* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download No Slide Title - WWF
Global warming controversy wikipedia , lookup
Climate change denial wikipedia , lookup
Climate engineering wikipedia , lookup
Citizens' Climate Lobby wikipedia , lookup
Climate governance wikipedia , lookup
Climatic Research Unit documents wikipedia , lookup
General circulation model wikipedia , lookup
Climate change adaptation wikipedia , lookup
Climate sensitivity wikipedia , lookup
Politics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Global warming hiatus wikipedia , lookup
Global warming wikipedia , lookup
Economics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in Saskatchewan wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
Media coverage of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Solar radiation management wikipedia , lookup
Climate change feedback wikipedia , lookup
Attribution of recent climate change wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on human health wikipedia , lookup
Instrumental temperature record wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Scientific opinion on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Public opinion on global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Physical impacts of climate change wikipedia , lookup
Surveys of scientists' views on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and poverty wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in Tuvalu wikipedia , lookup
Climate change, industry and society wikipedia , lookup
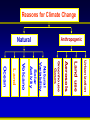
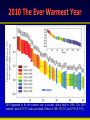
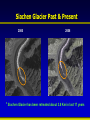
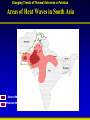
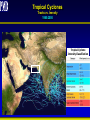
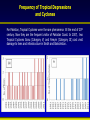
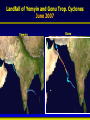
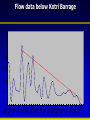
Synthesis Report 28th February 2013 Climate Data Modeling and Analysis of the Indus Ecoregion by Dr. Ghulam Rasul Chief Meteorologist Pakistan Meteorological Department [email protected] Reasons for Climate Change Anthropogenic Natural Urbanization Land use Aerosols Greenhouse Gases Natural Variability Solar Activity Volcano Land Ocean Climate System • Atmosphere: Troposphere, Stratosphere, Mesosphere, Thermosphere and Ionosphere • Hydrosphere: The oceans, rivers & inland water masses • Cryosphere: The snow, ice & permafrost • Biosphere: Vegetation, animals and human beings • Lithosphere: Soil, the deeper layer below soil, sea bed Global Warming Potential Global warming potential (GWP) is a measure of how much a given mass of greenhouse gas contributes to global warming. It is a relative scale which compares that gas to the same mass of carbon dioxide. The GWP depends on the following factors: • the absorption of infrared radiation by a given species • the spectral location of its absorbing wavelengths • the atmospheric lifetime of the species GWP values and lifetimes from 2007 IPCC AR4 Lifetime (years) GWP time horizon 20 years 100 years 500 years 12 72 25 7.6 Nitrous oxide 114 310 298 153 HFC-23 (hydrofluorocarbon) 270 12000 14800 12200 14 3830 1430 435 3200 16300 22800 32600 Methane HFC-134a (hydrofluorocarbon) Sulfur hexafluoride 2010 The Ever Warmest Year (WMO 2012) 2010 happened to be the warmest year in records dating back to 1880. The 2010 nominal value of 0.53°C ranks just ahead of those of 2005 (0.52°C) and 1998 (0.51°C), 7 Response of Glaciers to Climate Change IPCC 2007 AR4 Siachen Glacier Past & Present 2000 2006 * Siachen Glacier has been retreated about 3.8 Km in last 17 years Sea Level Rise along Pakistan Coast Sea level rise is resulting into saline water intrusion to the fertile cultivated lands of the Indus