* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plant Structures and Functions Booklet
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Biosequestration wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
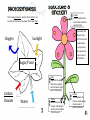
Possible Memories: I remember that plants give off water through transpiration in the water cycle. I remember that plants take in carbon dioxide and release oxygen in the carbon cycle. I remember that plants make their own food and are called producers. I remember that the process of making their own food is called photosynthesis and it requires water, carbon dioxide, and sunlight. Flower Attracts pollinators and makes seeds for reproduction. Plants are producers, which is their niche in an ecosystem, because they make their own food. Oxygen Eventually the flower turns into fruit once it is pollinated. Fruit protects the seeds and helps in seed distribution Sunlight Sugar/Food Carbon Dioxide Stem Supports the plant and carries water and nutrients to all parts of the plant Water Roots Holds the plant steady and takes in water and nutrients from the soil. Leaves This is where the food is made during the process of photosynthesis. Within the seed is a tiny plant waiting for the right conditions to sprout. Germination – when a plant first emerges from the seed. Seedling – Small plant, but it can make its own food now. Fruit or pods form and eventually seeds fall off and are carried away by wind, water, or animals. Photosynthesis produces oxygen which humans need to breathe. The animals would also die because they rely on plants for food and oxygen. 3 3 4 1 2