* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PANCREATIC HORMONES
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
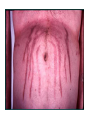
DISORDERS OF THE ADRENOCORTICAL HORMONES Dr. Ayisha Qureshi MBBS, Mphil Hypoadrenalism- ADDISON’S DISEASE ADDISON’S DISEASE DEFINITION: Addison’s disease results from the inability of the adrenal cortices to produce the adrenal hormones & this is most frequently caused by the primary atrophy of adrenal cortex. CAUSES: 1.Autoimmune disorder 2.Tuberculous destruction of the glands 3.Cancer 4.Secondary to impaired pituitary gland function leading to insufficient ACTH production. Signs & Symptoms Mineralocorticoid deficiency Glucocorticoid deficiency • Greatly decreased renal sodium reabsorption • Increased loss of Na, Cl & water in the urine • Decreased ECF/ hypovolemia • Hyponatremia • Hyperkalemia • Mild Acidosis • Increased RBC conc. Due to decreased ECF • Decreased CO • Shock • Death • Patient cannot maintain normal blood glucose levels as no gluconeogenesis b/w meals • Nausea, vomiting, fever, hypotension • All metabolisms effected • Patient highly susceptible to the deteriorating effects of stress. • Even mild infections can lead to death Signs & Symptoms • Extreme melanin pigmentation of the mucous membranes & skin. • Usually deposited in blotches • Cause is increased ACTH secretion as well as increased MSH secretion WHAT IS POMC & MSH? Proopiomelanocortin (POMC) is a preprohormone which when cleaved causes the formation of: • MSH (melanocyte stimulating hormone) which causes darkening of the skin by stimulating formation of melanin & dispersing it to the epidermis • Beta Lipoprotein • Beta endorphin & few others (ACTH also has 1/30 as much activity of MSH & so its hypersecretion also causes Hyperpigmentation of the skin.) TREATMENT • A person with complete destruction of the adrenal may die within a few days to 2 weeks b/c of weakness & circulatory shock. • However, if small quantities of mineralo & glucocorticoids are administered daily, they can live for years. Hyperadrenalism- Cushing’s Syndrome DEFINITION: Hypersecretion by the adrenal cortex causes a complex cascade of hormone effects called Cushing’s syndrome. CAUSES: • Exogenous - Factitious - Iatrogenic • ACTH-Dependant - Pituitary adenoma - Ectopic ACTH syndrome • ACTH-Independant - Adrenal adenoma - Adrenal carcinoma When Cushing’s syndrome is secondary to excess secretion of ACTH by the anterior pituitary, it is called CUSHING’S DISEASE. Signs & Symptoms • Truncal Obesity • Supraclavicular & dorsal fat pad • Buffalo hump • Moon Facies • Purple striae due to decreased collagen proteins • Thin skin • Capillary fragility & easy bruising • Hirsuitism • Diabetes Mellitus also called Adrenal Diabetes • Thin extremities and severe muscle weakness due to increased protein catabolism • Infections due to suppressed immune system with impaired wound healing • Osteoporosis • Hypertension Diagnosis & Treatment DIAGNOSIS: • Very challenging • Diagnose excess Cortisol (24 hour urine cortisol & midnight salivary cortisol level) • Dexamethasone suppression test TREATMENT: • Removal of the cause: Surgery of the adrenal tumour OR pituitary tumour • Drugs that block steroidogenesis.e.g. Ketaconazole • Drugs that inhibit ACTH secretion.e.g. Serotonin antagonists • Partial or total adrenalectomy PRIMARY ALDOSTERONISM (CONN’S SYNDROME) DEFINITION: Occasionally, a small tumor of the zona glomerulosa cells occurs & secretes large amounts of aldosterone; the resulting condition is called “Primary aldosteronism” or “ Conn’s disease”. CAUSES: • Small tumour of Zona Glomerulosa cells that secretes large amounts of Aldosterone. • Sometimes even hyperplastic adrenal cortices secrete aldosterone instead of cortisol. Signs & Symptoms • Severe hypokalemia causing muscle paralysis • Increased blood and ECF volume • Slight increase in Na conc. • Hypertension Usually, diagnosed by decreased plasma renin and increased aldosterone concentration. ADRENOGENITAL SYNDROME A syndrome that is caused by occasional adrenocortical tumour that secretes excessive quantities of androgens. Signs & Symptoms • - In Females: Virile characteristics Growth of a beard Deeper voice Occasionally baldness Masculine distribution of hair on the body Deposition of proteins in a masculine manner • In Males: - In prepubertal male, a virilizing adrenal tumour causes same characteristics as in the female plus rapid development of the male sex organs - In adult male, the virilising characteristics are often masked by the virilising effects of Testosterone - Diagnosis is made by the presence of excess 17-ketosteroids in the urine.