* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 슬라이드 1
Survey
Document related concepts
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Plant virus wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Endogenous retrovirus wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Promoter (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Gene regulatory network wikipedia , lookup
Expression vector wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
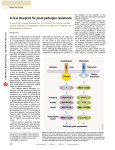
The WRKY superfamily of plant transcription factors Introduction Wrky ▶ WRKY (pronounced‘worky’) proteins, a large family of transcriptional regulators that has to date only been found in plants. ▶ The WRKY domain is defined by the conserved amino acidsequence WRKYGQK at its N-terminal end, together with a novel zinc-finger-like motif ▶ Many WRKY proteins having a regulatory function in the response to pathogen infection and other stresses. ▶ levels of WRKY mRNA, protein and DNA-binding activity havebeen reported to be induced by infection with viruses oomycetes fungal elicitors9 Signaling substances such as salicylic acid ▶ Comparative expression studies with several AtWRKY genes also suggest that certain family members have a role in the regulation of senescence. ▶ Transcript levels of AtWRKY4, 6, 7 and 11 are enhanced in senescent leaves. ▶ W boxes have been described as positive cis-acting elements upregulating transcription. 1.group I : two WRKY domains group II: one WRKY domains group III: newly define group 2.(Pc)sweet potato (Ib), Arabidopsis (At), tobacco (Nt), cucumber (Cs) and wild oat (Af ). WRKY domains are black nuclear localization signals are blue leucine zippers are pink serine–threonine-rich regions are yellow glutamine-rich regions are purple proline-rich regions are green acidic regions are red Fig. Phylogenetic analysis of 58 members of the AtWRKY family. Results Targets of AtWRKY6 regulation during plant senescence and pathogen defense ABSTRACT In Arabidopsis, ▶ WRKY factors large gene family of plant-specific transcriptional regulators controlling several types of plant stress responses. ▶ we identified targets of the senescence- and defense-associated WRKY6 factor. ▶ WRKY6 was found to suppress its own promoter activity, indicating negative autoregulation. ▶ WRKY6 positively influenced the senescence- and pathogen defenseassociated PR1 promoter activity, most likely involving NPR1 function. ▶ One novel identified target gene, SIRK, encodes a receptor-like protein kinase, whose developmental expression is strongly induced specifically during leaf senescence. SIRK is dependent on WRKY6 function. ▶ Senescing leaves of wrky6 knockout mutants showed a drastic reduction, green leaves of WRKY6 overexpression lines showed clearly elevated SIRK ▶ The SIRK gene promoter was activated by WRKY6 in vivo The Plant Journal En-1 transposon insertion Figure 1. Identification of wrky6 knockout mutants Figure 2. WRKY6 overexpression lines. The Plant Journal SAG:salicyilc acid glucoside ELI:plant defence Related gene The Plant Journal Knock out Figure 3. Repressor activity of WRKY6. promotor promotor overexepression promotor promotor GUS WRKY Knock out gene GUS WRKY overexpression Pathogen Rhizobacterium JA response SA jar1 NahG JA response ethylene response Ethylene response etr1 NPR npr1 Defensive compounds ISR PRS SAR PDF1.2 The Plant Journal Figure . Nuclear localization of endogenous AtWRKY6. The Plant Journal Figure 4. Effect of WRKY6 overexpression on PR1 and NPR1. R:root transcripts.R1-R154 P:aerieal part transcripts P1-P63 Table 1. cDNA-AFLP fragments and homologies to sequences in the Arabidopsis database Figure 5. Dependence of SIRK gene expression on WRKY6 Figure 6. Specificity of the WRKY6-SIRK promoter interaction SIRK WRKY6 ? Necrotic Pathogen infection Systemic signal SA NPR1 SAR Gene expression Enhanced Pathogen resistance