* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Table of Contents
Lactate dehydrogenase wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Metabolic network modelling wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Glyceroneogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
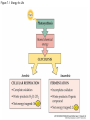
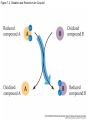
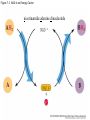
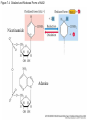
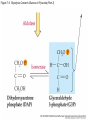
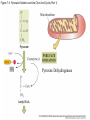
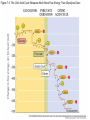
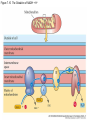
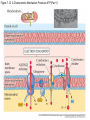
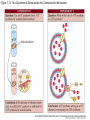
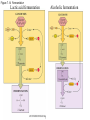
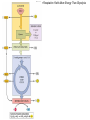
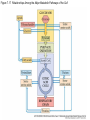
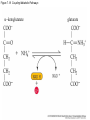
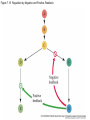
Figure 7.1 Energy for Life Figure 7.2 Oxidation and Reduction Are Coupled Figure 7.3 NAD Is an Energy Carrier nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide Figure 7.4 Oxidized and Reduced Forms of NAD Nicotinamide Adenine Figure 7.5 Energy-Producing Metabolic Pathways Figure 7.6 Glycolysis Converts Glucose to Pyruvate (Part 1) Figure 7.6 Glycolysis Converts Glucose to Pyruvate (Part 2) Figure 7.6 Glycolysis Converts Glucose to Pyruvate (Part 3) 2 2 Figure 7.6 Glycolysis Converts Glucose to Pyruvate (Part 4) 2 2 2 2 Figure 7.7 Changes in Free Energy During Glycolysis Figure 7.8 Pyruvate Oxidation and the Citric Acid Cycle (Part 1) Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Figure 7.8 Pyruvate Oxidation and the Citric Acid Cycle (Part 2) Figure 7.9 The Citric Acid Cycle Releases Much More Free Energy Than Glycolysis Does Figure 7.10 The Oxidation of NADH + H+ Figure 7.11 The Complete Respiratory Chain Figure 7.12 A Chemiosmotic Mechanism Produces ATP (Part 1) Figure 7.12 A Chemiosmotic Mechanism Produces ATP (Part 2) Figure 7.13 Two Experiments Demonstrate the Chemiosmotic Mechanism Figure 7.14 Fermentation Lactic acid fermentation Alcoholic fermentation Cellular Respiration Yields More Energy Than Glycolysis Figure 7.17 Relationships Among the Major Metabolic Pathways of the Cell Figure 7.18 Coupling Metabolic Pathways a-ketoglutarate glutarate Figure 7.19 Regulation by Negative and Positive Feedback Figure 7.20 Feedback Regulation of Glycolysis and the Citric Acid Cycle (Part 1) Table 7.1 Cellular Locations for Energy Pathways in Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes