* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Protein domain wikipedia , lookup
Protein (nutrient) wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Homology modeling wikipedia , lookup
Protein folding wikipedia , lookup
Circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
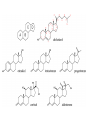
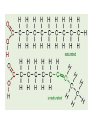
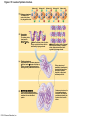
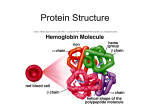
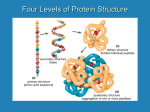
Figure 2.19 Levels of protein structure. Amino acid Amino acid Amino acid Amino acid Amino acid Primary structure: The sequence of amino acids forms the polypeptide chain. Secondary structure: The primary chain forms spirals ( -helices) and sheets (-sheets). -Helix:The primary chain is coiled to form a spiral structure, which is stabilized by hydrogen bonds. Tertiary structure: Superimposed on secondary structure. -Helices and/or -sheets are folded up to form a compact globular molecule held together by intramolecular bonds. Quaternary structure: Two or more polypeptide chains, each with its own tertiary structure, combine to form a functional protein. © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. -Sheet:The primary chain “zig-zags” back and forth forming a “pleated” sheet. Adjacent strands are held together by hydrogen bonds. Tertiary structure of prealbumin (transthyretin), a protein that transports the thyroid hormone thyroxine in blood and cerebrospinal fluid. Quaternary structure of a functional prealbumin molecule. Two identical prealbumin subunits join head to tail to form the dimer.