* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download T cell - Academic Resources at Missouri Western
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
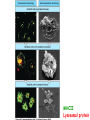
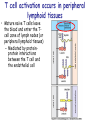
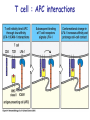
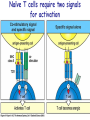
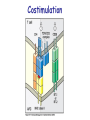
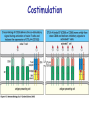
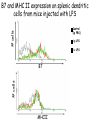
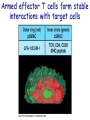
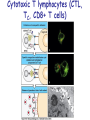
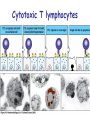
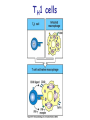
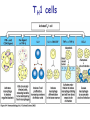
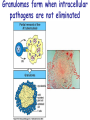
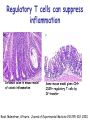
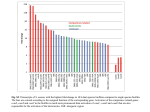
T cell-mediated immunity Chapter 8 Objectives • Describe the protein-protein interactions necessary for naïve T cell activation to occur • Illustrate or describe the changes that occur in a dendritic cell upon activation • Explain the basic mechanisms through which cytotoxic T cells, TH1 cells, and TH2 cells function • Briefly describe the functions of regulatory T cells • Predict appropriate target molecules for suppression of T cell function T cell-mediated immunity Mature naïve T cell (non self-reactive, MHC-restricted) Activation (stimulated by binding to specific antigen presented by APC) Clonal expansion and differentiation into armed effector T cells (CTL, TH1, TH2) Antigen presentation is required for T cell activation • “Professional” APCs are highly effective at activating mature naïve T cells > > Dendritic cell Macrophage B cell Professional APCs MHCII Lysosomal protein T cells that become activated remain in the lymph node T cell activation occurs in peripheral lymphoid tissues • Mature naïve T cells leave the blood and enter the Tcell zone of lymph nodes (or peripheral lymphoid tissues) – Mediated by proteinprotein interactions between the T cell and the endothelial cell T cell : APC interactions Naïve T cells require two signals for activation Costimulation Costimulation Costimulation • CTLA4 is expressed on T cells after they become activated • Signaling through CTLA4 sends an “off signal” to the T cell • CTLA4 knockout mice have been created • What would you expect the phenotype of these mice to be? Costimulation requirement helps prevent autoimmune responses Activated APCs express costimulatory molecules • Pathogens activate APCs by inducing high expression of costimulatory molecules – TLR signaling B7 and MHC II expression on splenic dendritic cells from mice injected with LPS # cells Control (ip PBS) ip LPS iv LPS # cells B7 MHCII Adjuvants induce costimulatory molecule expression on APCs Cellular events triggered by activation • Expression of highaffinity IL-2 receptor (CD25) • Secretion of IL-2 • Proliferation (clonal expansion) • Change in CAMs ( Lselectin) • Differentiation into armed effector T cells – No costimulation required Armed effector T cells Armed effector T cells form stable interactions with target cells Effector molecules produced by T cell subsets Cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL, TC, CD8+ T cells) Cytotoxic T lymphocytes Cytotoxic T lymphocytes •Cytotoxic T lymphocytes express cytotoxins: –Perforin forms pores in target cell membranes –Granzymes are proteases that cleave caspase-3 •Also express Fas ligand, IFN-, TNF Cytotoxic T lymphocytes •Effects of CTLs are highly specific TH1 cells TH1 cells Granulomas form when intracellular pathogens are not eliminated What determines whether helper T cells become TH1 or TH2 cells? • Cytokines expressed by APCs and phagocytes determines differentiation fate of helper T cells • TH1 cells suppress differentiation of TH2 cells, and vice versa Regulatory T cells • Regulatory T cells suppress the activity of other classes of T cells – Evidence for multiple subsets of regulatory T cells • CD4+/CD25+ T cells • TR1 • TH3 • Regulatory CD8+ cells – Some secrete IL-10 and/or TGF- – Some require contact with other T cells to have effects – Antigen-specific or “bystander” suppression Regulatory T cells can suppress inflammation Inflamed colon in mouse model of colonic inflammation Same mouse model given CD4+ CD25+ regulatory T cells by IV transfer Read, Malmstrom, & Powrie. Journal of Experimental Medicine 192:295-302, 2000. Discussion questions • What effect on T cell-mediated immunity would each have? – A blocking antibody to IL-2 or to the highaffinity IL-2 receptor – A blocking antibody to TNF- – Soluble CTLA-4 (mimics CTLA-4 activity) – A blocking antibody to IFN- – Collecting naïve T cells from a patient, stimulating them to become antigen-specific CTL against a tumor antigen, and injecting back into the patient