* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download (PS) rules - kuas.edu.tw
Cognitive semantics wikipedia , lookup
Comparison (grammar) wikipedia , lookup
Focus (linguistics) wikipedia , lookup
Serbo-Croatian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Swedish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Sloppy identity wikipedia , lookup
Zulu grammar wikipedia , lookup
Chinese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Probabilistic context-free grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Macedonian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Latin syntax wikipedia , lookup
Distributed morphology wikipedia , lookup
Spanish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Scottish Gaelic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Morphology (linguistics) wikipedia , lookup
Contraction (grammar) wikipedia , lookup
Turkish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Dependency grammar wikipedia , lookup
Musical syntax wikipedia , lookup
Japanese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Preposition and postposition wikipedia , lookup
Italian grammar wikipedia , lookup
French grammar wikipedia , lookup
Malay grammar wikipedia , lookup
Romanian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Yiddish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Esperanto grammar wikipedia , lookup
Antisymmetry wikipedia , lookup
Integrational theory of language wikipedia , lookup
Junction Grammar wikipedia , lookup
Transformational grammar wikipedia , lookup
Polish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Pipil grammar wikipedia , lookup
Determiner phrase wikipedia , lookup
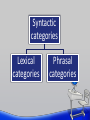
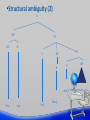
SYNTAX Introduction to Linguistics •BASIC IDEAS •What is a sentence? •A string of random words? • If it is a sentence, does it have to be meaningful? •Grammaticality • • • Grammatical vs. ungrammatical • well formed vs. ill formed • words must conform to specific patterns determined by the syntactic rules of the language based on • syntactic rules NOT based on • what is taught in school • whether it is meaningful • whether you have heard the sentences before. Syntactic categories Lexical categories Phrasal categories •Lexical categories Open lexical categories • nouns • verbs • adjectives • Adverbs Closed lexical categories • Pronouns • prepositions • Auxiliary verbs • determiners (articles, demonstratives, quantifiers) •PHRASE STRUCTURES •Phrasal categories • • • Verb phrase (VP) Noun phrase (NP) Prepositional phrase (PP) •Phrase structure (PS) rules • • What are PS rules? • How words of different parts of speech are connected. Different languages have different PS rules • English • An adjective is placed before a noun. • A beautiful woman • French • An adjective is placed either before or after a noun. • Une belle femme ‘a beautiful woman’ • Une femme fatale ‘an attractive woman’ •Writing PS Rules Books • NP->N • Read: An NP is composed of a noun. A book • NP -> Det N John’s book • NP -> Pos N Good books; a good book • NP -> Det Adj N • NP -> Adj N • NP -> (Det) (adj) N Books on the table • NP -> N (PP) The PS rule of an NP • NP -> (Det) (adj) N (PP) •Phrase structure (PS) rules in English • NP -> (Det) (adj) N (PP) • NP -> Pronoun • VP -> ? • AP -> ? • PP -> ? • CP -> COMP (that) S • •S COMP: complementizer=that, if, unless -> ? •Phrase structure (PS) rules in English NP -> (Det) (adj) N (PP) NP -> pronoun VP -> V (NP) (PP) (CP) AP -> Adj (PP) PP -> P NP CP -> COMP (that) S • COMP: complementizer=that, if, unless S -> NP (Aux) VP •A Tree Diagram S VP NP Det NP N PP V Det P The boy N N from Taiwan knew the answer •What does a tree diagram show? • Speakers’ syntactic knowledge of sentence structure the linear order of the words • the categorization of words into particular syntactic categories (i.e. constituents) • the hierarchical structure of the syntactic categories • •Grow your own trees. • The sun melted the ice. • The boy put the toy in the box. • The reporter realized that the senator lied. • A fast car with twin cams sped by the children on the grassy lane. • A stranger whispered to the Soviet agent that a dangerous spy from the CIA loved coffee. •What can tree diagrams explain? • Structural ambiguity •Structural ambiguity •A sentence may have two interpretations due to different structural compositions of constituents. • Example : • The boy left Mary with a broken heart. •Structural ambiguity S NP Det VP N NP V N PP P The boy left Mary with NP a broken heart •Structural ambiguity (2) S NP Det VP N V N The boy left PP NP Mary P NP with a broken heart Questions?