* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What is the Higgs Boson?
Quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
Double-slit experiment wikipedia , lookup
Peter Kalmus wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization group wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear structure wikipedia , lookup
Theory of everything wikipedia , lookup
An Exceptionally Simple Theory of Everything wikipedia , lookup
Electron scattering wikipedia , lookup
Strangeness production wikipedia , lookup
History of quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization wikipedia , lookup
Identical particles wikipedia , lookup
Quantum chromodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Boson sampling wikipedia , lookup
Weakly-interacting massive particles wikipedia , lookup
ALICE experiment wikipedia , lookup
Scalar field theory wikipedia , lookup
Supersymmetry wikipedia , lookup
Large Hadron Collider wikipedia , lookup
Compact Muon Solenoid wikipedia , lookup
ATLAS experiment wikipedia , lookup
Technicolor (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Grand Unified Theory wikipedia , lookup
Mathematical formulation of the Standard Model wikipedia , lookup
Future Circular Collider wikipedia , lookup
Higgs boson wikipedia , lookup
Elementary particle wikipedia , lookup
Minimal Supersymmetric Standard Model wikipedia , lookup
Higgs mechanism wikipedia , lookup
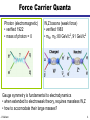
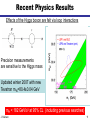
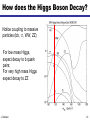
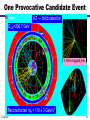
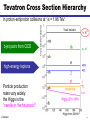
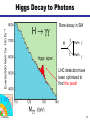
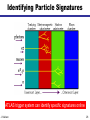
What is the Higgs Boson? And how do we search for it? Jason Nielsen SCIPP / UC Santa Cruz June 25, 2007 J. Nielsen VERTEX 2004 1 Challenge of Particle Physics • Unification of the basic forces and the origin of mass for the fundamental particles • Unexpected new physics or extra dimensions not included in Standard Model • Unknown new physics (forces or particles) hinted at by cosmology Particle collisions at the energy frontier enable us to pursue these and other questions about nature J. Nielsen 2 Fundamental Particles & Forces J. Nielsen 3 Force Carrier Quanta Photon (electromagnetic) • verified 1922 • mass of photon = 0 W,Z bosons (weak force) • verified 1983 • mW, mZ: 80 GeV/c2, 91 GeV/c2 Gauge symmetry is fundamental to electrodynamics • when extended to electroweak theory, requires massless W,Z • how to accomodate their large masses? J. Nielsen 4 Higgs Mechanism in Field Theory Electroweak “Standard Model” relies on broken symmetry Additional fields with constructed potential • just like gravitational field, electric field QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. Introduction of a pervasive Higgs field • Rotationally symmetric potential • But the stable minimum breaks the symmetry! J. Nielsen 5 Spontaneous Symmetry Breaking Came to particle physics from condensed matter physics above Tc below Tc Pencil on point Heisenberg ferromagnet Theory has rotational invariance; ground state is not invariant Symmetry has been broken by external factor J. Nielsen 6 Higgs Mechanism in Field Theory Spontaneous symmetry breaking • Lost degree of freedom -> Goldstone bosons Goldstone bosons give mass to W±,Z • One physical scalar boson: Higgs boson whose mass is unknown Discovery of the Higgs boson would help verify this approach Otherwise, much head-scratching and new theories! J. Nielsen 7 Why is the Top Quark So Massive? 180 mass (GeV/c2) 160 140 mt=175 GeV/c2 120 Interaction with Higgs quantum defines mass of fermions 100 80 60 40 20 0 u d s c b t Schwinger (1957): a coupling produces effective mass terms through the action of the vacuum fluctuations (Higgs boson) Top quark most affected by this “Higgs field molasses” Note: Higgs couplings explain fundamental fermion mass but not everyday mass! J. Nielsen 8 So What IS the Higgs boson? Higgs boson is a physical condensate of the pervasive postulated Higgs field Similar to photon, except Higgs boson is not a force carrier What kinds of particles do it couple to? • Its couplings are proportional to