* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 37_Hypersensitivity BA
Anti-nuclear antibody wikipedia , lookup
Immunocontraception wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Complement system wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
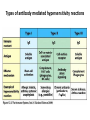
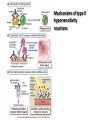
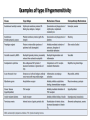
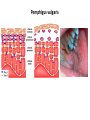
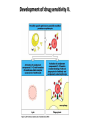
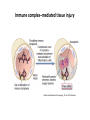
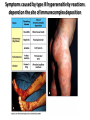
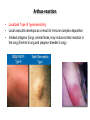
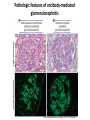
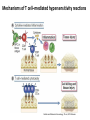
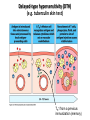
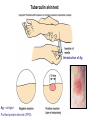
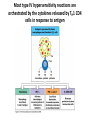
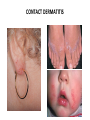
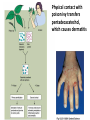
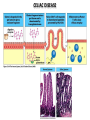
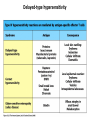
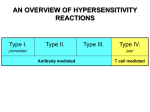
AN OVERVIEW OF HYPERSENSITIVITY REACTIONS Type I. Type II. „immediate” Type III. Type IV. „late” Antibody mediated T cell mediated Types of antibody mediated hypersensitivity reactions FcRIα) TYPE II HYPERSENSITIVITY IgG or IgM antibodies bound to antigens of particular cells or the extracellular matrix Mechanisms of type II hypersensitivity reactions Cellular and Molecular Immunology, 7th ed., 2012 Elsevier Frustrated phagocytosis mediated by IgG antibodies Binding Opsonization Internalization C3b C3b C3b C3b Enzyme release C3b C3R FcR The target, which cannot be phagocytosed, is damaged C3b Absorbed antigen Opsonized surface Binding Frustrated (drug) phagocytosis Enzyme release Examples of type II hypersensitivity Pemphigus vulgaris Development of drug sensitivity I. Development of drug sensitivity II. TYPE III HYPERSENSITIVITY Antibodies form immune complexes in the circulation, and the complexes are subsequently deposited in tissues, particularly in blood vessels, and cause injury Immune complex–mediated tissue injury Cellular and Molecular Immunology, 7th ed., 2012 Elsevier Tissue damage caused by deposited immune complexes Frustrated phagocytosis Immune complexes activate the complement system, neutrophils, basophils and thrombocytes Examples of human immune complex–mediated diseases Symptoms caused by type III hypersensitivity reactions depend on the site of immunecomplex deposition Arthus-reaction • Localized Type III hypersensitivity • Local vasculitis develops as a result of immune complex deposition • Inhaled antigens (fungi, animal feces) may induce similar reaction in the lung (Farmer’s lung and piegeon-breeder’s lung) Localized deposition of immune complexes within a tissue causes a type III hypersensitivity reaction Manifestation of type III hypersensitivity in lupus erythematosus Facial, malar "butterfly" rash with characteristic shape across the cheek Pathologic features of antibody-mediated glomerulonephritis Cellular and Molecular Immunology, 7th ed., 2012 Elsevier TYPE IV HYPERSENSITIVITY REACTION T lymphocytes injure tissues either by triggering inflammation or by directly killing target cells Type IV hypersensitivity reactions Mechanisms of T cell–mediated hypersensitivity reactions Cellular and Molecular Immunology, 7th ed., 2012 Elsevier Delayed-type hypersensitivity (DTH) (e.g. tuberculin skin test) TH1 from a previous immunization (memory) Tuberculin skin test Introduction of Ag Ag = antigen Purified protein derivate (PPD) Most type IV hypersensitivity reactions are orchestrated by the cytokines released by TH1 CD4 cells in response to antigen DTH as a result of a contact-sensitizing agent* CONTACT DERMATITIS *a contact-sensitizing agent is usually a small molecule that penetrates the skin then binds to self-proteins, making them “look” foreign CONTACT DERMATITIS Poison ivy Anacardiaceae (family), Toxicodendron (genus) Toxicodendron radicans or Rhus toxicodendron Physical contact with poison ivy transfers pentadecacatechol, which causes dermatitis CELIAC DISEASE Delayed-type hypersensitivity