Delta. Changing Trends of Thermal Extremes in Pakistan Areas of Heat Waves in South Asia Severe HW Moderate HW Tropical Cyclones Tracks vs. Inensity 1985-2005 Tropical Cyclone Intensity Classification Frequency of Tropical Depressions and Cyclones For Pakistan, Tropical Cyclones were the rare phenomena till the end of 20th century. Now they are the frequent visitor of Pakistan Coast. In 2007, two Tropical Cyclones Gonu (Category V) and Yemyin (Category III) cast vivid damage to lives and infrastructure in Sindh and Balochistan. Sea Surface Temperature Arabian Sea and Bay of Bengal Due to Rise in SST of Arabian Sea Cyclogenesis activity has enhanced to produce Tropical Cyclones which may hit coastal area of Pakistan frequently Landfall of Yemyin and Gonu Trop. Cyclones June 2007 Yemyin Gonu 1000 900 800 700 600 500 400 300 200 Punjab 600 400 200 0 Khyber Pakhtunkhaw 1901 1906 1911 1916 1921 1926 1931 1936 1941 1946 1951 1956 1961 1966 1971 1976 1981 1986 1991 1996 2001 2006 2011 800 1901 1906 1911 1916 1921 1926 1931 1936 1941 1946 1951 1956 1961 1966 1971 1976 1981 1986 1991 1996 2001 2006 2011 1901 1906 1911 1916 1921 1926 1931 1936 1941 1946 1951 1956 1961 1966 1971 1976 1981 1986 1991 1996 2001 2006 2011 Sindh 500 400 300 200 100 0 600 1100 1000 900 800 700 600 500 400 300 200 1901 1906 1911 1916 1921 1926 1931 1936 1941 1946 1951 1956 1961 1966 1971 1976 1981 1986 1991 1996 2001 2006 2011 1901 1906 1911 1916 1921 1926 1931 1936 1941 1946 1951 1956 1961 1966 1971 1976 1981 1986 1991 1996 2001 2006 2011 500 400 300 200 100 0 1901 1906 1911 1916 1921 1926 1931 1936 1941 1946 1951 1956 1961 1966 1971 1976 1981 1986 1991 1996 2001 2006 211 Annual Mean Precipitation(mm)1901-2011 Balochistan Gilgit-Baltistan 400 200 0 Kashmir Punjab 25 24 23 22 15 14.5 14 13.5 13 12.5 12 11.5 11 Khyber Pakhtunkhaw 1901 1906 1911 1916 1921 1926 1931 1936 1941 1946 1951 1956 1961 1966 1971 1976 1981 1986 1991 1996 2001 2006 2011 26 1901 1906 1911 1916 1921 1926 1931 1936 1941 1946 1951 1956 1961 1966 1971 1976 1981 1986 1991 1996 2001 2006 2011 1901 1906 1911 1916 1921 1926 1931 1936 1941 1946 1951 1956 1961 1966 1971 1976 1981 1986 1991 1996 2001 2006 2011 Sindh 23.5 23 22.5 22 21.5 21 20.5 20 19.5 19 0.0 -0.5 -1.0 -1.5 -2.0 -2.5 -3.0 -3.5 9 8.5 8 7.5 7 6.5 6 5.5 5 4.5 4 1901 1906 1911 1916 1921 1926 1931 1936 1941 1946 1951 1956 1961 1966 1971 1976 1981 1986 1991 1996 2001 2006 2011 1901 1906 1911 1916 1921 1926 1931 1936 1941 1946 1951 1956 1961 1966 1971 1976 1981 1986 1991 1996 2001 2006 2011 28 27.5 27 26.5 26 25.5 25 1901 1906 1911 1916 1921 1926 1931 1936 1941 1946 1951 1956 1961 1966 1971 1976 1981 1986 1991 1996 2001 2006 211 Annual Mean Temperature(oC)1901-2011 Balochistan Gilgit-Baltistan Kashmir 20 19 18 17 19 18.5 18 17.5 17 16.5 16 15.5 15 14.5 Punjab Khyber Pakhtunkhaw 1901 1906 1911 1916 1921 1926 1931 1936 1941 1946 1951 1956 1961 1966 1971 1976 1981 1986 1991 1996 2001 2006 2011 1901 1906 1911 1916 1921 1926 1931 1936 1941 1946 1951 1956 1961 1966 1971 1976 1981 1986 1991 1996 2001 2006 2011 Sindh 1901 1906 1911 1916 1921 1926 1931 1936 1941 1946 1951 1956 1961 1966 1971 1976 1981 1986 1991 1996 2001 2006 2011 1901 1906 1911 1916 1921 1926 1931 1936 1941 1946 1951 1956 1961 1966 1971 1976 1981 1986 1991 1996 2001 2006 2011 21 3.5 3 2.5 2 1.5 1 0.5 0 1901 1906 1911 1916 1921 1926 1931 1936 1941 1946 1951 1956 1961 1966 1971 1976 1981 1986 1991 1996 2001 2006 2011 9.5 9 8.5 8 7.5 7 6.5 6 5.5 5 1901 1906 1911 1916 1921 1926 1931 1936 1941 1946 1951 1956 1961 1966 1971 1976 1981 1986 1991 1996 2001 2006 211 Annual Mean Minimum Temperature(oC)1901-2011 16 15.5 15 14.5 14 13.5 13 12.5 12 11.5 11 -5.0 -5.5 -6.0 -6.5 -7.0 -7.5 -8.0 -8.5 -9.0 -9.5 -10.0 Balochistan Gilgit-Baltistan