* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Adrenal Disease
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
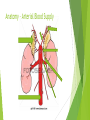
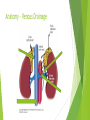
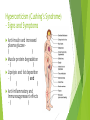
Adrenal Disease Alex Edwards [email protected] DAPSICAMP Definition Aetiology Pathophysiology Signs and Symptoms Investigations Complications Alternative Diagnosis Management Prognosis Anatomy – Arterial Blood Supply Anatomy – Venous Drainage Blood Supply - Summary Arterial Supply (same on both sides) Superior Middle Suprarenal Artery Inferior Suprarenal Artery Suprarenal Artery Venous Drainage LEFT Suprarenal Vein – into RIGHT Suprarenal Vein – into Adrenal Structure Cortex – Medulla – The Medulla Contains Chromaffin cells Secrete Secrete Secretion in response to stimulation by ( ) nerve fibres from thoracic segments ( ) fibres release ACh that binds to Nicotinic type 1 receptors on adrenal medulla NA/A secreted into circulation The Medulla - effects of cathecholamines Sympathetic Fight or Flight response Cause of excess catecholamines: Tachycardia,( ( ), tremor, sweating ) NA/A cause an increase in lipolysis, gluconeogenesis and glycogenolysis The Cortex – GFR! Zona G ( ) ( ) Zona F ( ) ( ) Zona R ( ) ( ) The Key Step ( ) Progesterone Mineralocorticoids (ALDOSTERONE) Glucocorticoids (CORTISOL) Zona Glomerulosa Zona Fasciculata Aldosterone - released by ZG in response to ( Angiotensinogen Angiotensin I Angiotensin II Vasoconstriction ALDOSTERONE ) Aldosterone - effects Increases renal ( ) in the late DCT Increases renal ( early collecting ducts Increases pressure ) in the blood volume and blood Hyperaldosteronism - aetiology Hyperaldosteronism - pathophysiology Aldosterone acts on principle cells in the late DCT/early collecting ducts causing: Expression of Na+ and K+ channels in luminal membrane Activity of Na+/K+ pump on basolateral membrane Therefore signs and symptoms include: INTERSTITIUM ALDOSTERONE Hyperaldosteronism - investigations Blood tests ECG – arrhythmias from electrolyte imbalance CT/MRI Special tests Lying Salt and standing aldosterone/renin levels loading and aldosterone/renin levels Cortisol - released by ZF in response to ( HPA axis: Hypothalamus Anterior Pituitary Gland -Corticotrophs Adrenal Cortex (Zona Fasciculata) CORTISOL ) Cortisol - effects Cortisol is a ( Anti-insulin ) stress hormone – increases plasma glucose Increases muscle protein degradation Increases lipolysis and fat deposition Anti-inflammatory Immunosuppressant Hypercorticism (Cushing’s Syndrome) - aetiology ACTH dependent (80-85%) Secondary Secondary S C M ACTH independent Primary Primary Iatrogenic C Hypercorticism (Cushing’s Syndrome) - Signs and Symptoms Anti-insulin and increased plasma glucose ( ) Muscle protein degradation –( ) Lipolysis and fat deposition –( ) and ( ) Anti-inflammatory and Immunosuppressant effects –( ) Hypercorticism (Cushing’s Syndrome) - investigations U&Es 24 hour urinary free cortisol (3 collections) Dexamethasone suppression test Dexamethasone supressed corticotropin releasing hormone (CRH) test Adrenal Insufficiency ADDISON’S DISEASE Adrenal cortex destruction Rare 90% autoimmune Aldosterone deficiency ( ( ) ) and ( ) Cortisol deficiency ( ( ) ) Caused by increased ACTH from negative feedback ACTH precursor causes pigmentation Adrenal insufficiency - investigations U&Es Blood cortisol levels ACTH stimulation (Synacthen) test Fails to produce cortisol in adrenal failure Managed by synthetic hormonal replacement Summary Any Questions? [email protected]