5) Are these pictures an example of isotopes? ____________________________ VALENCE ELECTRONS / ELECTRON SHELL DIAGRAMS / LEWIS DOT DIAGRAMS What is a valence electron? ______________________________________________________________ How can you figure out the number of valence electrons in an atom (using the Periodic Table?) __________________________________________________________________________ What is an electron configuration? _________________________________________________________ Write the electron configuration for each element. Write the number of valence electrons for that element. C: _________________________________________; Valence electrons: ______________________________ Al: ________________________________________; Valence electrons: ______________________________ Li: _________________________________________; Valence electrons: _____________________________ Fe: _________________________________________; Valence electrons: ____________________________ *Atoms that are chemically similar have the same number of __________________________. Lewis electron dot diagram: shows the _______________________________ ONLY around the element symbol. Draw the Lewis dot diagrams for C, Al, Li, and Fe below. CALCULATING AVERAGE ATOMIC MASS Formula: Use the information given to calculate the average atomic mass. 1. 80% 127I, 17% 126I, 3% 128I 2. 15% Fe-55, 85% Fe-56 3. 95%14N, 3%15N, 2%16N 4. Element X has two isotopes. If 72.0% of the element has an isotopic mass of 84.9 amu and 28.0% has an isotopic mass of 87.0 amu, the average atomic mass of element X is numerically equal to (1) (2.0 + 98.9)(28.0 + 87.0) (2) (72.0-84.9)(28.0-87.0) (3) (0.720)(84.9)+(0.280)(87.0) (4) (72.0)(84.9)+(28.0)(87.0) 5. The average isotopic mass of chlorine is 35.5 amu. Which mixture of isotopes (shown as percents) produces this mass? (1) 50% C-12 and 50% C-13) (2) 50% Cl-35 and 50% Cl-37) (3) 75% Cl-35 and 25% Cl-37) (4) 75% C-12 and 25% C-13) 6. Carbon exists as three isotopes: C-12, C-13, and C-14. Carbon has an average atomic mass of 12.0107 amu. This indicates that (1) any sample of carbon consists of an equal amount of each type of isotopes. (2) any sample of carbon consists of mostly the C-13 isotope. (3) any sample of carbon consists of mostly the C-12 isotope. (4) all carbon atoms have a mass of 12.0107 amu. (5) all carbon atoms have a mass of 12.0107 amu. On the picture below, label the orbital with the highest energy and the orbital with the lowest energy. Highest energy: ______________________ Lowest energy: ______________________ 1. If an electron gets “excited” , does it move to a higher or lower energy level? ______________________________________ 2. Is that electron absorbing or emitting energy? ________________________________________ 3. When an excited electron falls back to a lower energy, is it absorbing or emitting energy? _______________________________ NUCLEAR CHEMISTRY – TRANSMUTATION WHAT IS THE MOST IMPORTANT TOOL TO USE WHEN SOLVING NUCLEAR CHEMISTRY PROBLEMS??? _________________________________________________________ What are the 2 types of transmutation reactions? 1.) _____________________________________________________ 2.) _____________________________________________________ How can you tell the difference between the two? ____________________________________ Why does natural transmutation occur? What determines if a nucleus is stable? Using Tables N and O, write the nuclear decay equations for: 14C 53Fe 238U Use the graph below to answer the question. Explain why C-12 is a stable nuclide. a) Based on this graph, what particle is emitted during the nuclear decay of a Po-218 atom? b) Explain why the U-238 disintegration series ends with the nuclide Pb-206. Complete the following artificial transmutation reactions: 27Al 42K + 42He 10n + X + 0-1e 00 + 210n + X NUCLEAR CHEMISTRY – FISSION, FUSION, PRACTICAL APPLICATION Fission: Takes ____ ________________ nucleus and splits into ________ _______________ nuclei. Fusion: Takes ____ ________________ nuclei and joins to form _______ ______________ nucleus. Circle the correct answer: A fission or fusion reaction is started by bombarding (hitting) a nucleus or nuclei with (a high energy particle / a slow moving neutron). Do these reactions produce a little energy or high energy? ________________________ What is the energy form that they produce? ________________________________________ Draw a picture of a fission reaction: Draw a picture of a fusion reaction: Practical Uses of Radioisotopes (Why do we care??) Carbon-14 Iodine-131 Techmetium-99 Cobalt-60 Carbon-14 Uranium-238 CALCULATING NUCLEAR DECAY / HALF-LIFE Fraction remaining: what’s leftover compared to what we started with. Formula: __________________________________ What is n? ___________________________________________________________________________________ How can you figure out n? Fraction remaining = ________________________ ½ = 1/2n n = ¼ = 1/2n n = 1/8 = 1/2n n = 1/16 = 1/2n n = 1/32 = 1/2n n = Formula for calculating half-life and/or total time elapsed: Solve each problem based on the information given in the problem. If a scientist purifies 1.0 gram of radium-226, how many years must pass before only 0.50 gram of the original radium-226 sample remain unchanged? Which fraction of an original 20.00-gram sample of nitrogen-16 remains unchanged after 36.0 seconds? (1) 1/5 (2) 1/8 (3) 1/16 (4) 1/32 PRACTICE PROBLEMS! 1. Which equation represents a transmutation reaction? 7. 2. Which is an electron configuration for an atom of phosphorous in the excited state? (1) (2) (3) (4) 2-8-5 2-8-8 2-8-4-1 2-8-7-1 3. What is the total number of valence electrons in an atom of oxygen in the ground state? (1) (2) (3) (4) 8. Given the nuclear equation: 2 4 6 7 4. The amount of energy released from a fission reaction is much greater than the energy released from a chemical reaction because in a fission reaction (1) mass is converted into energy (2) energy is converted into mass (3) ionic bonds are broken (4) covalent bonds are broken 5. How many days are required for 200. grams of radon-222 to decay to 50.0 grams? (1) 1.91 days (2) 3.82 days (3) 7.64 days (4) 11.5 days 6. Which nuclear emission has the weakest penetrating power? (1) alpha particle (2) beta particle (3) gamma radiation (4) positron 9. Which type of reaction converts one element to another element? (1) (2) (3) (4) neutralization polymerization substitution transmutation 10. Which equation is an example of artificial transmutation? 11. Two atoms will always have the same atomic number if they have the same 1. mass number 2. number of protons 3. number of neutrons 4. number of nucleons 12. Which particles account for most of the mass of the atom? 1. protons and neutrons 2. protons and electrons 3. neutrons and electrons 4. neutrons and positrons