Kashmir Frequency of Extreme Events is Increasing Cloudburst Events 2001, 2003, 2007, 2008,2009, 2010, 2011, 2012 Prolonged Drought 1998-2002 Historic River Flooding 2010, 2011, 2012 Tropical Cyclones 1999,2007,2009,2010, 2011, 2012 Heat Waves in Spring 2006, 2007, 2010, 2011 (Reduced wheat yield) Snowmelt flooding 2005, 2007 and 2010 Drought at sowing stage 2009, 2010, 2011 Flow data below Kotri Barrage 120 100 80 60 40 20 0 Wheat Warmer February • 13 days above normal (2-3⁰C) temperatures caused 28% reduction in wheat yield in Ludhehana (India). Goswami et al., 2005 • In Sindh and southern Punjab, February (2006) was 2-4 ⁰ C warmer than normal and significant yield reductions were reported Wheat Warmer March 2010 • Over most of the low elevation agricultural plains, the temperatures during last week of February and first decade of march remained 3-6 ⁰ C above normal. • Early maturity did not allow to gain the normal weight, size and starch contents in the grains. Future Projections of Temperature • 23 Rainfall Projections for Sindh 24 Major Challenges • Pakistan is one of the most vulnerable nation to the challenges of climate change such as: • Reduction in productivity of crops and livestock due to heat stress and other adverse impacts of change in climate • Increase in water requirements of due to higher evapotranspiration at elevated Temperatures, while less water will be available • Uncertain timely availability of irrigation water due to variable river flows Major Challenges (Conti…) • Erratic and uncertain rainfall patterns may affect food production particularly in rain-fed areas • Increase in frequency and intensity of extreme climatic events such as floods, drought and cyclones • Abundance of insects, pests and pathogens in warmer and more humid environment, particularly after heavy rains and floods Major Challenges (Conti…) • Intrusion of sea water into deltaic regions of country, affecting coastal agriculture, forestry and biodiversity • Lack of technical capacity of public institutions and limited resources • Low adaptive capacity to adverse climate change impacts Recommendations • To mitigate the risks/threats due to climate change: • Effective implementation of approved climate change policy of Pakistan • Climate change monitoring and impact assessment activities should be organized on scientific basis by filling the observational gaps over low elevation plains and glaciers zones Recommendations (Conti…) • Climate resilient infrastructure should be built along the coastal belt and wind power potential already identified along Sindh coast be harnessed to initiate economic activity - a step towards green economy • Increasing losses of crops and livestock due to frequent floods, drought and tropical cyclones have been pressing the farming community’s marginal economic condition harder and harder, therefore, Insurance industry should be urged to play its role Recommendations (Conti…) • Low elevation and poor drainage have been causing water logging and salinity which required technically viable drainage infrastructure to reclaim the soils • Irrigation Efficient Methods such as use of sprinkler, drip and trickle irrigation systems be promoted Recommendations (Conti…) • Local Industry concerned with solar energy solutions should be encouraged to play its role using this precious natural resource as an initiative to green economy Summary “A key emerging issue in the climate change debate that exemplifies this challenge is food” “We need to grow much more food to feed the added population over coming decades” From probably less land and with less available water than we have now With much higher costs for energy, water and nutrients, in a much more hostile climate