* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download introduction to evolution - Fall River Public Schools
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Biogeography wikipedia , lookup
Objections to evolution wikipedia , lookup
Cambrian explosion wikipedia , lookup
History of biology wikipedia , lookup
Hindu views on evolution wikipedia , lookup
Acceptance of evolution by religious groups wikipedia , lookup
Saltation (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Vestigiality wikipedia , lookup
Catholic Church and evolution wikipedia , lookup
Aquatic ape hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Theistic evolution wikipedia , lookup
Creation and evolution in public education wikipedia , lookup
Precambrian body plans wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to evolution wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
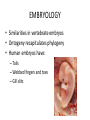
INTRODUCTION TO EVOLUTION Honors Biology INTRODUCTION TO EVOLTUION • Brainstorm – What is Evolution? OVERVIEW OF EVOLUTION • • • • • • Evolution is a change in species over time Many misconceptions Evolution is a theory Not one or another Overlying theme in Biology Earth is old! HOW DO WE KNOW EVOLUTION EXISTS? • • • • • Fossils Homologous Structure Vestigial Structures Embryology Similarities in Macromolecules FOSSILS • Fossil evidence shows a long history of life on Earth • Organisms live, last for awhile and disappeared; new forms live, last and disappear FOSSILS • A trace of a long dead organism • Many found in sedimentary rock – Sediment deposited by wind or water – Develop from hard elements of body – Minerals replace tissue fossil FOSSIL • Mold: – Imprint in rock that is shape of organism – Cast is a mold filled with hard material • Many different types of fossils – Tracks of animals – Mosquito trapped in amber FOSSILS • Distribution of fossils – Law of superposition: • • • • Layers of strata Lower levels are older; upper levels are newer Relative age of higher up is younger Can also figure absolute age – http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/evolution/library/04/3 /quicktime/l_043_01.html FOSSILS • Distribution of fossils – Succession of Forms • Fossils live and then become extinct • Mass extinctions FOSSILS • Biogeography – Study of geographical distribution of fossils and living organisms – Fossils in same area as ancestors – Giant fossil kangaroos are found in ________? HOMOLOGOUS AND ANALOGOUS STRUCTURES • Homologous Structures: – Similar features – Common ancestor – Forelimbs of vertebrates – Thumbs in primates • Analogous Structures: – Similar features – No common ancestor – Dolphins and shark VESTIGIAL STRUCTURES • Structures that were once needed and not needed anymore • Conserved • Examples – Human appendix – Hind limbs in whales – Human tail bone EMBRYOLOGY • Similarities in vertebrate embryos • Ontogeny recapitulates phylogeny • Human embryos have: – Tails – Webbed fingers and toes – Gill slits SIMILARITIES IN MACROMOLECULES • Compare DNA, RNA, Amino Acids • More recent common ancestor; more in common • Hemoglobin of humans and gorillas differ by 1 amino acid; humans and frogs by 67 amino acids • DNA of chimps and humans 99% similar (more similar than chimps and gorillas) WHAT DO I KNOW? • What is evolution? • What are 5 ways we know that evolution exists? • Be able to explain/give examples for each form of evolution. • What is the difference between a homologous and an analogous trait