the fermion masses • So it couples most strongly to the most massive particles This makes it clear how to search for it, if it exists… J. Nielsen 9 Wringing Out the Higgs Condensate Physical Higgs bosons can be produced, given enough energy e+ H Z* QuickTime™ and a TIFF (LZW) decompressor are needed to see this picture. (Here ECM > mH + mZ) Z eThat’s where the collider comes in But Higgs boson is fleeting: decays immediately to characteristic “final state” b b H Z q q That’s where the detector comes in J. Nielsen 10 Recent Physics Results Effects of the Higgs boson are felt via loop interactions Precision measurements are sensitive to the Higgs mass Updated winter 2007 with new Tevatron mW=80.4±0.04 GeV mH < 182 GeV/c2 at 95% CL (including previous searches) J. Nielsen 11 How does the Higgs Boson Decay? Notice coupling to massive particles (bb, tt, WW, ZZ) For low mass Higgs, expect decay to b quark pairs; For very high mass Higgs expect decay to ZZ J. Nielsen 12 Rare Higgs Decays (?) (Claus Grupen) J. Nielsen 13 Identifying b Quarks from Higgs B hadrons have lifetimes of 1.5 ps: find the decay vertex! proton-antiproton Interaction point B hadron Fit tracks together to form secondary vertex • measure flight distance of B hadron • typical flight distance is 0.5 cm from interaction point • close, precise measurement provided by silicon is crucial J. Nielsen 14 One Provocative Candidate Event HZ bbbb selection ECM=206.7 GeV 3 NN b-tagged jets Reconstructed mH = 110 ± 3 GeV/c2 J. Nielsen 15 Bumps in the Mass Spectrum Decay products of the Higgs boson form a mass resonance - similar to resonances from past discoveries of new particles QuickTime™ and a TIFF (LZW) decompressor are needed to see this picture. Strategy for identifying Higgs boson production: 1. Excess of events in Wbb signature (or other signature) 2. Higgs decay products form a invariant mass peak J. Nielsen 16 Tevatron Cross Section Hierarchy In proton-antiproton collisions at s = 1.96 TeV: b-jet pairs from QCD high-energy leptons 1 Particle production rates vary widely: the Higgs is the “needle in the haystack!” J. Nielsen 0.05 17 What kind of unit is a “barn?” Manhattan Project physicists gave the name to the typical nuclear cross-section defined as 10-24 cm2 Practically “as big as a barn” where (sub)-nuclear processes are concerned Photo: Reidar Hahn, Fermilab the term “barn” wasn't officially declassified until 1948 Apparently there was also a unit called the “shed”: 10- 48 cm2 This summer CDF will have collected 3 giga-sheds of data! J. Nielsen 18 bb Dijet Invariant Mass Distribution J. Nielsen 19 Large Hadron Collider at CERN Next generation collider: startup scheduled for 2008 Italy p 14 TeV Luminosity target: 1034cm-2 s-1 p Increased production of heavy particles like Higgs, top quark CMS ATLAS More particles at higher energy requires new detector design and technology J. Nielsen 20 Higgs Decay to Photons Rare decay in SM H t g t g LHC detectors have been optimized to find this peak! J. Nielsen 21 Higgs Decay to ZZ Requires precise measurement of muon curvature J. Nielsen 22 ATLAS Experiment at LHC J. Nielsen 23 ATLAS Experiment at LHC ATLAS collaborator J. Nielsen 24 ATLAS DETECTOR Nov. 2005 J. Nielsen 25 Installation of inner detector end-cap J. Nielsen 26 Prospects for SM Higgs at LHC Should discover SM Higgs regardless of mass value Low-mass Higgs channels: • Hgg ! (sm =1.5 GeV/c2) • W,Z boson fusion to Higgs: then HWW or Htt • ttH: top quark again! High-mass Higgs channels: • golden mode 4e/ opens >2mZ J. Nielsen 27 Identifying Particle Signatures ATLAS trigger system can identify specific signatures online J. Nielsen 28 “Hunt for Higgs” WWW Site One of the best I’ve seen at describing what really happens http://www.sciencemuseum.org.uk/antenna/bigbang/huntforhiggs/index.asp Let’s have a look together at the “Hunt for Higgs” J. Nielsen 29 Future of the Higgs Search • Tevatron experiments still searching • LHC turns on in 2008 – Commissioning and calibrating detectors • Understand non-Higgs backgrounds • Find the Higgs boson peak above the bkgd! • My guess is that it will take a few years to collect enough events to convince ourselves J. Nielsen 30 J. Nielsen 31