* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Microbial nutrition
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
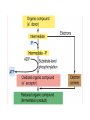
Microbial Nutrition Cell metabolism Nutritional Categories of Microorganisms • Microorganisms are often grouped according to the sources of energy they use: – Phototrophs use light as an energy source • Photosynthesis – Chemotrophs use chemicals as energy sources • Chemoorganotroph • Chemolithotroph Biochemical Components of Cells • Water: 80 % of wet weight • Dry weight – – – – Protein 40-70 % Nucleic acid 13-34% Lipid 10-15 % Also monomers, intermediates and inorganic ions Macronutrients • Cells make proteins, nucleic acids and lipids • Macronutrients – macromolecules, metabolism – C, H, O, N, S, P, K, Mg, Fe – Sources • Organic compounds • Inorganic salts Micronutrients • Elements needed in trace quantities – Co, Cu, Mn, Zn, V – Enzymes – tap water • Growth factors – Organic compounds – Vitamins Defined / Complex Media • Defined – Prepared with precise amounts of chemicals – Known composition • Complex – Exact composition unknown – Digests of beef, soybean, yeast Other Culturing Considerations • • • • pH Oxygen concentration Temperature Light / carbon dioxide (phototrophic organisms) Role of Oxygen in Nutrition • Obligate aerobes – require O2 • Obligate anaerobes – O2 is toxic • Facultative anaerobes • Microaerophilic organisms Transport of Nutrients into the Cell • Nutrients are obtained from the environment • Many of the nutrients are polar • Cannot diffuse across the cell membrane • Proteins embedded in the membrane • Transport against a concentration gradient active transport Bioenergetics • Living cells require energy for growth, biosynthesis, reproduction and transport • Energy needed to drive the biochemical reactions of cells is stored and transferred via adenosine triphosphate (ATP) Fermentation and Respiration • Chemoorganotrophs obtain their energy from oxidation of organic compounds – loss of electrons/removal of hydrogen • Fermentation – No terminal electron acceptor • Respiration – Terminal electron acceptor (e.g. O2) Glycolysis C6H12O6 glucose NAD+ ADP NADH + H+ ATP C3H4O3 pyruvic acid Substrate-level phosphorylation CH2 ADP ATP CH3 COPO3H2 C COOH COOH phosphoenol pyruvic acid O pyruvic acid Fermentation products • Need to regenerate NAD+ • Reduce pyruvic acid NADH + H+ C3H4O3 pyruvic acid NAD+ C3H5O3 lactic acid Oxidative phosphorylation • Occurs in respiration (aerobic and anaerobic) • Proton motive force – Electrons from NADH are passed along an electron transport chain – Protons are pumped across membrane – Electrochemical gradient – Drives ATP synthesis from ADP and Pi Summary • Nutrients – Macronutrients/micronutrients – Defined/complex media – Cell membranes • Energy production – Different modes Further reading Madigan MT, JM Martinko, J Parker, 2000. Brock Biology of Microorganisms, 9th Edition. Chapters 3 and 4.