* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Pedigrees/Sex-linked traits - Liberty Union High School District
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
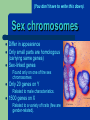
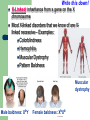
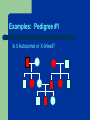
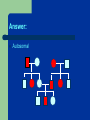
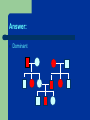
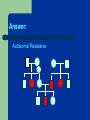
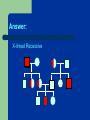
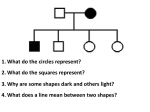
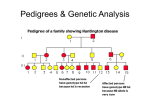
Genetics Part 3 Modes of Inheritance Remember… Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes Two types of chromosomes: Autosomes: all chromosomes except sex chromosomes Sex Chromosomes: X and Y Inheritance can be categorized according to the type of chromosome from which the trait comes. (You don’t have to write this down). In humans (and fruit flies), = Female = Male It is the presence of a Y chromosome that determines if an individual will be male or not. Autosomal Dominant: trait controlled by a dominant allele located on one of the autosomes Examples: Huntington’s Disease (brain disorder that causes mental illness)) Dwarfism Polydactyly (extra fingers or toes) A person with an autosomal dominant disorder can have a HH or Hh genotype Just because a trait is dominant does NOT mean it is more common in a population! Examples of people from a variety of human races who exhibit the albino trait. Autosomal Recessive: trait controlled by a recessive allele on one of the autosomes – Examples: Albinism (no pigmentation) Cystic Fibrosis (excessive mucus production in lungs) Sickle cell anemia (red blood cells are shaped like a “C” instead of round) A person with an autosomal recessive disorder must have a homozygous recessive genotype (hh). Carrier: a heterozygous person who does not have the disorder, but carries the recessive allele so that it can be passed on to future generations (Hh) (You don’t have to write this down). Sex chromosomes Differ in appearance Only small parts are homologous (carrying same genes) Sex-linked genes – Only 20 genes on Y – Found only on one of the sex chromosomes Related to male characteristics. 1500 genes on X – Related to a variety of traits (few are gender-related). Sex Linkage: inheritance from a gene located on one of the sex chromosomes Y-Linked: inheritance from a gene on the Y chromosome – only affects males The Y chromosome has very few genes that cause an observable phenotype so there is not a lot of y-linkage. – Ex: hypertrichosis pinnae (hairy ears) Write this down! X-Linked: inheritance from a gene on the X chromosome Most X-linked disorders that we know of are Xlinked recessive – Examples: Colorblindness Hemophilia Muscular Dystrophy Pattern Baldness Muscular dystrophy Male baldness: XbY Female baldness: XbXb Why is it more common for males to be affected by an Xlinked disorder than a female? ARE YOU COLORBLIND? http://www.toledo-bend.com/colorblind/Ishihara.html http://www.toledo-bend.com/colorblind/Ishihara.html http://www.toledo-bend.com/colorblind/Ishihara.html © Archimedes' Lab How they are written: Sex-Linked Recessive: Females who are XaXa and males who are XaY will express/show the recessive disease/trait being studied. A female who is XAXa is a carrier for it, but will not express it. Males have only one X and cannot be carriers. Genetics Part 4 Scientists observe how traits are inherited by studying phenotypes of a certain species from generation to generation One tool scientists have developed to study inheritance is a pedigree. Pedigree: A family tree diagram that shows how a trait is inherited over several generations. Draw all of the symbols and their meanings! Interpreting a Pedigree Diagram 1) Determine if the pedigree chart shows an autosomal or X-linked disease. If most of the males in the pedigree are affected, then the disorder is X-linked If it is a 50/50 ratio between men and women the disorder is autosomal. Interpreting a Pedigree Chart 2) Determine whether the disorder is dominant or recessive. If the disorder is dominant, one of the parents must have the disorder. If the disorder is recessive, neither parent has to have the disorder because they can be heterozygous. Examples: Pedigree #1 Is it Autosomal or X-linked? Answer: Autosomal Examples: Pedigree #1 Is the trait Dominant or Recessive? Answer: Dominant Examples: Pedigree #2 Is the trait Autosomal or X-linked? Dominant or Recessive? Answer: Autosomal Recessive Examples: Pedigree #3 Is the trait Autosomal or X-linked? Dominant or Recessive? Answer: X-linked Recessive