* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Adrenal Disease
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
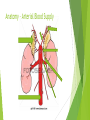
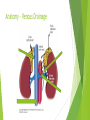
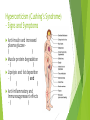
Adrenal Disease Alex Edwards [email protected] DAPSICAMP Definition Aetiology Pathophysiology Signs and Symptoms Investigations Complications Alternative Diagnosis Management Prognosis Anatomy – Arterial Blood Supply Anatomy – Venous Drainage Blood Supply - Summary Arterial Supply (same on both sides) Superior Middle Suprarenal Artery Inferior Suprarenal Artery Suprarenal Artery Venous Drainage LEFT Suprarenal Vein – into RIGHT Suprarenal Vein – into Adrenal Structure Cortex – Medulla – The Medulla Contains Chromaffin cells Secrete Secrete Secretion in response to stimulation by ( ) nerve fibres from thoracic segments ( ) fibres release ACh that binds to Nicotinic type 1 receptors on adrenal medulla NA/A secreted into circulation The Medulla - effects of cathecholamines Sympathetic Fight or Flight response Cause of excess catecholamines: Tachycardia,( ( ), tremor, sweating ) NA/A cause an increase in lipolysis, gluconeogenesis and glycogenolysis The Cortex – GFR! Zona G ( ) ( ) Zona F ( ) ( ) Zona R ( ) ( ) The Key Step ( ) Progesterone Mineralocorticoids (ALDOSTERONE) Glucocorticoids (CORTISOL) Zona Glomerulosa Zona Fasciculata Aldosterone - released by ZG in response to ( Angiotensinogen Angiotensin I Angiotensin II Vasoconstriction ALDOSTERONE ) Aldosterone - effects Increases renal ( ) in the late DCT Increases renal ( early collecting ducts Increases pressure ) in the blood volume and blood Hyperaldosteronism - aetiology Hyperaldosteronism - pathophysiology Aldosterone acts on principle cells in the late DCT/early collecting ducts causing: Expression of Na+ and K+ channels in luminal membrane Activity of Na+/K+ pump on basolateral membrane Therefore signs and symptoms include: INTERSTITIUM ALDOSTERONE Hyperaldosteronism - investigations Blood tests ECG – arrhythmias from electrolyte imbalance CT/MRI Special tests Lying Salt and standing aldosterone/renin levels loading and aldosterone/renin levels Cortisol - released by ZF in response to ( HPA axis: Hypothalamus Anterior Pituitary Gland -Corticotrophs Adrenal Cortex (Zona Fasciculata) CORTISOL ) Cortisol - effects Cortisol is a ( Anti-insulin ) stress hormone – increases plasma glucose Increases muscle protein degradation Increases lipolysis and fat deposition Anti-inflammatory Immunosuppressant Hypercorticism (Cushing’s Syndrome) - aetiology ACTH dependent (80-85%) Secondary Secondary S C M ACTH independent Primary Primary Iatrogenic C Hypercorticism (Cushing’s Syndrome) - Signs and Symptoms Anti-insulin and increased plasma glucose ( ) Muscle protein degradation –( ) Lipolysis and fat deposition –( ) and ( ) Anti-inflammatory and Immunosuppressant effects –( ) Hypercorticism (Cushing’s Syndrome) - investigations U&Es 24 hour urinary free cortisol (3 collections) Dexamethasone suppression test Dexamethasone supressed corticotropin releasing hormone (CRH) test Adrenal Insufficiency ADDISON’S DISEASE Adrenal cortex destruction Rare 90% autoimmune Aldosterone deficiency ( ( ) ) and ( ) Cortisol deficiency ( ( ) ) Caused by increased ACTH from negative feedback ACTH precursor causes pigmentation Adrenal insufficiency - investigations U&Es Blood cortisol levels ACTH stimulation (Synacthen) test Fails to produce cortisol in adrenal failure Managed by synthetic hormonal replacement Summary Any Questions? [email protected]