* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Respiration of plant seeds - CMA
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Biosequestration wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Glossary of plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
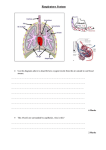
Respiration of plant seeds Science Background BIOLOGY Plant Physiology Cellular respiration Plants as animals need energy to live. When plants use sugars stored in their leaves or seeds they undergo cellular respiration. The cellular respiration harvests energy stored in a glucose molecule by oxidizing the sugar and reducing O2 to H2O. Cellular respiration releases chemical energy. C6H12O6 + 6H20 + 6 O2 6 CO2 + 12 H20 Sugar + Oxygen Carbon dioxide + Water + Energy (ATP) In this way cellular respiration converts the energy stored in food into a form of energy that plant cells use to carry out their life processes. During the respiration process, the plant uses oxygen and release carbon dioxide and water. Germinating seeds After a seed drops from a plant it usually goes into a resting period called dormancy. During dormancy the seed waits until conditions are right to germinate. Some seeds have to wait for years before they are able to germinate. During this time, seeds cannot photosynthesize as they lack leaves! Therefore, a seed needs to use stored energy reserves and undergo cellular respiration in order to stay alive or grow. Have you ever wondered why seeds and nuts have so many calories? The seed will use those calories to survive during dormancy and to begin germinating. Germination of a seed starts with water uptake by the seed. This is an essential step for the seed to germinate. The total water take up is about 2-3 times the weight of the seed. Whether or not a viable seed will germinate depends on a number of factors. The chemical environment of the seed must be right. Water must be available, oxygen has to be present since the seed must respire and no dangerous chemicals should be present. The physical environment must also be favorable. The temperature must be suitable as well as the light quality and quantity. A person may wonder why seeds are often buried underground. The reason is that this helps guarantee the seeds receive the correct amount of light for germination. Full sunlight can often prevent a seed from germinating. Respiration of germinating seeds As the seeds respire, they take up oxygen and respiring carbon dioxide. If you place germinating seeds in a closed system, it is possible to measure oxygen consumption and carbon dioxide production. The oxygen concentration level can be monitored by the O2 gas sensor and the carbon dioxide concentration level can be monitored by the Respiration of plant seeds – Science Background 1 CO2 gas sensor. Using both oxygen and carbon dioxide concentration levels, respiration of plant seeds can be determined. 2 CMA Learning and Teaching Resources